All UK & Rest of Europe articles – Page 13
-
 News
NewsUnprecedented decline in marine viruses in the western Mediterranean linked to climate change revealed
Researchers have described a sustained and unprecedented decrease in the abundance of marine viruses in the northwestern Mediterranean over the last two decades. The findingis based on the longest-known time series data on marine viruses to date.
-
 News
NewsNew editorial urges clinicians to address sex-based disparities in sepsis treatment
Standardized antibiotic dosing frequently ignores patient-level variability. A newly published editorial is calling attention to how biological sex and gender inequities contribute to suboptimal sepsis treatment, potentially compromising outcomes for women.
-
 News
NewsBacteria reveal how climate-damaging nitrous oxide forms in the ocean
Marine microorganisms produce large amounts of nitrous oxide, a highly potent greenhouse gas. Researchers investigated the exact processes involved during an expedition to the Pacific. The results are important for climate modeling.
-
 News
NewsFats provide clues to life at its limits in the deep sea
Extreme conditions on the ocean floor include high pressures and salinities, as well as extreme pH values and a limited supply of nutrients. A team of researchers has now been able to detect microbial life in two newly discovered mud volcanoes with very high pH values.
-
 News
NewsDrones reveal unexpectedly high emissions from wastewater treatment plants
Greenhouse gas emissions from many wastewater treatment plants may be more than twice as large as previously thought. This is shown in a new study in which the researchers used drones with specially manufactured sensors to measure methane and nitrous oxide emissions.
-
 News
NewsHorizon Awards 2025: Professor Elaine Cloutman-Green named as winner of Christiana Figueres Policy to Practice Award
Professor Elaine Cloutman-Green, Consultant Clinical Scientist at Great Ormond Street Hospital, has been named as the newest winner of the Christiana Figueres Policy to Practice Award.
-
 News
NewsHorizon Awards 2025: Professor Thomas Crowther named as winner of Rachel Carson Award 2025
British ecologist Professor Thomas Crowther has been named as the newest winner of the Rachel Carson Environmental Conservation Excellence Award.
-
 News
NewsNew study explores ‘legacy effects’ of soil microbes on plants across Kansas
A new study analyzes soils sampled across the state of Kansas to determine the importance of “legacy effects” — or how soils from a specific location are influenced by microbes that have evolved in response to the specific climate at that site for many years.
-
 News
NewsA nose for microbes: how hunger tunes the brain
New research reveals how missing just one essential amino acid can change gene expression and the brain’s sensory systems, prompting animals to seek out protein-rich yeast and gut bacteria that help them restore nutritional balance and survive in times of need.
-
 News
NewsBiochar and hydrochar show contrasting climate effects in boreal grasslands
Researchers tested how biochar and hydrochar, combined with nitrogen fertilizer, affected greenhouse gas emissions, soil carbon pools, and crop yield in a typical boreal legume grassland. They found that biochar and hydrochar influenced soil processes in opposite ways.
-
 News
NewsNew antibiotic for drug-resistant bacteria found hiding in plain sight
Chemists have discovered a promising new antibiotic that shows activity against drug-resistant bacterial pathogens, including MRSA and VRE. Pre-methylenomycin C lactone was ‘hiding in plain sight’ — as an intermediate chemical in the natural process that produces the well-known antibiotic methylenomycin A.
-
 News
NewsNew software tool fast-tracks identification and response to microbial threats
MARTi is an open-source software tool that powers real-time analysis and visualisation of metagenomic data. The team have created an accessible interface which increases the usability and accessibility of metagenomic analysis.
-
 News
News£4.56M Wellcome Discovery Award to investigate natural human resistance to Salmonella
The University of Liverpool’s Professor Jay Hinton and an international team have been awarded a £4,555,647 Wellcome Discovery funding to lead a five-year research programme exploring how some healthy humans are naturally protected from being infected by Salmonella Typhimurium.
-
 News
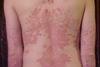
NewsPsoriasis-linked gene mutation also impacts gut health
A mutation previously linked to skin disorders like psoriasis may also play a surprising role in gut health, according to new research. This mutation activates skin immune responses but also affects the intestine, revealing a new connection between genetics, the immune system, and the gut.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows differences between documented and self-reported polio vaccination rates
Until poliovirus is eradicated worldwide, vaccination protection is important as the virus could be reintroduced at any time. Epidemiologists have now shown that many people in Germany do not know their vaccination status and cannot find it on their vaccination record.
-
 News
NewsWarmer Nordic springs double the incidence of avian malaria
A unique long-term study, in which biological samples were collected from the same population of blue tits over a 30-year period, shows that rising spring temperatures have doubled the incidence of avian malaria in southern Sweden.
-
 News
NewsGroundbreaking new projects launched to lower the cost of monoclonal antibody production
LifeArc and the Gates Foundation have awarded more than $5m to seven projects aimed at developing cheaper and more efficient ways to produce monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatments. The innovative approaches include using filamentous fungus to produce mAbs.
-
 News
NewsHorizon Awards 2025: Dr Manu De Rycker named as winner of WH Pierce Prize
Dr Manu De Rycker, a Principal Investigator at the University of Dundee, has been named as the newest winner of the WH Pierce Global Impact in Microbiology Prize.
-
 News
NewsDNA from Napoleon’s 1812 army identifies the pathogens likely responsible for the army’s demise during their retreat from Russia
Microbial paleogenomicists extracted DNA from the teeth of soldiers from Napoleon’s ill-fated invasion of the Russian Empire and found no trace of typhus. Instead, they identified two pathogens known to cause enteric fever and relapsing fever.
-
 News
NewsProtection against winter vomiting bug spread with arrival of agriculture
Norovirus clears up after a couple of days, but the protection it provides is short-lived, meaning that the same person can fall repeatedly sick in a short space of time. But some people cannot succumb to the virus, thanks to a particular gene variant whose historical spread has now been traced.
