All Editorial articles – Page 54
-
 News
NewsReview shows around one in three hospital infections involve antimicrobial resistance
With an estimated 1.14 million deaths worldwide annually caused by bacteria becoming resistant to antibiotics, a study shows that in hospital settings antimicrobial resistance is common and independently associated with a higher risk of death.
-
 News
NewsOkinawan marine sponges yield promising treatment for leishmaniasis
A family of compounds called onnamides shows remarkable potential against the parasite that causes a neglected tropical disease.
-
 News
NewsRivers’ hidden helpers: microbes that clean up nitrogen pollution across China
A new study has revealed how tiny microbes in rivers and wetlands across China help clean up excess nitrogen pollution, offering fresh insights into the health of freshwater ecosystems and the global nitrogen cycle.
-
 News
NewsKey to the riddle of sleep may be linked to bacteria
New research suggests a new paradigm in understanding sleep, demonstrating that a substance in the mesh-like walls of bacteria, known as peptidoglycan, is naturally present in the brains of mice and closely aligned with the sleep cycle.
-
 News
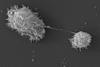
NewsTrojan horse: Amoebae as carriers for human Norovirus and Adenovirus
A new study reveals that common waterborne amoebae can ingest and protect human viruses, extending their environmental persistence. Human norovirus and human adenovirus can enter and persist within FLA.
-
 News
NewsStudy models how human behavior, lockdowns and restrictions shaped COVID’s spread
Researchers employed computer modeling and large datasets to better understand how COVID-19 was transmitted in one community in South Africa during the course of the worldwide pandemic.
-
 News
NewsFatty acids feed cancer-promoting bacteria: How chronic cellular stress alters the gut microbiome
Researchers have identified a cellular mechanism that alters the gut microbiome in a way that promotes cancer. An analysis of patient data shows that the findings also apply to humans.
-
 News
NewsNew study finds dried blood spot test reliably detects congenital CMV at birth
New research confirms that testing for congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) at birth using the routinely collected dried blood spot (DBS) is a reliable and effective method to identify newborns at risk for long-term developmental challenges.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how tick-borne encephalitis virus enters cells
The protein on human cells that tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) uses for infection has now been identified—a major step toward understanding how TBEV causes neurological disease and for developing antiviral drugs.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop a virus cocktail to combat superbugs
Researchers have developed a bespoke phage therapy, Entelli-02, a five-phage cocktail designed specifically to target Enterobacter cloacae complex (ECC), a group of bacteria responsible for severe, often difficult-to-treat infections.
-
 Careers
CareersSummer studentship: Amelia investigates how Streptococci aggregate with other oral bacteria
Amelia Rohim reports back on her AMI-sponsored summer studentship which focused on the investigation of inter-species aggregation between oral bacteria at the University of Michigan with Dr. Alexander Rickard.
-
 News
NewsHow viruses build perfectly symmetrical protective shells
Researchers used a new simulation framework to capture key biological factors like protein diffusion, genome flexibility, and shape-shifting behavior to model how viral proteins self-assemble into symmetric shells.
-
 News
NewsCholera vaccination campaign launched in Darfur to protect over 1.8 million people
A cholera vaccination campaign kicked off on 21 September 2025 in South Darfur, marking the start of a campaign that aims to reach 1.86 million people aged one year and older with oral vaccines in response to the ongoing outbreak.
-
 News
NewsNew single-dose, temperature-stable rabies vaccines could expand global access
Researchers have discovered a new way to make human rabies vaccines that could greatly expand access to immunization across the globe. The new method creates shots that are temperature-stable—meaning they don’t need to be stored at cold temperatures.
-
 News
NewsScientists show how to grow more nutritious rice that uses less fertilizer
Scientists have shown that nanoscale applications of selenium can decrease the amount of fertilizer necessary for rice cultivation while sustaining yields, boosting nutrition, enhancing the soil’s microbial diversity and cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
-
 News
NewsGut bacteria linked to how our genes switch on and off, research finds
The trillions of microbes that live in the human gut may play a bigger role in health than previously thought, according to a review highlighting how the gut microbiome can affect epigenetics, the process that turns genes on or off without changing the DNA itself.
-
 News
NewsFungal genome secrets unlocked in breakthrough for crop disease research
Scientists have developed a new method to improve the accuracy of gene mapping in complex organisms. Using an advanced bioinformatics tool, they re-annotated the genome of Zymoseptoria tritici, a major fungal pathogen responsible for septoria leaf blotch.
-
 News
NewsTropical diseases: Global health meeting showcases resilience of field under fire
At a moment of monumental challenges for global health, thousands of researchers, clinicians and public health professionals from over 100 countries will gather in Toronto for the 2025 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH).
-
 News
NewsTea plant defense: new insights into anthracnose resistance mechanisms
In a recent study, researchers identified key genetic factors that enhance tea plant resistance to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, the pathogen responsible for anthracnose, a devastating disease in tea cultivation.
-
 News
NewsNext-gen anti-bacterial and anti-viral surface modification technology inspired by Korean mussels
Researchers have successfully developed a next-generation surface modification technology with anti-bacterial and anti-viral contamination properties.While maximizing the bactericidal effect, a polydopamine layer, combined with an antibiotic, inhibits the adsorption of coronavirus.
