All USA & Canada articles – Page 27
-
 News
NewsScientists report the first use of CRISPR activation to treat a cardiac disease in mice
Researchers have demonstrated for the first time that CRISPR-based gene activation (CRISPRa) can be used to treat genetic heart disease in vivo. The study paves the way for novel targeted therapies for patients with genetic cardiac disorders.
-
 News
NewsResearchers uncover potential biosignatures in Bright Angel formation on Mars
A new study has revealed potential chemical signatures of ancient Martian microbial life in rocks examined by NASA’s Perseverance rover.
-
 News
NewsResearchers capture new antibiotic resistance mechanisms with trace amounts of DNA
Scientists have developed a method to isolate genes from amounts of microbial DNA so tiny that it would take 20,000 samples to weigh as much as a single grain of sugar.
-
 News
NewsAlkali waste dumped in the Pacific Ocean created alkalophilic microbial ecosystems
Barrels filled with industrial waste that were dumped in the sea near Los Angeles more than 50 years ago are creating new microbial ecosystems adapted to highly alkaline conditions.
-
 News
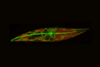
NewsExtreme diatoms inside the Arctic ice glide into the record books
Diatoms found in polar ice are active until temperatures drop to -15 C - the lowest ever recorded for movement by a eukaryotic cell.
-
 News
NewsLiving ink containing bacteria could help rebuild coral reefs
Researchers created a living material that encourages coral larvae to attach and settle down. Bacterial Reef Ink (BRINK) is a photopolymerized hydrogel hosting two native Hawaiian settlement-inducing bacterial strains.
-
 News
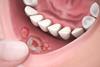
NewsResearchers reveal infection risks oral mucositis poses to stem cell transplant patients, introduce a superior AI tool to predict them
Researchers have completed a series of studies that reveal how much painful mouth sores known as oral mucositis increase infection risks in stem cell transplant patients and how artificial intelligence can be used to more accurately predict those risks.
-
 News
NewsFrom quantum mechanics to quantum microbes: A Yale scientist’s journey of discovery
Faced with a microbial mystery hidden deep in the soil, Nikhil Malvankar returned to his roots - with results that could shape the field of quantum computing.
-
 News
NewsPediatric investigation study re-examines chikungunya in neglected pediatric victims
Researchers and policymakers must recalibrate their outlook on pediatric chikungunya to develop effective control measures, a new paper warns.
-
 News
NewsWarming climate drives disease surge, study shows
Projections suggest future warming could raise dengue incidence by 49%–76%, depending on emissions scenarios, if other factors remain constant. Cooler areas are expected to see the biggest increases, while hotter locations may experience slight declines.
-
 News
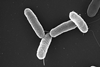
NewsResearcher developing electronic nose to detect foodborne illness
A researcher is working on developing an electronic nose (e-nose) to detect abnormalities from their version of the sniff test. The method would revolutionize food safety by relying on what the e-nose can detect rather than only the appearance of the food.
-
 News
NewsBlood test identifies HPV-associated head and neck cancers up to 10 years before symptoms
Researchers show that a novel liquid biopsy tool called HPV-DeepSeek can identify HPV-associated head and neck cancer up to 10 years before symptoms appear.
-
 News
NewsCan the ‘good’ bacteria in your mouth act as probiotic cavity fighters?
Discovery of clumping molecules made by gene clusters in the oral microbiome may lead to ways to reengineer the microbes in plaque, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsCan a healthy gut microbiome help prevent childhood stunting?
Researchers find gut microbiome turnover in children is linked to poor growth outcomes, pointing to microbiome-based diagnostics for malnutrition.
-
 News
NewsGiving food waste fermentation a ‘jolt’ increases chemical production
Adding an electrical jolt to fermentation of industrial food waste speeds up the process and increases the yield of platform chemicals that are valuable components in a wide range of products, new research shows.
-
 News
NewsOcean warming puts vital marine microbe Prochlorococcus at risk
A new study finds that Prochlorococcus prefers ocean water between 66 and 86 degrees and doesn’t tolerate water much warmer. Climate models predict that subtropical and tropical ocean temperatures will exceed that threshold in the next 75 years.
-
 News
NewsCoral-inspired pill offers a new window into the hidden world of the gut
Marine corals have evolved intricate, porous structures that shelter diverse microbial communities. Researchers have borrowed this biological blueprint to create an ingestible pill that can sample bacteria from one of the most inaccessible regions of the human body: the small intestine.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows not all dietary proteins are digested the same way
As protein-rich diets become increasingly popular, a new study suggests that categorizing dietary proteins as either animal- or plant-based fails to effectively capture the source-specific differences in their composition, digestive efficiency and accessibility to the gut microbiota.
-
 News
NewsNew antibiotic to fight superbug C. diff proves effective in clinical trial
As the effectiveness of antibiotics meant to fight the deadly superbug Clostridioides difficile wanes, a research team is seeing positive results of a new antibiotic on the scene – ibezapolstat – which is proving successful in fighting these infectious bacteria in clinical trials.
-
 News
NewsResearchers map key human proteins that power coronavirus replication, pointing to new treatment strategies
Scientists have pinpointed dozens of human proteins that SARS-CoV-2 needs to complete its full life cycle, from entering a cell to replicating and releasing new viral particles.
