All Bacteria articles – Page 111
-
 News
NewsJust one single molecule can disrupt symbiosis
Researchers have found that the bacterial species Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica lives happily in the hyphae of the fungus Rhizopus microsporus only when the bacteria produce a certain protein.
-
 News
NewsInvestigational three-month TB regimen is safe but ineffective
The first clinical trial of a three-month tuberculosis (TB) treatment regimen is closing enrollment because of a high rate of unfavorable outcomes with the investigational course of treatment.
-
 News
NewsPackaging tray can signal Salmonella contamination before food is unwrapped
Researchers have created a new packaging tray that can signal when Salmonella or other dangerous pathogens are present in packages of raw or cooked food such as chicken.
-
 News
NewsArtificial cells show that ‘life finds a way’
Scientists studying a synthetically constructed minimal cell that has been stripped of all but its essential genes have found it can evolve just as fast as a normal cell.
-
 News
NewsVaginal suppository with lactobacilli can prevent recurrent cystitis
Scientists find that administration of Lactobacilli could mitigate the differences in vaginal microbiota between women with and without recurrent cystitis.
-
 News
NewsNew bacterial blueprint will help fight antibiotic resistance
Scientists have gained high-res structural insights into a key bacterial enzyme, which may help chemists design new drugs to inhibit it and thus suppress disease-causing bacteria.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover secrets of bacteria threatening Vidalia onion production
Researchers have confirmed which genes in the bacterial pathogen Pantoea ananatis high virulence cluster are essential and which genes contribute partially to a disease that causes rotting symptoms in Vidalia onions.
-
 News
NewsAlarming antibiotic resistance discovered in war-torn Ukraine
Microbiologists investigating bacterial resistance among the war-wounded Ukrainian patients treated in hospitals have warned that the entire European region is under threat after finding that many were affected by bacteria that exhibited an extremely high level of antibiotic resistance.
-
 News
NewsNatural molecule added to toothpaste may help prevent plaque and cavities
Scientists have discovered that 3,3′-Diindolylmethane (DIM), a naturally occurring molecule also known as bisindole, reduces the biofilms that produce plaque and cavities by 90% and is also found to have anti-carcinogenic properties.
-
 News
NewsNearly half of TB cases in prisons worldwide go undetected
In the first global assessment of tuberculosis among incarcerated people, a new study found consistently high TB case rates and low case detection in prisons.
-
 News
NewsNew enzyme designed using Antarctic bacteria and computer calculations
For the first time, researchers have succeeded in predicting how to change the optimum temperature of an enzyme using large computer calculations and based on a cold-adapted enzyme from an Antarctic bacterium.
-
 News
NewsFuture medicines could feature ingredients targeting bacterial motility and chemotaxis
Future medicines will probably be made up of a cocktail of compounds that inhibit different bacterial targets, including some that act against their motility and chemotaxis mechanisms, a new review suggests.
-
 Opinion
OpinionMicrobial hydrogen cycling - the good, the bad and the ugly
With global populations looking likely to top 10 billion by the year 2050, the practices that we use to grow food need to adapt in kind - and what better way is there but to harness the innate power of microbes!
-
 News
News‘Hospital pathogen’ widespread in Vietnam’s environment
A pathogen considered to be a cause of hospital infection is widespread in Vietnam, turning up in farm soil and pig faeces as well as hospital beds and toilet floor surfaces, with 70% of isolates found to be resistant to at least one class of antimicrobials.
-
 News
NewsMicroneedle array with antibacterial nanoparticles targets acne
Researchers have designed a new microneedle patch engineered with ultrasound-responsive zinc-based metal-organic framework (MOF) antibacterial nanoparticles, promising pain-free delivery to treat bacterial infection on skin tissue and facilitate skin repair.
-
 News
NewsMolecular insights may inform new treatments for drug-resistant TB
Researchers have used state-of-the-art imaging to examine two new compounds that target ATP synthase, potentially stopping TB bacteria from producing the energy they need to survive.
-
 News
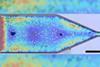
NewsResearchers can use ultrasound to control orientation of small particles, including bacteria
Using ultrasound technology and a nozzle, scientists have separated, controlled and ejected different particles based on their shape and various properties, with implications for drug delivery and bioprinting.
-
 News
NewsD-amino acids play role in cholera bacterium’s bid to escape
Cholera bacteria use specific D-amino acids to escape unfavourable niches and form complex ecological systems, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsStreptomycetes reveal their arsenal of signalling compounds
Streptomyces bacteria produce a group of signalling molecules that trigger a variety of processes, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsSmall ruminant farms could spread human diarrhoea causing bug
Goat and sheep dairy farms are a potential transmission source for a bacteria that can cause human gastroenteritis, according to a new study.
