All visceral leishmaniasis articles
-
 News
NewsHorizon Awards 2025: Dr Manu De Rycker named as winner of WH Pierce Prize
Dr Manu De Rycker, a Principal Investigator at the University of Dundee, has been named as the newest winner of the WH Pierce Global Impact in Microbiology Prize.
-
 News
NewsCompound derived from Brazilian plant acts against parasite that causes visceral leishmaniasis
A compound derived from Nectandra leucantha, a tree native to southern Brazil (local names canela-seca or canela-branca), has the potential to be used to treat visceral leishmaniasis, a neglected tropical disease.
-
 News
NewsResearch points the way to lifesaving antiparasitic drugs while unlocking a scientific mystery
A breakthrough in understanding how a single-cell parasite makes ergosterol (its version of cholesterol) could lead to more effective drugs for human leishmaniasis, a parasitic disease that kills about 30,000 people around the world every year.
-
 News
NewsPromising patient-friendly oral drug against visceral leishmaniasis enters Phase II clinical trial in Ethiopia
The new molecule has the potential to revolutionize treatment for the deeply neglected and hard-to-treat disease, as the Eastern Africa region charts the way to its elimination.
-
 News
NewsNanoparticles containing lupeol treat visceral leishmaniasis with scant side effects
In animal tests conducted at São Paulo State University (UNESP), the strategy reduced spleen and liver parasite numbers by 99.9%.
-
 News
NewsTest detects co-infection by novel parasite in severe cases of visceral leishmaniasis
The test developed by Brazilian researchers accurately identifies the causative agent in less than two hours, so that treatment can be properly targeted.
-
 News
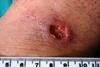
NewsGenetic fingerprint suggests cutaneous leishmaniasis may be gaining foothold in US
Analysis reveals DNA evidence of a US-acquired strain of cutaneous leishmaniasis - the prospect of a growing threat comes amidst concerns that domestic sand flies could acquire a deadly form of the disease via dog imports.
-
 News
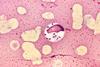
NewsLeishmania’s secret weapon is ability to infect non-immune cells
The parasites that cause visceral leishmaniasis appear to have a secret weapon, new research suggests - they can infect non-immune cells and persist in those uncommon environments.
-
 News
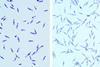
NewsCo-infection by novel species of parasite found in visceral leishmaniasis patient
Genome sequencing of clinical samples from a child has revealed the simultaneous presence of the protozoan Leishmania infantum and an as-yet unnamed parasite that was identified earlier in a fatal case of visceral leishmaniasis.
