All Ecology articles – Page 7
-
 News
NewsRain showers can dramatically impact fungal communities in urban lakes
Rainfall can have dramatic effects on the microbial communities living in urban lakes, a new paper published in the Journal of Applied Microbiology reveals.
-
 News
NewsNorthward jet stream shift hits phytoplankton in the Mediterranean Sea
In just over 20 years, the northward shift of the subtropical jet stream — a high-altitude airflow — caused by climate change has reduced primary production in the northwestern Mediterranean by about 40%, affecting the base of the marine food web.
-
 News
NewsResearchers pinpoint fungal hotspots of ‘dark taxa’ across Earth’s underground ecosystems
A new study finds that 83% of ectomycorrhizal fungi are known only by their DNA sequences that can’t be linked to named or described species, posing problems for conservation.
-
 News
NewsEndangered mountain caribou possess unique gut microbiome that may be important for recovery efforts
Endangered mountain caribou in British Columbia possess a unique gut microbiome in late winter when they feed on tree lichens, a finding that could guide caribou recovery efforts, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsFish ‘beauty salons’ offer insight into how microbes move within reefs
A new study highlights the potential impact of cleaner fish in coral reefs and the need to demystify their role in shaping reef microbial diversity and transmission.
-
 News
NewsBacteria hitch a ride on yeast puddles to zoom around
Researchers found that bacteria can speed up by using the fluid pockets shaped by neighboring yeast cells. These microscopic moisture trails allow bacteria to swim farther and spread faster—revealing a new way for microbes to travel through soil, plants, and the human body.
-
 News
NewsStudy resolves diatom tree of life - and could offer clues to Earth’s puzzle
A new study finds that diatoms evolved slowly for the first 100 million years of their existence. Then, 170 million years ago, they reached an inflection point characterized by a burst of rapid speciation orders of magnitude faster than anything that had preceded it.
-
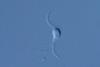 News
NewsResearchers discover unusual new marine flagellate
A newly discovered species of unicellular organism found in seawater belongs to the protist group Endomyxa and is notable for possessing a persistent flagellum — the first recorded instance of such a flagellate within this group.
-
 News
NewsTrees vs. disease: Tree cover reduces mosquito-borne health risk
A new study shows that in Costa Rica, even modest patches of tree cover can reduce the presence of invasive mosquito species known to transmit diseases like dengue fever.
-
 News
NewsInvasive rats and rainforest mammals are sharing gut microbes as urban areas grow
As urban development continues to creep further into Earth’s oldest and most diverse rainforests, a study reveals native and invasive small mammals aren’t just adapting to their changing habitats—they may also be sharing their microbes.
-
 News
NewsNew giant virus isolated in Jyväskylä for the first time in Finland
For the first time in Finland, researchers have isolated a giant virus, which was named Jyvaskylavirus. The discovery shows that giant viruses are more common in northern regions than researchers have thought.
-
 News
NewsDeadly rodent-borne hantavirus is an emerging disease with pandemic potential
Researchers have found three hotspots of hantavirus circulation in wildlife in the US – Virginia, Colorado, and Texas – and identified 15 rodent species as carriers, including six species that had not previously been identified as hosts of the virus.
-
 News
NewsReduced movement of starlings with parasite infections has a negative impact on offspring
Researchers have shown for the first time that the impaired reproductive success in individuals with parasites is connected to altered movement behaviour. Infected starlings have a smaller action radius, which limits their access to high-quality foraging habitats.
-
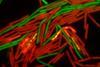 News
NewsSpinning into resistance: the flagella’s hidden role
New research uncovers a direct connection between the rotation of bacterial flagella—structures used for movement—and the activation of genes that enable bacteria to transfer DNA to one another.
-
 News
NewsScientists link a phytoplankton bloom to starving dolphins in Florida
In 2013, 8% of the bottlenose dolphins living in Florida’s Indian River Lagoon died. Investigations have now revealed that the dolphins may have starved because key habitats for nutritious prey were destroyed by a phytoplankton bloom driven by the accumulation of fertilizer, effluent from septic tanks, and other by-products of human activity.
-
 News
NewsNew carrier birds brought avian flu to Europe, Americas
Unexpected wild species, from pelicans to peregrine falcons, are transporting the virus from poultry farms to new places around the world and changing where the risk of outbreaks is highest.
-
 News
NewsMuseum collections reveal worldwide spread of butterfly disease
A new study of museum butterfly collections explore how these specimens can be used to track the spread of disease. Ophryocystis elektroscirrha (OE) is a protozoan parasite that can hamper a butterfly’s growth and flight.
-
 News
NewsChemical radar enables bacteria to detect and kill predators
Researchers have identified a previously unknown defense mechanism of Pseudomonas syringae. They were able to show how the bacterium uses a chemical radar to recognize and eliminate hostile amoebae.
-
 News
NewsDistinct patterns of soil bacterial and fungal communities in the treeline ecotone
A study was carried out to understand the biodiversity of the microbial communities in the treeline ecotone that might affect alpine ecosystems and other potential ecological effects in response to climate change.
-
 News
NewsRed coral colonies survive a decade after being transplanted in the Medes Islands
The red coral colonies that were transplanted a decade ago on the seabed of the Medes Islands have survived successfully. They are very similar to the original communities and have contributed to the recovery of the functioning of the coral reef.
