All USA & Canada articles – Page 20
-
 News
NewsBruker announces FDA Clearance of Claims 7 and 8 for the MALDI Biotyper® CA System
Bruker has announced FDA clearance of Claim 7 and Claim 8 for its MALDI Biotyper® CA System, marking a significant advancement in clinical microbial identification capabilities.
-
 News
News’Footprint of Death’ gives new clues to cell life, spread of disease
Scientists at La Trobe University have discovered a previously unknown way viruses could spread around the body, potentially paving the way for more effective drug development. Source: La Trobe University Dead cells after the self-destruction and fragmentation process. The large green areas are the “eat me” signals ...
-
 News
NewsAre there living microbes on Mars? Check the ice, researchers say
By recreating Mars-like conditions in the lab, researchers demonstrated that fragments of the molecules that make up proteins in E. coli bacteria, if present in Mars’ permafrost and ice caps, could remain intact for over 50 million years.
-
 News
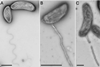
NewsSurprising bacteria discovery links Hawaiʻi’s groundwater to the ocean
A new species of bacteria has been discovered off the coast of Oʻahu, shedding light on how unseen microbial life connects Hawaiʻi’s land and sea ecosystems.
-
 News
NewsMiniature noses to help prevent infections and promote nasal health
To better understand how different bacteria interact with the lining of the human nose, researchers used a miniature model of the human nose to study how bacteria can live in nasal passages.
-
 News
NewsEngineers solve the sticky-cell problem in bioreactors and other industries
Their system uses electrochemically generated bubbles to detach cells from surfaces, which could accelerate the growth of carbon-absorbing algae and lifesaving cell therapies.
-
 News
NewsNew monoclonal antibody shows promise for preventing malaria infections
A new early-stage clinical trial has found that a novel monoclonal antibody provided dose-dependent full protection against the malaria parasite with minimal side effects.
-
 News
NewsStudy finds COVID-19 mRNA vaccine sparks immune response to fight cancer
Patients with advanced lung or skin cancer who received a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine within 100 days of starting immunotherapy drugs lived significantly longer than those who did not get the vaccine, researchers have found.
-
 News
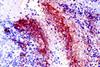
NewsStudy reveals how bacteria in tumors drive treatment resistance in cancer
Researchers have uncovered a previously unknown way for microbes within tumors to contribute to treatment resistance in certain cancers. The study finds these microbes push cancer cells into a reversible resting state, allowing them to become resistant to certain chemotherapies.
-
 News
NewsGut microbiome affects alcohol preference by influencing brain’s reward system
A new study shows how an overgrowth of Candida albicans - overly abundant in people with alcohol use disorder - increases levels of inflammatory molecules that can cross the blood-brain barrier and affect the desire for alcohol.
-
 News
NewsAfrican wildlife poop sheds light on what shapes the gut ecosystem
A study of elephants, giraffes and other wildlife in Namibia’s Etosha National Park underscores the ways in which the environment, biological sex, and anatomical distinctions can drive variation in the gut microbiomes across plant-eating species.
-
 News
NewsResearch alert: Bacterial chatter slows wound healing
Researchers have discovered a previously unrecognized mechanism by which Staphylococcus aureus delays wound healing. The study finds that quorum sensing is a key driver of delayed healing in wounds infected by S. aureus.
-
 News
NewsBiologist links stable gut bacteria to healthy childhood growth
New research reveals that the stability of gut bacteria in early life plays a critical role in whether children thrive or struggle with undernutrition – a global health challenge affecting millions.
-
 News
NewsIn chromosome of key biotech bacterium, different setups bring different strengths
New research has found that the effectiveness of biotech bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens’ virulence varies, depending on how its chromosome is arranged.
-
 News
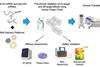
NewsHuman Organ Chip technology sets stage for pan-influenza A CRISPR RNA therapies
Human lung alveolus chip infection model enables investigation of viral replication, inflammatory responses, and genetic off-target effects of a novel pan-influenza CRISPR therapy.
-
 News
NewsFriendly soil microbes can boost protein in staple crops
Researchers investigated how a bacterium naturally found in the soil that is beneficial to human health can enhance the levels of the amino acid and antioxidant ergothioneine in spring wheat.
-
 News
NewsBiochar shows big promise for climate-friendly soil management
Turning agricultural and organic waste into biochar could help store more carbon in the soil and slow climate change, according to a new study. Recent findings show that biochar improves soil health, boosts microbial diversity, and captures carbon.
-
 News
NewsSynthetic biology reprograms plant–microbe partnerships for resilient agriculture
By integrating engineering principles with plant biology, a new review highlights how redesigned genetic pathways and plant-based biosensors can deepen understanding of plant responses to both harmful and beneficial microbes.
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover method to combat antibiotic treatment failure
Researchers explored ways to alter our own immune cells to help antibiotics work more effectively. They identified a small molecule that alters the body’s immune cells, forcing them to ’wake up’ dormant bacteria and make them more vulnerable to antibiotic treatment.
-
 News
NewsResearchers partner on $28M initiative to build a precision phage platform for promoting public health
Researchers have embarked on a five-year initiative that aims to harness the natural predators of bacteria – known as phages – as precision tools to shape the human microbiome and promote health.
