All Bacteria articles – Page 112
-
 News
NewsStudy unveils gene expression of photosynthetic symbiont in marine diatom
A new study explores the genetic expression of a photosynthetic symbiont that lives inside an abundant marine organism.
-
 News
NewsRule-breaking anoxic bacteria infected with viruses
Researchers investigating why green and purple bacteria in northeast Washington didn’t obey the usual rules found they had genes in their metagenome that came from viruses.
-
 News
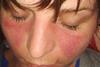
NewsLupus flare-ups linked to Ruminococcus blautia gnavus blooms in gut
A new study found that bacterial blooms of the gut bacterium Ruminococcus blautia gnavus occurred at the same time as disease flare-ups in five of 16 women with lupus of diverse racial backgrounds studied over a four-year period.
-
 News
NewsMagnetic bacteria found on deep sea vents
Magnetotactic bacteria that ‘sense’ the Earth’s magnetic field have been found on deep undersea vents.
-
 News
NewsDevice holds promise for diagnosing TB’s missing millions
Investigators collaborating on new chip-based technology using dielectrophoresis to selectively isolate <i>Mycobacterium tuberculosis</i> from sputum from suspected TB patients in underserved areas report promising results
-
 News
NewsHospital infection shows dual colonisation strategy
Researchers have uncovered why one of the most dangerous nosocomial pathogens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, is so difficult to combat - it follows a dual strategy, with some bacteria colonizing the tissue surface while others spread in the body.
-
 News
NewsPredatory bacteria offer vision of chlorine-free drinking water
Researchers investigating what would happen if chlorine was omitted from drinking water have found that a harmless predatory bacteria grew in numbers and devoured most of the other bacteria.
-
 News
NewsBioactive glass doped with silver delivers longer-lasting antimicrobial wound protection
Researchers at the University of Birmingham have demonstrated that silver retains antimicrobial activity for longer when it is impregnated into ‘bioactive glass’, and shown for the first time how this promising combination delivers more long-lasting antimicrobial wound protection than conventional alternatives.
-
 News
NewsFermentation process transforms agri-waste into lactic acid
Researchers have used consolidated bio-saccharification (CBS) to take the raw material of lignocellulose and produce lactic acid through a fermentation process.
-
 News
NewsResearch tool reveals how staph hides in human cells
Researchers have discovered how Staphylococcus aureus, a common bug that can cause one of the most serious bacterial infections, hides inside human cells to avoid detection by the immune system.
-
 News
NewsEarly warning sensor changes colour when wound becomes infected
A team at Queen’s University Belfast have developed a non-invasive sensor that changes colour when a wound becomes infected, alerting healthcare staff hours before symptoms become visible to the eye.
-
 News
NewsOral probiotic can treat dry eye disease
Researchers have found that oral administration of a commercially available probiotic bacterial strain improved dry eye disease in an animal model.
-
 News
NewsTreatment with enzyme inhibitor can help combat antimicrobial resistance
Researchers have shown that intravenous treatment with MK-3402, a metallo-beta-lactamase inhibitor, can be an effective strategy in fighting antimicrobial resistance.
-
 News
NewsMapping evolution of E. coli virulence factor offers refined drug target
Researchers have presented evidence that targeting the K1 capsule can be used as the basis of treatment, paving the way to prevent serious E. coli infections.
-
 News
NewsProbiotic supplementation can help adults with Major Depressive Disorder
A study shows improvements in depression and anxiety scores among individuals supplementing with probiotics alongside standard antidepressant medication.
-
 News
NewsTargeting Fusobacterium reduces formation of endometriosis lesions
Researchers have discovered that using an antibiotic to target Fusobacterium reduced the formation of lesions associated with endometriosis, a gynaecological disorder characterized by endometrial tissue usually found inside the uterus being found outside it.
-
![Low-Res_pseudomonas aeruginosa 2[87]](https://d3rmrttq0bsnxi.cloudfront.net/Pictures/100x67/9/0/4/2904_lowres_pseudomonasaeruginosa287_978595_crop.jpg) News
NewsScientists discover small RNA that regulates bacterial infection
Researchers have identified the major mechanism behind the transition between chronic and acute P. aeruginosa infections.
-
 News
NewsConsortium awarded €9M to create better tuberculosis vaccine
Researchers from the University of Leicester are among those hoping to create an improved vaccine to fight tuberculosis as part of a €9 million Euro project.
-
 News
NewsCholera bacteria form aggressive biofilm to kill immune cells
Resarchers have discovered that the bacterial pathogen that causes cholera forms a novel type of bacterial community on immune cells: an aggressive biofilm that is lethal for the cells.
-
 News
NewsVaccine primes frog microbiome for future exposure to deadly fungal outbreak
A new study has found that a new vaccine against the deadly chytrid fungus in frogs can shift the composition of the microbiome, making frogs more resilient to future exposure to the fungus.
