More USA & Canada News – Page 98
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover evolutionary “tipping point” in fungi
Scientists have found a ‘tipping point’ in the evolution of fungi that throttles their growth and sculpts their shapes, demonstrating how small changes in environmental factors can lead to huge changes in evolutionary outcomes.
-
 News
NewsCandida albicans toxin plays a special role in the colonization of the digestive tract
Comparative studies on mice with a complete microbiome and a microbiome reduced by antibiotics now show that the previous assumption that the yeast form of Candida albicans is better suited for colonization needs to be revised.
-
 News
NewsNew vaccine against a highly fatal tropical disease – and potential bioterror weapon – demonstrates efficacy in animal studies
In a mouse study, researchers tested a vaccine against the bacterium that causes melioidosis and found it was highly protective against the disease, which is endemic in many tropical areas.
-
 News
NewsIn Lake Erie, climate change scrambles zooplankton’s seasonal presence
A new analysis of zooplankton in western Lake Erie shows that their biomass and seasonal behavioral patterns have been drastically altered by human-driven changes in water temperature and food webs.
-
 News
NewsNew soil model integrates microbes and large perennial grasses
A new soil model integrates soil microbes and the distinct physiological traits of large perennial grasses into DayCent.
-
 News
NewsCommunity-based cohort study to track short- and long-term effects of multiple respiratory viruses
Scientists are initiating a critical two-year prospective epidemiologic study in the spring of 2024 to track acute respiratory infections across the United States.
-
 News
NewsResearchers carry out first peer-reviewed study of fecal microbiota transplants in dolphins
Scientists have successfully carried out pioneering fecal microbiota transplantations on Navy bottlenose dolphins that showed signs of gastrointestinal disease.
-
 News
NewsAfrican catfish skin mucus yields promising antibacterial compound
Scientists report they have extracted a compound with powerful antibacterial properties from the skin of farmed African catfish.
-
 News
NewsSigns of life potentially detectable in single ice grain emitted from extraterrestrial moons
A new lab-based study shows that individual ice grains ejected from the moons of Saturn and Jupiter may potentially contain enough material for instruments headed there in the fall to detect signs of life, if such life exists.
-
 News
NewsResearchers invent artificial intelligence model to design new superbug-fighting antibiotics
Researchers have invented a new generative artificial intelligence model which can design billions of new antibiotic molecules that are inexpensive and easy to build in the laboratory.
-
 News
NewsNon-culturable Legionella identified with sequencing
Researchers have described a cost-effective approach for using whole genome sequencing to identify Legionella pneumophila that doesn’t require culturing.
-
 News
NewsArchitect asks if a probiotic for your house could prevent asthma and keep illness at bay
Homes have become ‘too clean’ and could benefit from the introduction of ‘healthy germs’ which introduce friendly bacteria to potentially stave off a host of childhood illnesses, including asthma, experts suggest.
-
 News
NewsAI can now detect COVID-19 in lung ultrasound images
Artificial intelligence can spot COVID-19 in lung ultrasound images much like facial recognition software can spot a face in a crowd, new research shows.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals possible triggers for inflammatory bowel disease
A new study finds a complex interplay between diet, genes, and the gut microbiota that could explain why IBD develops.
-
 News
NewsNew blood test cuts infection diagnosis time from months to hours
Researchers have designed a platform to perform blood-based diagnoses of nontuberculosis mycobacteria, simplifying and shortening a long-complicated procedure from 6 months to 2 hours.
-
 News
NewsPowerful new AI can predict people’s attitudes to vaccines
A powerful new tool in artificial intelligence is able to predict whether someone is willing to be vaccinated against COVID-19. The predictive system uses a small set of data from demographics and personal judgments such as aversion to risk or loss.
-
 News
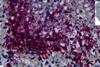
NewsBacteria subtype linked to growth in up to 50% of human colorectal cancers
A new study suggests that a subtype of Fusobacterium nucleatum underlies colorectal cancer growth in humans and could be useful in screening and treatments.
-
 News
NewsExperts warn climate change will fuel spread of infectious diseases
A team of infectious diseases experts called for more awareness and preparedness in the medical field to deal with the impact of climate change on the spread of diseases. Their article, published in JAMA, raises the alarm about the emergence and spread of harmful pathogens. The authors ...
-
 News
NewsProtein found in human sweat may protect against Lyme disease
Researchers also found that a variant of the protein is not as protective against the bacterium and increases susceptibility to the disease.
-
 News
NewsSARS-CoV-2 spike protein sensitizes pain receptors in mice
A study aiming to investigate whether the spike protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can sensitize nociceptors and promote pain-like behaviors in mice was presented at the 102nd General Session of the IADR.
