All Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology articles
-
 News
NewsStudy unravels Black Sea nitrous oxide conundrum
A new study unravels the ’Black Sea nitrous oxide conundrum’, investigating why large amounts of nitrous oxide are mainly produced in ocean areas that lack oxygen, yet the Black Sea - the world’s largest anoxic basin - appears to emit only little N2O.
-
 News
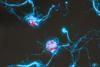
NewsIlluminated sugars show how microbes eat the ocean’s carbon
A team of scientists have designed a molecular probe that lights up when a sugar is consumed. They described how the probe helps to study the microscopic tug-of-war between algae and microbial degraders in the ocean.
-
 News
NewsNitrogen loss on sandy shores: The big impact of tiny anoxic pockets
Denitrification in tiny anoxic pockets on sand grains could account for up to one-third of total nitrogen loss in silicate shelf sands, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsResilient algae may speed up Greenland ice melt
Microscopic algae darken glacier surfaces and can accelerate melting. A new study investigating where the small algae get the necessary nutrients to survive in this hostile environment reveals how they absorb and store nutrients.
-
 News
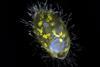
NewsUnusual endosymbionts crop up all over the world
Scientists have discovered peculiar mitochondria-like symbionts all over the world, and unveiled their surprising metabolic capacities in a new study.
-
 News
NewsDeep-sea corals are home to previously unknown bacteria with extremely small genomes
Scientists have discovered two highly unusual bacterial species in the tissue of deep-sea corals from the Gulf of Mexico. The previously unknown coral symbionts have an extremely reduced genome and lack the ability to obtain energy from carbohydrates.
-
 News
NewsA metabolic secret of ethane-consuming archaea unraveled
Scientists have presented a study on the degradation of ethane, the second most abundant alkane in seeps on the deep seafloor. They characterized enzymes involved in the process and found that their reaction breaks an established dogma in the field of anaerobic biochemistry.
-
 News
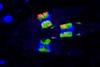
NewsHijacking the command center of the cell: nuclear parasites in deep-sea mussels
Researchers have revealed how a bacterial parasite thrives inside the nuclei of deep-sea mussels, a remarkable feat given that the nucleus is the control center of the cell.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how bacteria in lakes fight climate change
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas frequently produced in the sea and in fresh water. Lakes in particular release large quantities of this climate-killer. Fortunately, however, there are microorganisms that counteract this: They are able to utilize methane to grow and generate energy, thus preventing it from being released into ...
-
 News
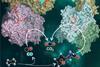
NewsLong-standing marine mystery solved: How algae get nitrogen to grow
In a new study, scientists have shed light on an unexpected partnership: a marine diatom and a bacterium that can account for a large share of nitrogen fixation in vast regions of the ocean.
-
 News
NewsSea zombies: Viruses keep the most common marine bacteria in check
The ocean waters surrounding the German island of Helgoland provide an ideal setting to study spring algae blooms, a focus of research at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology since 2009. Source: Jan Brüwer/Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology Sunset over the island of Helgoland in ...
-
 News
NewsNew Rhizobia-diatom symbiosis discovery solves long-standing marine mystery
Scientists solve a longstanding marine mystery by uncovering a partnership between a diatom and a bacterium that can account for a large share of nitrogen fixation in vast regions of the ocean, with exciting implications also for agriculture.
-
 News
NewsRNA as a common language, presented in extracellular speech-bubbles
Decoding the conversations between microbes of hypersaline environments reveals insights into the origins of complex life.
-
 News
NewsBacteria in the Arctic seabed are active all year round
Despite the pronounced seasonality in their habitat, the bacterial community in Arctic sediments is taxonomically and functionally very stable, a new study finds.
-
 News
NewsResearchers reveal how archaea toggle the nitrogen-uptake switch
By tightly regulating nitrogen uptake, microorganisms avoid overeating nitrogen and thus wasting energy. Scientists now reveal how some methanogenic archaea manage to do so.
-
 News
NewsTiny vesicles exchange genetic information between cells in the sea
Extracellular vesicles play a much greater role in horizontal gene transfer in the ocean than previously assumed.
-
 News
NewsBacteria use organic phosphorus and release methane in the process
Researchers have investigated how bacteria inadvertently release methane in order to obtain phosphorus – with significant effects on atmospheric greenhouse gases.
-
 News
NewsNew microscopy method reveals host-microbe interactions
Researchers are developing a method that reveals the chemical communication between microbes and their host.
-
 News
NewsMicrobial enzyme captures CO2 with electricity
Scientists isolate a microbial enzyme and branch it on an electrode to efficiently and unidirectionally convert CO2 to formate.
-
 News
NewsResearchers reveal sulphate assimilation pathway for methanogen
Study uncovers how a methanogenic microbe reassembles a metabolic pathway piece by piece to transform sulphate into a cellular building block.
