More Healthy Land – Page 69
-
 News
NewsNew research centre to calculate gas impact of microbes on atmosphere
One of the first research centres in the world to specialise in how much gas is released by plants, soil, fungi and bacteria has opened at the University of Copenhagen.
-
 Features
FeaturesPromoting plant growth with the help of yeasts
How can microbe-based solutions be used as plant growth promoters for a more sustainable agriculture?
-
 News
NewsAI plus microbes could unlock higher biogas production for UK
Researchers are using artificial intelligence to develop better microorganism-led processes that efficiently devour products such as food waste, wastewater and animal manure to help boost the UK’s burgeoning green industry.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes thriving in groundwater and producing oxygen in the dark
Aancient groundwaters harbour not only diverse and active microbial communities, but also unexpectedly large numbers of microbial cells.
-
 News
NewsGut microbiota shouldn’t be discounted from climate change studies
A new review suggests climate change doesn’t just impact the distribution and habitats of wild animals - it can affect their internal environment as well, with implications for biodiversity.
-
 News
NewsElectromicrobiology conference sparks Sustainable Microbiology themed collection
The new not-for-profit open access journal Sustainable Microbiology is to run a special themed edition on electromicrobiology.
-
 News
NewsPlanting choices nurture microbes that break down petroleum contamination
Planting grasses or adding fertilizer, or a combination of both, to a contaminated site has surprisingly persistent effects on the microbes associated with local vegetation, a study has found.
-
 News
NewsVaccine primes frog microbiome for future exposure to deadly fungal outbreak
A new study has found that a new vaccine against the deadly chytrid fungus in frogs can shift the composition of the microbiome, making frogs more resilient to future exposure to the fungus.
-
 News
NewsDisturbance could boost microbe protection of mangroves
Engineering disturbance in mangrove sediments could help to conserve these habitats by boosting their microbiome, a new study suggests.
-
 News
NewsPlant and microbial innovation hub in Norwich gets green light
Funding has been confirmed for the development of a ground-breaking plant and microbial science and innovation hub, providing world-class facilities for the John Innes Centre (JIC) and The Sainsbury Laboratory (TSL).
-
 News
NewsTectonics matter when it comes to microbial life in hot springs
Microbial community composition is distinctly different in two tectonic settings, scientists report.
-
 News
NewsScientists closing in on long-lasting swine flu vaccine
A successful long-term experiment with live hogs indicates scientists may be another step closer to achieving a safe, long-lasting and potentially universal vaccine against swine flu.
-
 Opinion
OpinionHow AI gives us food for thought
Michael Ukwuru reveals the many ways in which artificial intelligence could address global food safety challenges.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes are most important players in storing carbon in soil - by far
Microbes are by far the most important factor in determining how much carbon is stored in the soil, according to a new study with implications for mitigating climate change and improving soil health for agriculture and food production.
-
 News
NewsResearchers reveal sulphate assimilation pathway for methanogen
Study uncovers how a methanogenic microbe reassembles a metabolic pathway piece by piece to transform sulphate into a cellular building block.
-
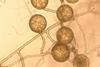 News
NewsEarth’s fungal networks could be essential to reaching net zero
Fungi stores a third of carbon from fossil fuel emissions and could be essential to reaching net zero, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsFungal proteins act to suppress host plant immunity
Researchers have identified and categorized four fungal proteins called effectors responsible for suppressing host plant immunity from infection.
-
 News
NewsNovel bacterial strain in feed boosts broiler chicken growth and changes gut microbiome
A novel bacterial strain added as a supplement to broiler chicken feed not only boosts their growth rate, but significantly alters their caecal microbiome, enhancing the capacity for microbial amino acid and vitamin biosynthesis, a new study shows.
-
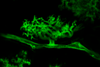 News
NewsSymbiotic and pathogenic fungi may use similar tools to manipulate plants
Scientists have discovered that remotely related fungi are using a similar group of proteins to manipulate and live within plants.
-
 News
NewsCats can play a role in family transmission of COVID-19
Cats can play a role in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and their contaminated environment can be infectious, according to new research.
