More Asia & Oceania News
-
 News
NewsStreptococcus suis serotype 2 collagenase-like protease promotes meningitis by increasing blood-brain barrier permeability
Streptococcus suis serotype 2 (SS2) is an emerging zoonotic pathogen that causes meningitis in humans and pigs. Researchers have investigated the role and mechanism of the SS2 Clp in promoting the passage of the bacterium across the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
-
 News
NewsMutated baker’s yeast at the forefront of petroleum substitute tech
Researchers engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce 2,3-butanediol (2,3-BDO) introduced mutations into the genomic DNA. The researchers engineered four altered strains and subjected them to ethanol, heat, and low pH stressors.
-
 News
NewsEngineering oncolytic bacteria as precision cancer therapeutics
A new review summarizes recent advances in the design and application of synthetic biological strategies that enhance bacterial precision, safety, and efficacy in tumor therapy.
-
 News
NewsApplications of AI in antimicrobial resistance prevention and control
Researchers have published a review shedding light on how AI is revolutionizing the prevention and control of AMR. The article illustrates how machine learning and deep learning are transforming surveillance, diagnosis, treatment optimization, and drug discovery.
-
 News
NewsScalable nanoengineered gauze with sustained natural product release
A multi-institutional Chinese research team has developed PPCZ@Gauze – a novel nanoengineered dressing that synergistically combines antibacterial, anti-adhesive, and pro-angiogenic functions.
-
 News
NewsScientists create microneedle system to deliver living biofertiliser directly into plants, boosting growth with less waste
A dissolving patch delivers beneficial microbes into leaves and stems, speeding growth in vegetables while using over 15 per cent less biofertiliser than soil application.
-
 News
NewsNew method to accelerate vaccine and drug development for norovirus
Researchers have developed a simple and efficient system for understanding the functions of specific norovirus genes, providing new avenues for developing antivirals and vaccines.
-
 News
NewsNew review reveals how microbial communities accelerate the global spread of antibiotic resistance
A new scientific review has uncovered how complex microbial communities, including those in the human gut and the natural environment, act as powerful engines that drive the evolution and spread of antimicrobial resistance.
-
 News
NewsInstitutions team up to advance first AI-designed mRNA vaccine against deadly tick-borne disease
Scientists are developing what could become the world’s first mRNA vaccine against severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS)—a tick-borne viral disease associated with this condition.
-
 News
NewsEverolimus alleviates ulcerative colitis via inflammation suppression and microbiota remodeling
A new study reveals how targeting the CLEC4E receptor and reshaping the gut metabolite axis offers a promising therapeutic avenue for inflammatory bowel disease.
-
 News
NewsHow did Bronze Age plague spread? Ancient sheep might solve the mystery
Researchers have found the first evidence of a Bronze Age plague infection in a non-human host. The scientists discovered Y. pestis DNA in a 4,000-year-old domesticated sheep from Arkaim, a fortified settlement located in the Southern Ural Mountains of present-day Russia.
-
 News
NewsStudy unlocks the key microbes contributing to postnatal growth retardation
Postnatal growth retardation (PGR) has a high incidence during early postnatal development of piglets and humans. Researchers have found that hindgut-enriched Methanobrevibacter smithii compromises the weight gain in the pig PGR model.
-
 News
NewsYeast cell factory developed to convert methanol into L-lactate
Researchers developed a yeast cell factory to produce L-lactate from methanol as the sole carbon source, and evaluated the commercial potential and environmental impacts of this bioprocess.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals how natural humic substances reshape soil carbon cycling and boost antibiotic resistance
Researchers have uncovered surprising links between natural humification processes in soil, carbon metabolism, and the spread of antibiotic resistance. Subtle shifts in the composition of humic substances can reshape microbial metabolism and alter the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes.
-
 News
NewsClimate extremes triggered rare coral disease and mass mortality on the Great Barrier Reef
Marine biologists have identified a devastating combination of coral bleaching and a rare necrotic wasting disease that wiped out large, long-lived corals on the Great Barrier Reef during the record 2024 marine heatwave.
-
 News
NewsPlant phenolic acids supercharge old antibiotics against multidrug resistant E. coli
Plant derived phenolic acids can dramatically enhance the activity of existing antibiotics against multidrug resistant E. coli, offering a promising new tool in the global fight against antimicrobial resistance.
-
 News
NewsMicroenvironment-feedback hydrogel enables precise staged repair of infected wounds
A research team has developed a hydrogel that can sense changes in wound pH and automatically switches its therapeutic behavior from fighting infection to promoting tissue repair.
-
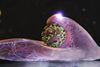 News
NewsResearchers watch live as influenza viruses enter human cells
Using a microscopy technique that they developed themselves, scientists can zoom in on the surface of human cells in a Petri dish, observing live and in high resolution how influenza viruses enter a living cell. They found the cells are not passive, but actively attempt to capture the virus.
-
 News
NewsChemical structures of surface polysaccharides from Acinetobacter baumannii for glycoconjugate vaccines
Researchers provided a comprehensive analysis of the molecules that make up the protective layer of complex sugars on the surface of Acinetobacter baumannii - known as capsular polysaccharides (CPS) and lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and essential for the bacterium’s virulence.
-
 News
NewsComplex life developed earlier than previously thought, study reveals
New research indicates that complex organisms evolved long before there were substantial levels of oxygen in the atmosphere, something which had previously been considered a prerequisite to the evolution of complex life.
