All USA & Canada articles – Page 24
-
 News
NewsNew study supports gene-tailored radiation doses to treat HPV+ throat cancer
Genetic testing can identify patients with HPV-positive throat cancer who may benefit from lower radiation doses, according to a new study that builds on a growing body of evidence that radiation treatment can be personalized using tumor genomics.
-
 News
NewsBeyond viruses: Expanding the fight against infectious diseases
The newly renamed Gladstone Infectious Disease Institute has broadened its mission to address global health threats ranging from antibiotic resistance to infections that cause chronic diseases.
-
 News
NewsDespite increase in U.S. cases, worry about West Nile virus remains low
Despite this season’s growing number of cases, relatively few Americans worry about becoming infected by West Nile or by dengue fever, another mosquito-borne illness, according to a survey of nearly 1,700 U.S. adults.
-
 News
NewsVirologist leading team to bolster Canada’s ability to respond to future pandemics, public health emergencies
With $3M in new federal funding over two years, University of Ottawa Faculty of Medicine molecular virologist Dr. Marc-André Langlois and a multidisciplinary team of collaborators will be a vital part of Canada’s ability to respond effectively to infectious disease threats & future pandemics.
-
 News
NewsMeta-analysis: COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy is safe and beneficial for mother and infant
Vaccination is associated with better neonatal outcomes without added maternal risk, according to research presented during the American Academy of Pediatrics 2025 National Conference & Exhibition.
-
 News
NewsMilk matters: How donor human milk storage affects preemie gut health
A study reveals that shorter storage durations of donor human milk are linked to reduced gastrointestinal complicatoins in premature infants, including necrotizing enterocolitis. These findings suggest that minimizing milk storage time may help to preserve protective properties crucial for preterm gut health.
-
 News
NewsIn pregnant mice with severe flu, harmful molecules can breach fetal barriers
A new study shows, for the first time, that severe flu infection in pregnant mice leads to a breakdown in placental and brain barriers, leading to the accumulation of potentially harmful molecules in the fetal brain. Fibrinogen can pass into developing fetal brains.
-
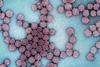
 News
NewsHeadspace invaders: How mosquito-borne viruses breach the brain’s defenses
Using a stem cell-based model of the human blood-brain barrier, researchers compared two closely related Sindbis virus strains — one brain-invading and one not — and found that small changes in viral surface proteins called glycoproteins dictate whether the virus can cross.
-
 News
NewsKey to the riddle of sleep may be linked to bacteria
New research suggests a new paradigm in understanding sleep, demonstrating that a substance in the mesh-like walls of bacteria, known as peptidoglycan, is naturally present in the brains of mice and closely aligned with the sleep cycle.
-
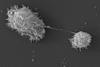 News
NewsTrojan horse: Amoebae as carriers for human Norovirus and Adenovirus
A new study reveals that common waterborne amoebae can ingest and protect human viruses, extending their environmental persistence. Human norovirus and human adenovirus can enter and persist within FLA.
-
 News
NewsStudy models how human behavior, lockdowns and restrictions shaped COVID’s spread
Researchers employed computer modeling and large datasets to better understand how COVID-19 was transmitted in one community in South Africa during the course of the worldwide pandemic.
-
 News
NewsNew study finds dried blood spot test reliably detects congenital CMV at birth
New research confirms that testing for congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) at birth using the routinely collected dried blood spot (DBS) is a reliable and effective method to identify newborns at risk for long-term developmental challenges.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how tick-borne encephalitis virus enters cells
The protein on human cells that tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) uses for infection has now been identified—a major step toward understanding how TBEV causes neurological disease and for developing antiviral drugs.
-
 News
NewsMore than 50 scientific societies issue letter to Congress expressing concerns regarding executive order on federal grantmaking
A coalition of more than 50 scientific societies has issued a letter to the United States Congress, expressing concerns over provisions in the 7 August 2025 Executive Order (EO) titled “Improving Oversight of Federal Grantmaking.”
-
 News
News NIH grant to UC Riverside supports research on dangerous emerging virus
Researchers have been awarded an NIH grant of about $3.4 million over five years to lead an international study focused on developing protective antibodies against Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV), a biosafety level 4 pathogen and a Category A bioterrorism agent.
-
 Careers
CareersSummer studentship: Amelia investigates how Streptococci aggregate with other oral bacteria
Amelia Rohim reports back on her AMI-sponsored summer studentship which focused on the investigation of inter-species aggregation between oral bacteria at the University of Michigan with Dr. Alexander Rickard.
-
 News
NewsHow viruses build perfectly symmetrical protective shells
Researchers used a new simulation framework to capture key biological factors like protein diffusion, genome flexibility, and shape-shifting behavior to model how viral proteins self-assemble into symmetric shells.
-
 News
NewsNew single-dose, temperature-stable rabies vaccines could expand global access
Researchers have discovered a new way to make human rabies vaccines that could greatly expand access to immunization across the globe. The new method creates shots that are temperature-stable—meaning they don’t need to be stored at cold temperatures.
-
 News
NewsScientists show how to grow more nutritious rice that uses less fertilizer
Scientists have shown that nanoscale applications of selenium can decrease the amount of fertilizer necessary for rice cultivation while sustaining yields, boosting nutrition, enhancing the soil’s microbial diversity and cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
-
 News
NewsGut bacteria linked to how our genes switch on and off, research finds
The trillions of microbes that live in the human gut may play a bigger role in health than previously thought, according to a review highlighting how the gut microbiome can affect epigenetics, the process that turns genes on or off without changing the DNA itself.
