All Editorial articles – Page 40
-
 News
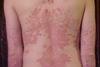
NewsPsoriasis-linked gene mutation also impacts gut health
A mutation previously linked to skin disorders like psoriasis may also play a surprising role in gut health, according to new research. This mutation activates skin immune responses but also affects the intestine, revealing a new connection between genetics, the immune system, and the gut.
-
 News
NewsPowered by mushrooms, living computers are on the rise
Researchers have discovered that common edible fungi, such as shiitake mushrooms, can be grown and trained to act as organic memristors, a type of data processor that can remember past electrical states. They could also be used to create other types of low-cost computing components.
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover microbes turning food waste into energy
Researchers have identified a previously unknown microbe that plays a crucial role in converting food waste into renewable natural gas, using a molecular tagging approach that could also detect other elusive microbes - including those that are breaking down microplastics in the ocean.
-
 News
NewsLighting up life: scientists develop glowing sensors to track cellular changes as they happen
Researchers have engineered living cells to use a 21st amino acid that illuminates protein changes in real time, providing a new method for observing changes within cells. The technique is effective in bacteria, human cells and live tumor models, making it possible to study complex diseases like cancer more ethically.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows differences between documented and self-reported polio vaccination rates
Until poliovirus is eradicated worldwide, vaccination protection is important as the virus could be reintroduced at any time. Epidemiologists have now shown that many people in Germany do not know their vaccination status and cannot find it on their vaccination record.
-
 News
NewsWarmer Nordic springs double the incidence of avian malaria
A unique long-term study, in which biological samples were collected from the same population of blue tits over a 30-year period, shows that rising spring temperatures have doubled the incidence of avian malaria in southern Sweden.
-
 News
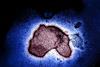
NewsStudy identifies viral combinations that heighten risk of severe respiratory illnesses in infants
A new study has revealed that, while a wide range of viruses can cause lower respiratory tract illnesses (LRIs) in infants, certain viruses and viral combinations dramatically increase the risk of severe disease.
-
 News
NewsMicrobial iron mining: turning polluted soils into self-cleaning reactors
Scientists have presented “microbial iron mining,” a process where soil microbes activate natural iron cycling. Microbes reduce and mobilize iron minerals, producing tiny iron nanoparticles that act as powerful traps for a variety of pollutants.
-
 News
NewsHow HIV’s shape-shifting protein reveals clues for smarter drug design
Researchers determined the structure of HIV protein integrase during newly discovered function, enabling the development of better HIV therapeutics.
-
 News
NewsHarnessing solar energy for environmental cleanup: Iron mineral-bacterial biofilms degrade pollutants
Researchers offer a sustainable, efficient, and scalable method for addressing soil and groundwater pollution, opening new possibilities for clean-up strategies in diverse ecosystems. This process significantly enhances the degradation of antibiotics like tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH) and chloramphenicol (CPL).
-
 News
NewsGroundbreaking new projects launched to lower the cost of monoclonal antibody production
LifeArc and the Gates Foundation have awarded more than $5m to seven projects aimed at developing cheaper and more efficient ways to produce monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatments. The innovative approaches include using filamentous fungus to produce mAbs.
-
 News
NewsRhizosphere metabolites influence the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in soil-plant systems
A study sheds new light on the complex mechanisms by which plants and their associated microorganisms contribute to the migration of ARGs through the environment, offering important implications for food safety and public health.
-
 News
NewsNew biochar-powered microbial systems offer sustainable solution for toxic pollutants
Researchers have unveiled a promising strategy to address persistent organic pollutants. Their latest review highlights how biochar-supported microbial systems can revolutionize the remediation of these contaminants.
-
 News
NewsReview explores roles, mechanisms and applications of intra-tumoral microbiota in cancers
A recent review provides an overview of the hallmarks, roles, molecular mechanisms, and clinical applications of intra-tumoral microbiota in multiple human cancers.
-
 News
NewsHorizon Awards 2025: Dr Manu De Rycker named as winner of WH Pierce Prize
Dr Manu De Rycker, a Principal Investigator at the University of Dundee, has been named as the newest winner of the WH Pierce Global Impact in Microbiology Prize.
-
 News
NewsMaking yeast more efficient ‘cell factories’ for producing valuable plant compounds
Researchers have discovered a new way to make yeast cells more efficient “factories” for producing valuable plant compounds. By studying a plant membrane protein called AtMSBP1, they uncovered a mechanism that helps yeast cells better support plant cytochrome P450 enzymes.
-
 News
NewsDNA from Napoleon’s 1812 army identifies the pathogens likely responsible for the army’s demise during their retreat from Russia
Microbial paleogenomicists extracted DNA from the teeth of soldiers from Napoleon’s ill-fated invasion of the Russian Empire and found no trace of typhus. Instead, they identified two pathogens known to cause enteric fever and relapsing fever.
-
 News
NewsProtection against winter vomiting bug spread with arrival of agriculture
Norovirus clears up after a couple of days, but the protection it provides is short-lived, meaning that the same person can fall repeatedly sick in a short space of time. But some people cannot succumb to the virus, thanks to a particular gene variant whose historical spread has now been traced.
-
 News
NewsFunctional extinction of Florida’s reef-building corals following the 2023 marine heatwave
The record-breaking 2023 marine heatwave has killed nearly all of Florida’s critically endangered Acropora coral colonies, marking the species’ functional extinction in Florida’s Coral Reef (FCR), researchers report.
-
 News
NewsStudy uncovers origins of urban human-biting mosquito, shedding light on uptick in West Nile virus spillover from birds to humans
The research disproves the theory that the mosquito evolved in the London underground by dating the mosquito’s origin back over 1,000 years and identifies the genetic links between bird-biting and human-biting mosquitoes, key to West Nile transmission.
