All Editorial articles – Page 2
-
 News
NewsBBSRC-backed spin-out launches rapid DNA air sequencing technology
New spin-out, Agnos Biosciences, has launched AirSeq, a rapid DNA air sequencing technology to transform pathogen detection across health, food and biosecurity. It brings to market a powerful new approach to detecting biological threats in the air.
-
 News
NewsScientists demonstrate first-ever single-shot HIV vaccine neutralization success
Scientists have developed an HIV vaccine candidate that achieves something never before observed in the field: inducing neutralizing antibodies against HIV after a single immunization in nonhuman primates.
-
 News
NewsHow a single protein helps a fungal pathogen invade tea oil trees
Scientists report the discovery of a key mitophagy regulator in Colletotrichum camelliae, the fungus responsible for anthracnose in tea oil trees. A SUN family protein, CaSun1, directly recruits the autophagy protein CaAtg8 to mitochondria, enabling mitophagy during infection.
-
 News
NewsPlants influence the composition and function of their surrounding microbiome to suit their needs
An investigation into plant–microbe interactions at the genetic, metabolic and physiological levels revealed that 203 bacterial gene sequences were strongly shaped by the host plant, for example through their metabolic products. One bacterial genus was found to enhance root development even in nitrogen-limited soils.
-
 News
NewsClinical data gaps keeping life-saving antibiotics from children
Antibiotics that could treat severe infections in babies and children aren’t accessible due to a lack of data around safety and dosage. Of 12 antibiotics recommended for serious bloodstream infections caused by a harmful, Gram-negative bacteria, only six were licensed in children aged under 12 and just three in babies.
-
 News
NewsScientists fight superbugs with nets, light switches - and egg white
A new gel could combat resistant bacteria in wounds and around implant sites, while also supporting healing. The hydrogel, which is inspired by natural immune defences, has produced highly promising results in animal models.
-
 News
NewsRisk for Lyme disease in Ohio is equal to Connecticut, study shows
The risk for being bitten by a tick infected with bacteria that cause Lyme disease is as high in Ohio as it is for those living in Northeast states that have dealt with Lyme disease for over 50 years, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsWhy aren’t more older adults getting flu or COVID-19 shots?
This winter’s brutal flu season isn’t over, and COVID-19 cases have risen recently too. But a new poll taken in recent weeks shows that vaccination against both viruses lags among people 50 and over, and the US survey reveals key reasons why.
-
 News
NewsHigh consumption of ultraprocessed foods may be linked to cancer survivors’ risk of death
Cancer survivors who consumed higher amounts of ultraprocessed foods as part of their diet had a significantly increased risk of both all-cause and cancer-specific death, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsWHO calls for mental health to be central to neglected tropical disease care
A major new World Health Organization publication sets out, for the first time, a practical, evidence-based package of care to address the mental health impacts of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) and the stigma that can prevent people from seeking care and participating fully in society.
-
 News
NewsLab-grown algae removes microplastics from water
Scientists have applied a revolutionary strain of algae toward capturing and removing harmful microplastics from polluted water. The aim is to repurpose the collected microplastics into safe, bioplastic products such as composite plastic films.
-
 News
NewsCommon bacteria discovered in the eye linked to cognitive decline
Chlamydia pneumoniae can linger in the eye and brain for years and may aggravate Alzheimer’s disease. Research suggests this bacterium can amplify Alzheimer’s disease and points to potential interventions including inflammation-limiting therapies and early antibiotic treatment.
-
 News
NewsWetlands do not need to be flooded to provide the greatest climate benefit
Contrary to expectations, wetlands do not need to be completely flooded to provide the greatest climate benefit. Instead, the water table should be below the soil surface and remain stable, according to a new study.
-
 News
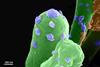
NewsHow brick-building bacteria react to toxic chemical in Martian soil
Researchers investigated how bacteria that can mould Martian soil into brick-like structures fare in the presence of perchlorate, a toxic chlorine-containing chemical discovered in Martian soil. It slows down bacterial growth - but surprisingly leads to the formation of stronger bricks.
-
 News
NewsResearchers uncover the invisible worlds beneath our feet
An analysis of a natural aquifer revealed that despite their close spatial contact and possible interactions, the microorganisms in the water and on the rock form two strongly contrasting ecological communities.
-
 News
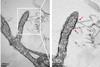
NewsHow bacteria learned to target numerous cell types, revealed
A new study shows how bacteria adapted a virus-derived injection system to recognize and attach to many different types of cells. By identifying thousands of rapidly evolving receptor-binding proteins, the researchers explain how these systems can be retargeted in nature by swapping the part that binds to cells.
-
 News
NewsSediment core yields evidence of an unexpected climate feedback in Antarctica
Researchers have concluded that global warming may lead to reduced uptake of carbon dioxide than at present in the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean if the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is considered unstable, continues to shrink.
-
 News
NewsHow fire-loving fungi learned to eat charcoal
Wildfire causes most living things to flee or die, but some fungi thrive afterward, even feasting on charred remains. A new study is among the first to investigate how fungi that are barely detectable in the soil before a fire are able to proliferate wildly once an area has burned.
-
 News
NewsVaping zebrafish suggest E-cigarette exposure disrupts gut microbial networks and neurobehavior
Researchers hope to spark broader public discussion on the health risks of e-cigarettes and provide scientific evidence to support a reassessment of existing regulations.
-
 News
NewsNew dashboard helps predict and plan for disease outbreaks
When infectious diseases surge, response often comes down to whether communities can position the right people and supplies before case counts spike. Researchers have designed a new platform to translate academic disease forecasting into actionable guidance for decision-makers.
