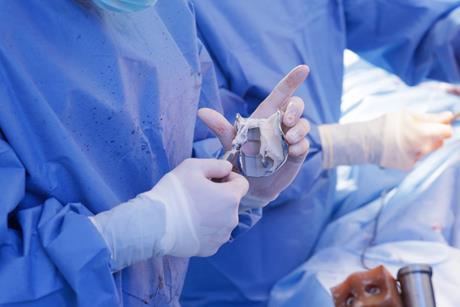
Webinar: Unraveling periprosthetic joint infection
The free ‘Unraveling Periprosthetic Joint Infection’ webinar on March 25 explores one of the most challenging complications in modern orthopedic medicine, sitting at the intersection of microbiology, surgery, and patient care.
- Previous
- Next
A journey to run a polymerase chain reaction in the kitchen
Did you know an air fryer can thermocycle?
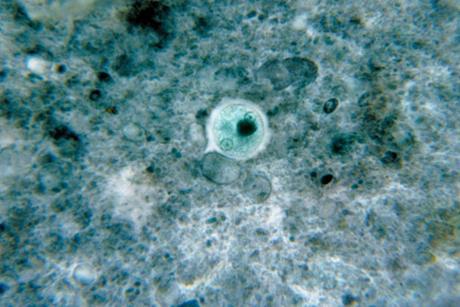
Read storyRethinking Blastocystis: a One Health perspective on a common and controversial gut protist worth our attention
Here’s the reality: a stool report that reads “Blastocystis detected” still provokes strong reactions. Some clinicians worry and reach for antibiotics. Some laboratories add a note about “uncertain significance.” Patients search online and find polarised claims ranging from harmless commensal to stealth pathogen. The truth is more nuanced and more ...
The world’s fermented foods in health and history
The use of microbes in food fermentation dates back thousands of years; archaeological evidence suggests that fermented beverages such as rice wine were produced in China as early as 7000 BC, while bread and beer were staples in ancient Egypt.
Yeast-plant interactions: nature’s silent partnership for ecosystems and agriculture
Plant–microbe interaction studies have increased greatly in recent years. This sharp increase in studies is attributed to the need to better understand these interactions, which in turn can be used to enhance crop productivity and stress tolerance, reduce fertilizer inputs, and improve plant health. This is vital to meet the ...
Under the Lens video series
The Microbiologist: Under the Lens | Episode 2
The Microbiologist: Under the Lens | Episode 1
Get unlimited access to The Microbiologist
The Microbiologist provides detailed information on the latest research, topics, reviews, events and news on a wide variety of microbiological topics.
Members of Applied Microbiology International get unlimited access as a benefit. Find out more about AMI Membership
Listeria: the inconvenient truth that shaped our industry
Director General of the Chilled Food Association, Karin Goodburn MBE, who sits on AMI’s Food Security Advisory Group, reveals why the publication of new Listeria guidance for the UK food industry is regarded as a landmark moment.
We couldn’t get people interested in science - until we started speaking their language
In 2020, Puerto Rico faced a misinformation crisis. Melanie Ortiz Alvarez De La Campa reveals how five STEM undergraduates created a sci-comm organization that helped pass legislation, educated thousands, and created an inclusive database of Caribbean scientists.
The politics behind the global divide in bacteriophage therapy
The therapeutic potential of bacteriophages (or ‘phages’) has been widely dismissed for decades in the West, despite being regularly used to treat patients worldwide in the early and mid-20th century. In an age rife with disinformation, can the true potential of clinical phage technology be communicated to a public already uneasy about scientific intervention?
Introducing AMI’s Diversity & Inclusion Strategy
Just over a month ago, AMI launched its first Diversity & Inclusion Strategy — the culmination of almost two years spent brainstorming, drafting, discussing, editing, and reviewing our role, responsibility, and ambitions within this vital space. Now that our strategy is live and visible to all, we’re proud to share the vision we’ve been building behind the scenes.
Summer Studentship: novel antivirals and host-virus interactions
Jessica Harris reports back on her Summer Studentship at De Montfort University, and her research into how plant-derived compounds affect viruses, and whether combining these antivirals might increase viral inhibition.
The National Collection of Pathogenic Viruses (NCPV): a critical resource for virology and public health
It’s now 25 years since the National Collection of Pathogenic Viruses (NCPV) was founded as a dedicated, secure, and relevant national virus repository for the UK. Jane Burton, Teresa Ramalho and Tilly Maybery explore how the collection has evolved - and is tackling future global health concerns.
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce Covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
In a large, randomized trial, researchers have found that high-dose vitamin D3 did not reduce COVID-19 infection severity, but may impact long COVID outcomes.
Mothers' exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
A study dives into new depths to explore why only some babies develop severe infection to common bacteria. The research revealed that the babies that became most severely ill from E. coli infections also had markedly lower levels of germ-fighting antibodies transferred from their mothers.
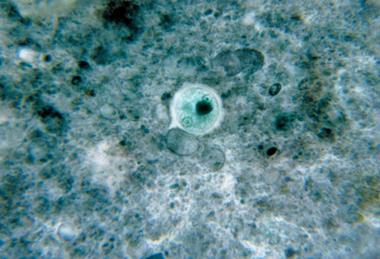
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
Reported adverse effects associated with the current first-line treatment for amoebiasis, coupled with the evolution of resistance to it, call for the need to search for plant-based alternatives. This study systematically reviews medicinal plants with activity against Entamoeba histolytica.
Food security
Everyday foods could hide fungal risks for mothers and children
A collaborative, multi-institutional project will examine how exposure to zearalenone – a mycoestrogen produced by mold with estrogen-like activity – may affect pregnancy outcomes and children’s growth.
Clean Water
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
Reported adverse effects associated with the current first-line treatment for amoebiasis, coupled with the evolution of resistance to it, call for the need to search for plant-based alternatives. This study systematically reviews medicinal plants with activity against Entamoeba histolytica.
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
In 2019, a marine heat wave struck a coral reef on the island of Moorea in French Polynesia, killing much of the coral and the beneficial algae that colonized it. A long-term study of the area is challenging scientists’ understanding of the cycles of destruction and repair that can occur on a coral reef.