All Ecology & Evolution articles – Page 3
-
 News
NewsComplex life developed earlier than previously thought, study reveals
New research indicates that complex organisms evolved long before there were substantial levels of oxygen in the atmosphere, something which had previously been considered a prerequisite to the evolution of complex life.
-
 News
NewsAll life copies DNA unambiguously into proteins. Archaea may be the exception.
A study shows how a methane-producing member of the Archaea, interprets one three-letter sequence — normally a stop codon that signals the end of a protein — in two different ways, synthesizing two different proteins seemingly at random, though biased by conditions in the environment.
-
 News
NewsA viral fitness-constraint strategy exploits the structural and functional limitations of viral evolution
Researchers have revealed two innovative strategies for the development of durable and broadly neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Their study proposes the immune trajectory strategy and the viral fitness-constraint strategy.
-
 News
NewsAcid rain may be training soil bacteria to become more deadly
Acid rain from fossil fuel pollution may be quietly training soil bacteria to become longer-lived, more transmissible, and more deadly, according to a new study that tracks how a notorious foodborne pathogen rapidly evolved under simulated acid deposition.
-
 News
NewsDr José Luis Balcazar named as winner of John Snow Public Health Innovation Prize
Dr José Luis Balcazar, Senior researcher at the Catalan Institute for Water Research (ICRA-CERCA), Spain, has been named as the newest winner of the John Snow Public Health Innovation Prize.
-
 News
NewsClues to origins of complex life revealed with discovery of new unicellular organism and phylum
A new paper describes the discovery of Solarion arienae, a previously unknown unicellular organism that provides new insight into the earliest stages of complex life on Earth. This microscopic protist displays two distinct cell types and a unique predatory structure unlike any seen before.
-
 News
NewsTeam discovers cyanobacteria activate different genes by day and by night
By analyzing gene expression in the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme, scientists discovered that during daylight, the cells focus on metabolism. But under cover of darkness, they turn to the control of genome repair and activate various genetic elements.
-
 News
NewsResearchers subvert plasmids to combat antibiotic resistance
Scientists have devised a way to track the evolution and spread of antibiotic resistance in individual bacteria by measuring competition among plasmids. Plasmids evolve independently but also help drive bacterial evolution, including the development of resistance to antimicrobial compounds. They are the primary way that resistance can jump from one type of bacteria to another.
-
 News
NewsThe road ahead: why conserving the invisible 99% of life is fundamental to planetary health
A new paper outlines how scientists came together to put together the first microbial conservation roadmap under the leadership of Applied Microbiology International President, Professor Jack Gilbert.
-
 News
NewsResearchers expand virus-based treatment options for antibiotic-resistant infections
Phages are extremely specific about which strains of a bacterial species they will attack. This has limited their effectiveness against the most antibiotic-resistant strains. To overcome this problem, the research team “trained” the phages by allowing them to evolve together with the bacteria in a controlled laboratory setting for 30 days.
-
 News
NewsSingle-celled organisms found to have a more complex DNA epigenetic code than multicellular life
Researchers discovered that in more ‘primitive’ unicellular organisms, both the adenine and the cytosine bases are methylated. This would suggest that in some ways, these unicellular organisms are more complex than their multicellular peers.
-
 News
NewsWild birds are driving the current U.S. bird flu outbreak
Researchers traced the introduction and spread of highly pathogenic H5N1 viruses during the first 18 months in North America using genomic sequencing and migratory flyway analysis, discovering that the viruses were spread primarily by wild migrating birds.
-
 News
NewsHorizon Awards 2025: Microbes and Social Equity Working Group named as team winner of Dorothy Jones Diversity & Inclusion Achievement Award
The Microbes and Social Equity Working Group (MSE) has been named as the team winner of the Dorothy Jones Diversity & Inclusion Achievement Award.
-
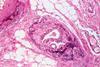 News
NewsNew DNA analysis approach could transform understanding of disease evolution
By adapting techniques originally used to study ancient DNA from archaeological specimens, researchers were able to recover genetic information from nearly century-old medical samples.
-
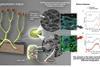 News
NewsAdvanced imaging reveals new fungus species in 407-million-year-old plant fossil from Scotland
Researchers have identified a new species of ancient symbiotic fungus preserved within a 407-million-year-old plant fossil from Scotland. The discovery provides unprecedented three-dimensional insight into one of the earliest known plant–fungus partnerships.
-
 News
NewsHow life first got moving: nature’s motor from billions of years ago
Research has cast light on the evolutionary origins of one of nature’s first motors, which developed 3.5 billion to 4 billion years ago to propel bacteria. Scientists have created the most comprehensive picture yet of the evolution of bacterial stators.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover global patterns and drivers of orchid mycorrhizal interactions
A global meta-analysis of orchid-fungal associations leads to a general conclusion: an orchid’s fungal community is driven more strongly by its ecophysiology and biogeography than by its phylogeny.
-
 News
NewsNew study shows invasive Group A Streptococcus outcomes shaped by treatment strategies, not species lineage
Researchers highlight the role of early clindamycin prescription in improving the recovery rate of patients with invasive Group A Streptococcus infections in a study that examined the evolving epidemiology of such infections.
-
 News
NewsEvolving antibiotic resistance under pressure may lead to personalized treatment
A new study demonstrates the use of an experimental evolution approach to map genetic mutations in Acinetobacter baumannii treated with one of two uncommon antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsERC Synergy Grant awarded to physicist Michael Lässig and virologist Florian Klein
Researchers have been awarded a Synergy Grant by the European Research Council (ERC) for the project CoEvolve, which investigates the co-evolution of viruses and the immune system.
