All Early Life Microbiome articles – Page 6
-
 Careers
CareersHealthy guts with diverse and mature bacteria linked to less allergy-related wheezing and asthma in early childhood
Babies and young children with more mature communities of bacteria present in their gut are less likely to develop allergy-related wheezing or asthma.
-
 News
NewsCovid pandemic may have changed gut bacteria of infants
Infants who spent most of their first year in the pandemic have fewer types of bacteria in their gut than infants born earlier, according to a team of developmental psychology researchers.
-
 News
NewsHuman milk-based synbiotic safely modulates damaged adult gut microbiomes
Bacteria found in the gut of nursing infants, combined with certain sugars from human milk, may enable ‘precision microbiome engineering’ as live biotherapeutics.
-
 News
NewsRacial and ethnic differences in gut microbiome emerge at 3 months old
Gut microbiome variation associated with race and ethnicity arises after three months of age and persists through childhood, according to a new study.
-
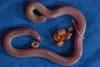 News
NewsWormlike animals are first amphibians shown to pass microbes to their offspring
Skin-feeding does more than provide nutrients for young caecilians - it also helps the mother pass microbes from her skin and gut down to her young, inoculating them to jump-start a healthy microbiome.
-
 News
NewsMapping evolution of E. coli virulence factor offers refined drug target
Researchers have presented evidence that targeting the K1 capsule can be used as the basis of treatment, paving the way to prevent serious E. coli infections.
-
 News
NewsPreemie infections may come from gut microbiomes
Dangerous bacterial bloodstream infections in premature babies may originate from the infants’ gut microbiomes, according to researchers.
-
 Careers
CareersThe Stewart Lab
The Stewart Lab at Newcastle University are working to harness the infant gut microbiome to predict disease and personalise preventative therapy.
-
 News
NewsNew mode of horizontal gene transfer between maternal and infant gut microbiome uncovered
Researchers have discovered a new mode of vertical mother-to-infant microbiome transmission, where microbes in the maternal gut shared genes with microbes in the infant gut during the perinatal period starting immediately before birth and extending though the first few weeks after birth.
-
 Features
FeaturesThe usually sterile womb
Culture-independent next-generation sequencing technologies have given us a far deeper understanding of the microbiome composition of various important health-related niches.
