All Research News articles – Page 50
-
 News
NewsEarly challenges to the immune system disrupt oral health
Researchers identified changes over time in the oral microbiome of children living with HIV, offering insights into how early immune challenges shape not only oral health but also systemic health.
-
 News
NewsNew network to address malaria among school-aged children in sub-Saharan Africa
A new network aims to improve malaria prevention among school-aged children in sub-Saharan Africa. The new partnership will unite researchers, policymakers, healthcare practitioners and other stakeholders across multiple countries to better understand and address the burden of malaria in children.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop new approach to fighting many viruses at once
Scientists have developed a research pipeline to fuel the development of “universal vaccines,” that would address broad viral families and mutated viral variants.
-
 News
NewsEnvironmental antibiotic resistance unevenly addressed despite growing global risk, study finds
Antibiotic resistance in the environment is a growing and largely overlooked crisis receiving inconsistent attention, according to a new study. Worryingly few studies have explored how antibiotic resistance spreads in the air, oceans or green spaces.
-
 News
NewsNovel immunologic surveillance study provides new insights into post-pandemic return of respiratory viruses
Non-pharmaceutical interventions such as masking and distancing targeted towards SARS-CoV-2 during the pandemic also decreased circulation rates of and population immunity to common respiratory pathogens in children, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsCopper antimicrobials can drive antibiotic resistance in bacteria, but there’s a fix, scientists say
Microbiologists have found that heavy use of copper antimicrobials can drive antibiotic resistance in bacteria. However, resistance quickly diminishes without copper exposure, suggesting that copper could help reduce antibiotic resistance if alternated with other measures.
-
 News
NewsInvestigating regional-specific gut microbial distribution: an uncharted territory in disease therapeutics
A new perspective highlights the critical role of region-specific gut microbial distribution across intestinal segments (e.g., duodenum, colon) in regulating host metabolism and immunity, challenging traditional fecal-centric approaches.
-
 News
NewsNational study urges expanded vaccine screening in emergency departments
About 49% of people are unaware of one or more vaccines recommended for them. Further, 86% have not received one or more of these vaccines, according to the first national comprehensive vaccine surveillance study conducted in emergency departments.
-
 News
NewsMaple compound offers new way to fight tooth decay
A new study highlights the potential of using a natural compound from maple to combat the bacteria responsible for tooth decay: Streptococcus mutans. Epicatechin gallate is a powerful and safe alternative to traditional plaque-fighting agents.
-
 News
NewsRevealed: New vaccine target to block malaria transmission
Researchers have visualised a key protein complex in malaria parasites for the first time, uncovering a new target for next-generation vaccines that could help stop the disease from spreading.
-
 News
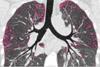
NewsScientists home in for a close look at lung infections
A new study has meticulously sampled different lung regions in people with cystic fibrosis to understand why infections persist after new treatments.
-
 News
NewsRNA immunity: A silent defender against viruses in mammals
Researchers propose that small RNA molecules play a direct and specific role in fighting viral infections in mammals. RNA immunity relies on the base-pairing precision of small RNA fragments, such as microRNAs, to recognize and suppress viral genetic material.
-
 News
NewsResearch probes the gut microbiome and its metabolite short-chain fatty acids in postmenopausal osteoporosis
Postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP) is framed as a systemic bone disease driven by estrogen withdrawal, but a new review positions gut dysbiosis and its fermentation products—short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)—as equally influential regulators of skeletal fate.
-
 News
NewsSweet disguise: the human body hides RNA with sugar coatings
To our immune system, naked RNA is a sign of a viral or bacterial invasion and must be attacked. But our own cells also have RNA. To ward off trouble, our cells clothe their RNA in sugars, a new study reports.
-
 News
NewsAP2-domain transcription factor WRI5a-regulated MtABCB1 promotes arbuscule development in mycorrhizal symbiosis
A new study of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) symbiosis suggests that the MtABCB1 gene likely influences arbuscule development by modulating the distribution and homeostasis of auxin within symbiotic cells.
-
 News
NewsThe microbiome of the indri, a critically endangered lemur, has been described
An international study has ascertained the composition of the intestinal microbiome of the indri, a critically endangered lemur in Madagascar. It has found up to 47 unknown species of bacteria, and revealed the indri’s microbiome is transmitted within their social group.
-
 News
NewsResearchers create improved natural blue food dye from algae
Food scientists have created a natural blue food dye made of algae protein that could replace petroleum-based artificial food colorants with a stable, adaptable option.
-
 News
NewsCorals in Brazilian archipelago capture carbon equivalent to the burning of 324,000 liters of gasoline per year
A single species found in the Alcatrazes Archipelago, brain coral, produces around 170 tons of calcium carbonate annually. This represents the retention of approximately 20 tons of carbon in mineral form, which can last for centuries or millennia.
-
 News
NewsM42 announces breakthrough results for its AI-powered tuberculosis screening
A new study is among the largest real-world clinical validations of an AI-driven healthcare solution to date, analyzing over one million chest X-rays (CXRs) to evaluate the efficacy and scalability of AI in TB screening.
-
 News
NewsDancing against the current: Microbial survival strategy
In scalding hot water rushing through narrow channels, some bacteria have evolved a surprising survival technique: they cling to surfaces, stand upright, and sway rhythmically—like tiny street dancers fighting the flow.
