More Healthy Land – Page 56
-
 News
NewsClimate change alters the hidden microbial food web in peatlands
A study of protists shows that a neglected part of the peatlands’ microbial food web is sensitive to climate change, and in ways that are currently not accounted for in models that predict future warming.
-
 News
NewsProtein fragments ID two new “extremophile” microbes—and may help find alien life
Scientists used proteotyping to identify two potentially new types of extremophile bacteria. These results suggest proteotyping could be a more complete solution for identifying extremophile microorganisms from small biological samples.
-
 Careers
CareersLaboratorio Calidad de Aguas
The Water Quality Laboratory of the National University of Salta, founded by Dr Mónica Salusso and Dr. Liliana Moraña, is going from strength to strength - but faces challenges posed by major budget cuts to science and research in Argentina.
-
 News
NewsGenes identified that allow bacteria to thrive despite toxic heavy metal in soil
Some soil bacteria can acquire sets of genes that enable them to pump the heavy metal nickel out of their systems, a study has found. This enables the bacteria to not only thrive in otherwise toxic soils but help plants grow there as well.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals “considerable farmer knowledge” on different aspects of antibiotics risk
A study has revealed “considerable farmer knowledge” on different aspects of antibiotics risks – including antimicrobial resistance – associated with their use on livestock in Kenya.
-
 News
NewsStudy reviews valorization of depolymerized lignin using microorganisms
Lignin is an abundant natural polymer which is eliminated as a byproduct in the pulp and paper industry. A recent review article explored different microbial processes available for sustainable lignin valorization, yielding not only environmental, but also economic benefits. Researchers highlighted the current advancements as well as ...
-
 News
NewsTurns out that eating poo can be vital for birds’ survival
New research explains how eating faeces, known as coprophagy, shapes wild birds’ digestive tracts, enabling them to absorb lost or deficient nutrients and adjust to seasonal variations in food sources.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover new microbial insights hiding above a 60-year-old fire
Soil microbes near the Centralia mine fire reveal new information about how nature responds to — and potentially recovers from — unnatural disasters.
-
 News
NewsCanals used to drain peatlands are underappreciated hotspots for carbon emissions
A study found that one-third of the organic carbon leached from peatland soils into canal waters gets broken down and released into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
-
 News
NewsBeer byproduct behind Marmite could help us recycle metal waste
When we recycle electronic devices we can no longer use, we expect to make the most out of the precious natural resources that went into building them. But electronic waste is notoriously difficult to recycle, because it’s hard to separate the different metals in the waste from each other. ...
-
 News
NewsScientists harness fungal bioluminescence to create glow-in-the-dark plants
Synthetic biologists have reported the discovery of multiple plant enzymes – hispidin synthases – that can perform the most complex reaction of the bioluminescence pathway.
-
 News
NewsResearch reveals novel herpesvirus in South American pinnipeds
Scientists detected Otariid gammaherpesvirus 1 (OtGHV1) in free-ranging South American pinnipeds, and a novel herpesvirus Otariid gammaherpesvirus 8 (OtGHV8) in South American sea lions (Otaria byronia) in the Southern Hemisphere.
-
 News
NewsScientists ID new genus of fungi on grasses
This study examined a mushroom species, Campanella subdendrophora, also known as Tetrapyrgos subdendrophora, which fruits on grasses in the US Pacific Northwest, and determined that a new genus, Metacampanella was needed for this taxon.
-
 News
NewsStudy explains how a fungus can control an extremely harmful pest
The research was conducted at SPARCBio, a center established by FAPESP and biological control company Koppert at the University of São Paulo’s Luiz de Queiroz College of Agriculture.
-
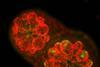 News
NewsMarine algae implants could boost crop yields
Scientists have discovered the gene that enables marine algae to make a unique type of chlorophyll. They successfully implanted this gene in a land plant, paving the way for better crop yields on less land. Source: Robert Jinkerson/Tingting Xiang/UCR Fluorescence image of coral Acropora juvenile polyps hosting the ...
-
 News
NewsAMI experts issue warning over UK’s Sustainable Farming Initiative
Applied Microbiology International has urged the UK government to take microbiological considerations into account when creating initiatives like the Sustainable Farming Incentive - warning that the potential benefits arising from such schemes will be limited otherwise.
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough discovery will improve medical monitoring, preventive care for elephants
Researchers have found that population-based reference values for blood cell counts are not sensitive enough to detect critical deviations that frequently occur with active Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus infection.
-
 News
NewsMagnetic resonance imaging shows how infection progresses in strawberry crown
Researchers from the Department of Technical Physics and the Department of Environmental and Biological Sciences at the University of Eastern Finland have used magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, to investigate how the pathogen Phytophthora cactorum affects the growth and development of strawberry plants. This pathogen causes crown rot in strawberries and ...
-
 News
NewsStudy supports disease-challenged broiler chickens through nutrition
New research suggests diet changes might help to ensure optimal growth during outbreaks of the parasitic infection coccidiosis in broiler chickens.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover 18 new species of gut microbes in search for origins of antibiotic resistance
Scientists have found 18 novel species of a type of bacteria called enterococci, which are gut microbes found in most land animals.
