All Editorial articles – Page 126
-
 News
NewsNew insights into phage–bacteria interactions in the gut microbiome
Researchers studied the interactions between bacteria and phages within the gut microbiome and highlighted the significance of the phage community to shape the microbiome that contributes to host health and diseases.
-
 News
NewsDesigning self-destructing bacteria to make effective tuberculosis vaccines
Preclinical studies have demonstrated a more effective tuberculosis (TB) vaccine through engineering bacteria to self-destruct and swiftly stops the infection on cue, which activates a more robust immune response.
-
 News
NewsScientists build robot to track plant-fungal trade networks, revealing nature’s underground supply chains
New research uses advanced robotics to track the hyper-efficient supply chains formed between plants and mycorrhizal fungi as they trade carbon and nutrients across the complex, living networks that help regulate the Earth’s atmosphere and ecosystems.
-
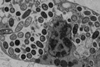 News
NewsBacteria consumed by immune cells become part of the cell
Immune cells that eat bacteria in the body don’t stash them in specialized compartments as once thought, but turn them into critical nutrients that build proteins, create energy and keep the cells alive, according to a new study.
-
 Opinion
OpinionThe problem of microplastics in the oceans: it’s time for effective solutions
Francielly Bruna Neto Francisco and Ricardo Henrique Krüger, from the University of Brasília (UNB), warn that we urgently need technologies that will effectively eliminate partially or nonbiodegradable polymers from the marine environment.
-
 News
NewsGenetic switch controlling microbiota impact could help control leaf growth in poor soils
A new study has identified a genetic circuit in plants that controls individual leaf growth and allows the plants to adapt to their environment. The findings could help the development of more drought-resistant crops.
-
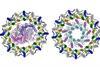 News
NewsStudy probes light-harvesting proteins of purple sulfur bacteria in high-salt, high-alkaline environments
Halorhodospira halophila, a purple sulfur bacterium, is believed to perform photosynthesis efficiently by integrating light harvesting protein complexes LH2 and LH1-RC. Researchers employed cryo-electron microscopy to investigate.
-
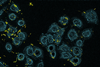 News
NewsSuperbugs in our food: a new hope for tackling drug resistance
Researchers highlight the potential of quorum sensing inhibitors (QSIs) as a novel approach to tackle Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The study explores the mechanisms of action of various QSIs and potential applications in food safety and healthcare.
-
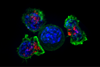 News
NewsStudy reveals how bacteria in microbiome medicine trigger tumor-killing cells
Microbiotica has presented new data on the mechanism of action of MB097, a clinical-stage drug candidate being developed as a co-therapy in combination with KEYTRUDA® (pembrolizumab) in patients with advanced melanoma.
-
 News
NewsFungi more vulnerable than bacteria in degrading alpine ecosystems
A new study provides the first evidence that alpine pioneer community degradation led to declines of 27% in fungal richness, 8% in bacterial richness and about 50% of endemic microorganisms.
-
 News
NewsBeacon Technology Solutions, Illinois Tech awarded grant to advance far-UVC disinfection research
Beacon Technology Solutions, with collaborators at Illinois Institute of Technology, has been awarded a grant to support a novel study on how Far-UVC technology can help mitigate the spread of infectious diseases in public spaces.
-
 News
NewsNeutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and its correlation with tuberculosis infection
A new study reveals a significant negative correlation between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the risk of tuberculosis infection (TBI), particularly in males and individuals with hypertension.
-
 News
NewsLung abnormalities seen in children and teens with long COVID
An advanced type of MRI uncovers significant lung abnormalities in children and adolescents with long COVID, according to a new study. PREFUL MRI doesn’t require the use of radiation or intravenous contrast agents and can be done while the patient breathes freely.
-
 News
NewsHeat-stressed reefs may benefit from coral-dwelling crabs
A species of branching coral is able to recover from heat stress and wounds due to its mutualistic relationship with crabs in the Great Barrier Reef Corals, a new study shows. This evolutionary partnership will inspire coral reef restoration strategies in the future.
-
 News
NewsUnexpected species-specific patterns in study of giraffe gut flora
The gut bacteria of giraffes are not primarily determined by what they eat, but by the species they belong to., according to a new study analysing the link between diet and gut flora in three giraffe species in Kenya. The study also provides new knowledge that can help secure the food supply of endangered giraffe species.
-
 News
NewsHerpesviruses may contribute to Alzheimer’s disease via transposable elements
Researchers have outlined the pathway human herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV1) can use to contribute to Alzheimer’s disease in aging brains, and also share two FDA-approved, commercially available drugs that reverse this pathway in a laboratory setting.
-
 News
NewsNew paper-based device boosts HIV test accuracy from dried blood samples
Scientists have trialled a more precise medical device to measure HIV viral loads by engineering a paper device with wax-printed patterns that create precise channels and collection spots, ensuring it consistently collects the same volume of blood.
-
 News
NewsAs dengue spreads, researchers discover a clue to fighting the virus
Children who experience multiple cases of dengue virus develop an army of dengue-fighting T cells, according to a new study. Most children who experienced two or more dengue infections showed very minor symptoms—or no symptoms at all—when they caught the virus again.
-
 News
NewsNew study calls for ethical framework to protect Indigenous genetic privacy in wastewater monitoring
Researchers have called for new ethical frameworks to protect Indigenous communities’ genetic privacy in the growing field of wastewater surveillance. The study examines how analysis of community wastewater raises significant privacy concerns for Indigenous populations.
-
 News
NewsLaser-powered device tested on Earth could help us detect microbial fossils on Mars
Scientists hoping to identify fossil evidence of ancient Martian microbial life have now found a way to test their hypothesis, proving they can detect the fossils of microbes in gypsum samples that are a close analogy to sulfate rocks on Mars.
