All Editorial articles – Page 268
-
 News
NewsMicrobes in gastrointestinal tracts may foretell Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
Researchers have found that healthy, anti-inflammatory gut bacteria are less abundant among people who are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease.
-
 News
NewsAntibacterial material developed for use with internal medical devices
Researchers have developed an effective and flexible antimicrobial material that could be used to coat medical devices placed inside the body, such as hip replacements or pacemakers.
-
 News
NewsRole of microhabitats in shaping diversity of periphytic diatom assemblages
Researchers have studied the importance of microhabitat heterogeneity (emergent, submerged and floating macrophytes) in maintaining diverse periphytic diatom assemblages.
-
 News
NewsBacteria engineered to biosynthesize intricate protein complexes
Researchers have developed an innovative bioengineering approach using genetically modified bacteria that can incorporate protein cages around protein crystals, producing highly customized protein complexes.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover how bacteria recognize viral invasion and activate immune defenses
Researchers have discovered that bacteria sense phages via a defensive response called CBASS that detects viral RNA.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes could help reduce the need for chemical fertilizers
Chemical engineers have developed a coating that protects nitrogen-fixing bacteria from heat and humidity, which could allow them to be deployed for large-scale agricultural use.
-
 News
NewsFourth dose of COVID vaccine boosts protection in patients with rheumatic disease
A new study suggests that the recommendation for patients receiving disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs to receive a fourth dose of the mRNA vaccine has saved lives and reduced hospitalizations among patients in this high-risk group.
-
 News
NewsNovel C. diff structures are required for infection and offer new therapeutic targets
Iron storage ‘spheres’ inside the bacterium C. diff — the leading cause of hospital-acquired infections — could offer new targets for antibacterial drugs to combat the pathogen.
-
 News
NewsNew report outlines microbial solutions to mediate methane emissions
A new report highlights recommendations to further the scientific community’s understanding of microbial processes of methane production and consumption to mitigate methane emissions and address climate change.
-
 News
NewsNew method detects bird flu on wetlands beloved of waterfowl
Researchers have developed a method that can detect infectious bird flu virus in wetlands frequented by waterfowl.
-
 News
NewsVegan diet fosters changes in gut microbiome that reduce hot flashes by 95%
A low-fat vegan diet that includes soy fosters changes in the gut microbiome that decrease postmenopausal vasomotor symptoms, or hot flashes, overall by 95%, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsDangerous bee virus growing less deadly in at least one US forest, researchers find
The findings suggest the virus can evolve to be less severe and could help inform solutions to mitigate the virus in managed honey bee colonies.
-
 News
NewsTiny hinges bend the infection-spreading spikes of a coronavirus
Disabling those hinges could be a good strategy for designing vaccines and treatments against a broad range of coronavirus infections, including COVID-19.
-
 News
NewsStudy uncovers mediators of persistent HIV viremia
Researchers examining people with non-suppressible HIV viremia (NSV) despite receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) have found large reservoirs of proviruses inserted into transcriptionally active regions of immune cell genomes.
-
 News
NewsBook scopes out marine natural compounds in search for anti-infective medicines
The latest volume of the Bentham Science book series, Frontiers in Antimicrobial Agents, scopes out the potential of marine natural compounds in the search for anti-infective medicines.
-
 News
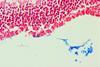
NewsIron linked to blindness in ocular toxoplasmosis - offering hope for treatment
Researchers have identified the role of iron in ocular toxoplasmosis (OT), a form of toxoplasmosis that causes blindness, and found that treatment of mice with a compound that decreases iron was successful in reducing their symptoms.
-
 News
NewsSaudi Public Health Authority and BGI Genomics sign MoU to advance public health
BGI Genomics has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Saudi Public Health Authority (PHA) to inject new impetus into the cause of public health in Saudi Arabia.
-
 News
NewsGenomic surveillance needed to help fight antimicrobial resistance
An international group of researchers is calling for the potential of genomic surveillance to be harnessed to tackle antimicrobial resistance (AMR), a major global challenge.
-
 News
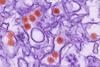
NewsMaternal dengue immunity worsens birth defects caused by Zika virus
A new study finds prior dengue antibodies substantially raise the risk of microcephaly and fetal defects with Zika infection.
-
 News
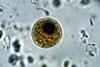
NewsHow green algae count cell divisions reveals key step needed for multicellular life
Scientists have made an unexpected discovery of a biased counting mechanism used by the single-celled green alga Chlamydomonas to control cell division.
