All Editorial articles
-
 News
NewsCARB-X to support development of typhoid fever diagnostic from Chembio
CARB-X is awarding US$1.8 million to Chembio Diagnostic Systems, Inc. to develop a rapid point-of-care test for the detection of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies to diagnose acute infection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals dual forces driving SARS-CoV-2 evolution: Immune pressure and viral fitness
New research clarifies the complex role of neutralizing antibodies in shaping disease outcomes and the evolution of SARS-CoV-2.
-
 News
NewsOysters play unexpected role in protecting blue crabs from disease
Oysters famously filter their surrounding water, but it turns out they are removing more than algae and excess nutrients. New research shows they can also reduce the spread of disease in nearby marine species, including Chesapeake Bay’s prized blue crabs.
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough in human norovirus research: Researchers overcome major obstacle to grow and study the virus
Researchers have overcome a major obstacle that limited their ability to continuously grow human norovirus. They identified factors that restrict viral replication and developed a way to overcome them to optimize long-term viral cultivation.
-
 News
NewsResearchers probe how natto produces supersulfide molecules in fermentation
Natto, a Japanese food made from soybeans fermented with the Bacillus subtilis var. natto microorganism, is rich in supersulfide molecules, which are attracting attention in the medical and nutritional fields. Researchers extensively analyzed supersulfide content in natto fermentation using various methods.
-
 News
NewsMalaria: Newly identified ‘crown’ stage controls parasite reproduction
Researchers studying Plasmodium falciparum have found that the parasite relies on a brief but essential stage, nicknamed the “Crown” stage, to make sure a crucial internal structure is passed on correctly when it divides.
-
 News
NewsTesting menstrual blood for HPV could be “robust alternative” to cervical screening
Testing menstrual blood for human papillomavirus (HPV) could be a “robust alternative or replacement” for current cervical cancer screening by a clinician, finds a study. The researchers say using menstrual blood for HPV testing is convenient and non-invasive.
-
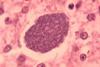 News
NewsA rapid evolutionary process provides Sudanese Copts with resistance to malaria
An international study investigating the genomic diversity of the Sudanese population reveals that the Copts originating in Egypt –who settled in the country between the seventh and eleventh centuries– have acquired a genetic variant that protects them from contracting malaria.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals a minimalist bacterial defense that disrupts viral assembly
Researchers describe how a single protein named Rip1 recognizes bacteriophages, the viruses that infect bacteria, and cause infected bacteria to die prematurely, thereby ending the chain of transmission.
-
 News
NewsA mint idea becomes a game changer for medical devices
Researchers have developed a high‑performance coating made from peppermint essential oil that can be applied to the surfaces of many commonly used medical devices, offering a safer way to protect patients from infection and inflammation.
-
 News
NewsYeast cells can be used for rapid testing of cancer immunotherapy
An international research team has developed a new yeast-based biotechnological platform that makes it possible to test and understand advanced cancer treatments much faster and cheaper than before. It can reduce development time for new types of cancer immunotherapy from months to days or weeks.
-
 News
NewsForest soils increasingly extract methane from atmosphere
Researchers evaluated the world’s most comprehensive data set on methane uptake by forest soils. They discovered that under certain climate conditions, which may become more common in the future, their capacity to absorb methane actually increases.
-
 News
NewsBlood test may give insights into a person’s infection history
Which infections have you already come into contact with? In the future, a simple blood test may be all you need to answer that question. Researchers intend to investigate the sensors the immune system uses to identify pathogens.
-
 News
NewsGreen chemistry: Friendly bacteria can unlock hidden metabolic pathways in plant cell cultures
Co-culturing plant cells with harmless bacteria can expand the diversity of obtainable plant-derived compounds for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agrochemicals, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsSugar molecules point to a new weapon against drug-resistant bacteria
Researchers have developed a powerful new way to target deadly, drug-resistant bacteria by designing antibodies that recognise a sugar found only on bacterial cells – an advance that could underpin a new generation of immunotherapies for multidrug resistant hospital-acquired infections.
-
 News
NewsPreviously unknown viruses discovered in groundwater
Researchers have created a comprehensive picture of viral diversity and function in a groundwater system. They identified over 257,000 viral operational taxonomic units, i.e. viruses at species level, 99 % of which were previously unknown.
-
 News
NewsGut microbe–derived butyrate activates immune cells to enhance vaccine efficacy
Researchers have uncovered a new mechanism showing how butyrate—a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut commensal bacteria—enhances T follicular helper (Tfh) cell activity to promote antibody production and strengthen mucosal vaccine efficacy.
-
 News
NewsResearchers urge focus on child obesity and gut health to reduce risk of diabetes
Researchers are calling for more study of obesity, gut bacteria and metabolic conditions that arise in childhood and adolescence, with an eye to curbing the global rise of type 2 diabetes.
-
 News
NewsSoil pH shapes nitrogen competition between wheat and microbes, new study finds
A new study reveals that soil acidity plays a critical role in determining how wheat competes with soil microorganisms for nitrogen, a nutrient essential for plant growth and global food production.
-
 News
News A fungus living in our body can make melanoma more aggressive
A study has for the first time established the mechanism by means of which the Candida albicans fungus makes melanoma more aggressive. It activates several signalling pathways in the melanoma cells, creating an environment that helps to reprogram angiogenesis and metabolism.
