All The Microbiologist articles in Web Issue – Page 307
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover microbes turning food waste into energy
Researchers have identified a previously unknown microbe that plays a crucial role in converting food waste into renewable natural gas, using a molecular tagging approach that could also detect other elusive microbes - including those that are breaking down microplastics in the ocean.
-
 News
NewsPowered by mushrooms, living computers are on the rise
Researchers have discovered that common edible fungi, such as shiitake mushrooms, can be grown and trained to act as organic memristors, a type of data processor that can remember past electrical states. They could also be used to create other types of low-cost computing components.
-
 News
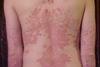
NewsPsoriasis-linked gene mutation also impacts gut health
A mutation previously linked to skin disorders like psoriasis may also play a surprising role in gut health, according to new research. This mutation activates skin immune responses but also affects the intestine, revealing a new connection between genetics, the immune system, and the gut.
-
 News
NewsNutritional supplements boost baby coral survival
Feeding coral larvae a coral ’baby food’ can dramatically increase their chances of survival, offering a new avenue for reef restoration as climate change continues to threaten coral ecosystems, a new study finds.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop floral-scented fungus that lures mosquitoes to their doom
Taking advantage of the mosquito’s natural attraction to flowers, an international team of researchers engineered a new strain of Metarhizium fungus that imitates a flower’s sweet scent and lures the bloodsucking bugs to their deaths.
-
 News
News£4.56M Wellcome Discovery Award to investigate natural human resistance to Salmonella
The University of Liverpool’s Professor Jay Hinton and an international team have been awarded a £4,555,647 Wellcome Discovery funding to lead a five-year research programme exploring how some healthy humans are naturally protected from being infected by Salmonella Typhimurium.
-
 News
NewsNew software tool fast-tracks identification and response to microbial threats
MARTi is an open-source software tool that powers real-time analysis and visualisation of metagenomic data. The team have created an accessible interface which increases the usability and accessibility of metagenomic analysis.
-
 News
NewsNew antibiotic for drug-resistant bacteria found hiding in plain sight
Chemists have discovered a promising new antibiotic that shows activity against drug-resistant bacterial pathogens, including MRSA and VRE. Pre-methylenomycin C lactone was ‘hiding in plain sight’ — as an intermediate chemical in the natural process that produces the well-known antibiotic methylenomycin A.
-
 News
NewsNew 2025 data shows COVID-19 vaccines provide effective, durable protection
Updated COVID-19 vaccines are still providing effective protection against infection, emergency department visits, hospitalization and death, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsScientists identify cells by seeing how high they levitate
A new cell-sorting device uses electromagnetic levitation to precisely direct the movement of cells. It can be used to separate different types of cells — cancer cells from healthy cells, or live cells from dead cells, for example — with many potential applications in the lab and in the clinic.
-
 News
NewsRebalancing the gut: how AI solved a 25-year Crohn’s disease mystery
Researchers have settled a decades-long debate surrounding the role of the first Crohn’s disease gene to be associated with a heightened risk for developing the auto-immune condition.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop novel gene therapy for hereditary hearing loss
Scientists have introduced an innovative gene therapy method to treat impairments in hearing and balance caused by inner ear dysfunction. The treatment holds promise for treating a wide range of mutations that cause hearing loss.
-
 News
NewsBiochar and hydrochar show contrasting climate effects in boreal grasslands
Researchers tested how biochar and hydrochar, combined with nitrogen fertilizer, affected greenhouse gas emissions, soil carbon pools, and crop yield in a typical boreal legume grassland. They found that biochar and hydrochar influenced soil processes in opposite ways.
-
 News
NewsEurope backs first cervical cancer vaccination campaign in Angola
Angola’s first national vaccination campaign will immunise over 2 million girls aged 9–12 against cervical cancer. The national rollout began this week with coordinated delivery across schools, clinics, and communities in all 21 provinces.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop an efficient method of producing proteins from E. coli
Proteins sourced from microorganisms are attracting attention for their potential in biomanufacturing a variety of products, including pharmaceuticals, industrial enzymes, and diagnostic antibodies. These proteins can also be used for converting resources into biofuels and bioplastics, which could serve as viable alternatives to petroleum-based fuels and products. Therefore, efficiently producing ...
-
 News
NewsMissing nutrient in breast milk may explain health challenges in children of women with HIV
A new study reveals that breast milk from women living with HIV contains significantly lower levels of tryptophan, an essential amino acid likely important for infant immune function, growth, and brain development.
-
 News
NewsScientists to probe how microbes break down water-soluble polymers in wastewater
Scientists and industry have teamed up to investigate how microbes in wastewater interact with and potentially biodegrade polymers called viscosifiers.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals how immune cells help defend against candida infections
New research shows that eosinophils, immune cells usually linked to allergies, also play a protective role against Candida infections by using the CD48 receptor to recognize the fungus and release proteins that stop its growth.
-
 News
NewsA nose for microbes: how hunger tunes the brain
New research reveals how missing just one essential amino acid can change gene expression and the brain’s sensory systems, prompting animals to seek out protein-rich yeast and gut bacteria that help them restore nutritional balance and survive in times of need.
-
 News
NewsViral infections at the heart of why honey bees overthrow their queen
Common viral infections shrink a queen bee’s ovaries, reducing both her egg-laying capacity and her production of methyl oleate, a pheromone that normally keeps worker bees loyal. When methyl oleate levels drop, workers will “smell” the queen’s weakness - and begin preparing her successor.
