All Ecology articles – Page 2
-
 News
NewsTeam shows how viral lysis of blue-green algae enhances ecosystem-scale productivity
Newly published interdisciplinary research shows viral infection of blue-green algae in the ocean stimulates productivity in the ecosystem and contributes to a rich band of oxygen in the water.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes that break down antibiotics help protect ecosystems under drug pollution
A new study shows that certain microbes can act as community protectors by breaking down antibiotics and stabilizing entire microbial ecosystems, offering a new way to rethink environmental risk assessment and pollution management.
-
 News
NewsUrban wild bees act as “microbial sensors” of city health
A new study shows that the guts of urban-dwelling wild bees contain detailed microbial signatures that reflect both bee health and the quality of the surrounding environment, offering a powerful new tool for monitoring ecological well-being in cities.
-
 News
NewsDeep ocean earthquakes drive Southern Ocean’s massive phytoplankton blooms, study finds
Researchers have uncovered evidence that deep underwater earthquakes can spur the growth of massive phytoplankton blooms at the ocean surface. The new findings point to a previously unknown relationship between the ocean floor and life at the surface.
-
 News
NewsFrom prey to predator: How carnivores spread beneficial fungi
New research reveals that carnivores play an important role in ecosystem function by providing a largely overlooked mechanism for long-distance dispersal of beneficial mycorrhizal fungi.
-
 Careers
CareersA day in the life of a soil microbial ecologist
Dr. Taniya RoyChowdhury, a soil microbial ecologist and biogeochemist at the Woodwell Climate Research Center, describes a typical day.
-
 News
NewsLivestock-induced changes in soil properties and microbial dominance determine soil microbial diversity in a conifer forest
In the critical habitat of the giant panda, livestock grazing is reshaping the invisible yet vital world of soil microbes in an unexpected way. A new study reveals that while grazing alters soil properties, it paradoxically leads to an increase in soil bacterial diversity.
-
 News
NewsStage-specific microbial dynamics underpin ecosystem restoration on tropical coral islands
Facilitating the establishment of self-sustaining plant communities has become a crucial scientific and technological issue that urgently needs to be addressed in advancing marine ecological civilization and maintaining ecological safety on tropical coral islands.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how ocean’s most abundant bacteria diversify
New research has found that SAR11 marine bacteria are not a single, uniform population as often thought. Instead, they are organized into stable, ecologically distinct groups, essentially specialized “teams” adapted to specific environments, such as the coast versus the open ocean.
-
 News
NewsProtists revealed as key players in soil carbon storage: Dual role uncovered in long-term study
A groundbreaking 27-year field study reveals that how soil protists differentially control fungal and bacterial necromass accumulation—a key process governing SOC storage.
-
 News
NewsA coral reef’s daily pulse reshapes microbes in surrounding waters
A new study shows that coral reefs don’t just provide a home for ocean life, they also help set the daily “schedule” for tiny microbes living in the water nearby. Over the course of a single day, the quantity and types of microbes present can shift dramatically.
-
 News
NewsHarnessing the positive health benefits of microbes
A new article introduces the ‘Database of Salutogenic Potential’, a world-first prototype open-access repository that catalogues microbes and natural compounds linked to positive health outcomes.
-
 News
NewsStudy showcases resilience and rapid growth of ‘living rocks’
South Africa is home to some of the oldest evidence of life on Earth, contained in rocky, often layered outcroppings called microbialites. Like coral reefs, these complex “living rocks” are built up by microbes absorbing and precipitating dissolved minerals into solid formations. Source: Rachel Sipler, Bigelow Laboratory for ...
-
 News
NewsPandemic ‘beneath the surface’ has been quietly wiping out sea urchins around the world
Over the last four years, an unrecognized pandemic that has been wiping out sea urchins around the world has hit the Canary Islands. The consequences on marine ecosystems aren’t yet fully known, but likely profound.
-
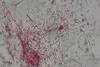 News
NewsStudy reveals how bacteria resist hostile attacks from rival bacteria
When attacked by bacteria from a different species, Pseudomonas rapidly assembles the type VI secretion system (T6SS) – to inject its aggressor with a toxic cocktail. A new study probes how Pseudomonas can strike back when it has already been hit by a deadly cocktail itself.
-
 News
NewsPreviously unrecognized pathway in plants and phytoplankton offers mercury-detox powers
Primary producers—including phytoplankton—possess a previously overlooked ability to internally break down and detoxify methylmercury. The demethylation pathway rapidly converts methylmercury into less toxic inorganic mercury, which is subsequently reduced to gaseous Hg⁰.
-
 News
NewsLargest study of nose microbiome helps highlight those at risk of staph aureus infection
People who persistently carry Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) in their nose have fewer species of other bacteria, while certain bacteria may help to prevent S. aureus colonisation, according to the findings of the largest-ever study of the nasal microbiome.
-
 News
NewsMichigan cherry farmers find a surprising food safety ally: falcons
By shooing cherry-pecking birds away, kestrels also keep them from contaminating crops with their droppings, a new study shows. Kestrels were associated with a 3-fold reduction in droppings spotted on branches.
-
 News
NewsIsland-wide field surveys illuminate land-sea connections in Mo‘orea
A multi-year scientific expedition determined that land use on tropical islands can shape water quality in lagoons and rainfall can be an important mediator for connections between land and lagoon waters.
-
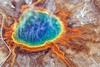 News
NewsEarthquakes shake up Yellowstone’s subterranean ecosystems
Researchers chronicled the ecological changes in subsurface microbial communities that took place after a swarm of small earthquakes rattled the Yellowstone Plateau Volcanic Field in 2021.
