All Asia & Oceania articles – Page 10
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals how a common antibiotic disrupts nitrogen cycling and boosts greenhouse gas emissions in estuaries
Antibiotics may have far reaching impacts on wetland chemistry, according to a new study that identifies the bacteria responsible for breaking down the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole and links this process to increased emissions of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
-
 News
NewsCircadian rhythms as a modulator of gut microbiota-tumor microenvironment crosstalk
A new review examines how circadian disruption modifies the diversity and metabolic functions of gut microbiota, resulting in alterations of microbial metabolites, including short-chain fatty acids and secondary bile acids.
-
 News
NewsEmerging human and canine leptospirosis in New South Wales shows separate transmission pathways
A geospatial study of leptospirosis outbreaks in New South Wales suggests that humans and dogs may have largely independent transmission pathways.
-
 News
NewsNew Arkansas Clean Plant Center partnership to boost Indian agriculture
The University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture has entered a five-year agreement with the Indian National Horticulture Board and Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare to help farmers in India improve agricultural production by limiting spread of pathogens.
-
 News
NewsNatural, non-engineered bacterium selectively targets colorectal cancer
Scientists have demonstrated that the marine bacterium Photobacterium angustum exhibits potent antitumor effects against colorectal cancer. The natural bacterium requires no genetic modification yet selectively accumulates in tumor tissues with minimal impact on healthy organs.
-
 News
NewsToxic gut bacteria may drive ulcerative colitis by killing protective immune cells
A toxin-secreting gut bacterium may fuel ulcerative colitis by killing protective immune cells that maintain intestinal homeostasis, according to a new study. The findings suggest potential for new treatment strategies.
-
 News
NewsMicrobial nano-selenium breakthrough boosts tea quality and safety
Scientists developing selenium-enriched tea have identified a powerful selenium-reducing bacterium, Raoultella ornithinolytica S-1, capable of converting inorganic selenium into selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) while simultaneously promoting plant growth.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal molecular cause behind “stuck” beer fermentation
Premature yeast flocculation (PYF) is a persistent issue in beer brewing, where yeast settles too early during fermentation. New research identifies multiple differential metabolites and confirmed galangin as a key factor that promotes early yeast aggregation.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop world’s first modular co-culture platform for the one-pot production of rainbow-colored bacterial cellulose
The team engineered Komagataeibacter xylinus for bacterial cellulose synthesis and Escherichia coli for natural colorant overproduction. A co-culture of these engineered strains enabled the in situ coloration of bacterial cellulose.
-
 News
NewsLivestock manure linked to the rapid spread of hidden antibiotic resistance threats in farmland soils
Scientists have uncovered how even “low-risk” organic fertilizers like dried poultry manure can inadvertently drive a dramatic surge in dangerous antibiotic resistance genes, once released into vegetable plots used for food crops.
-
 News
NewsResearchers diagnose disease with a drop of blood, a microscope and AI
Scientists have developed an automated, high-throughput system that relies on imaging droplets of biofluids for disease diagnosis in an attempt to reduce the number of consumables and equipment needed for biomedical testing.
-
 News
NewsImpact of pasteurization on dairy calves’ gut microbiota: A study of milk feeding and early microbial colonization
A new study highlights the impact of pasteurization on microbial diversity in dairy calves, underlining the importance of balancing pathogen safety and microbial health. It suggests that while pasteurization prevents pathogen transmission, it also reduces beneficial microbial transfer.
-
 News
NewsGenetically engineered fungi are protein packed, sustainable, and taste similar to meat
Researchers used CRISPR to increase a fungus’s production efficiency and cut its production-related environmental impact by as much as 61%—all without adding any foreign DNA. The genetically tweaked fungus tastes like meat and is easier to digest than its naturally occurring counterpart.
-
 News
NewsResearchers boost biosynthetic capacity in yeast through extended lifespan
Scientists have demonstrated that combining lifespan engineering strategies with metabolic pathway optimization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae enables highly efficient sclareol biosynthesis, marking an advance in improving microbial production through lifespan engineering.
-
 News
NewsBacteria ‘pills’ could detect gut diseases — without the endoscope
Researchers report that they’ve developed a sensor made of tiny microspheres packed with blood-sensing bacteria that detect markers of gastrointestinal disease. Taken orally, the miniature “pills” also contain magnetic particles that make them easy to collect from stool. Excreted from mouse models with colitis, the bacterial sensor detected gastrointestinal bleeding within minutes.
-
 News
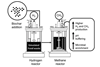
NewsBiochar boosts clean energy output from food waste in novel two-stage digestion system
A new study from researchers at the University of Western Australia and Universitas Brawijaya has found that adding biochar to advanced food waste recycling systems can significantly increase the clean energy yields of hydrogen and methane. This breakthrough offers promising strategies for municipalities and industries aiming to turn food scraps ...
-
 News
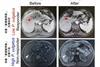
NewsGut bacterium impairs liver cancer treatment, inducing immunotherapy resistance
Researchers discovered that transplanting the gut bacterium Phocaeicola vulgatus into mouse models of liver cancer induced immunotherapy resistance. The finding is consistent with clinical observations in patients, showing that patients with low levels of P. vulgatus responded better to treatment.
-
 News
NewsScientist who harnesses bacteria to deliver green solutions is winner in 2025 Tata Transformation Prize
A scientist who harnesses bacteria to deliver green solutions has been named as one of the winners of the 2025 Tata Transformation Prize. Balasubramanian Gopal, PhD, Indian Institute of Science, has been named Sustainability Winner in the awards.
-
 News
NewsGreen chemistry for sustainable personal care
A recent review examined microbial biosurfactants as sustainable alternatives to synthetic surfactants in shampoo formulations. The authors addressed the growing demand for environmentally friendly and dermatologically safe cleansing agents, and emphasized the need to transition from petrochemical-based ingredients such as sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) to biodegradable biosurfactants.
-
 News
NewsApriori Bio and A*STAR Infectious Diseases Labs Announce strategic partnership to advance next generation influenza vaccines
Apriori Bio and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research Infectious Diseases Labs (A*STAR IDL) announced a strategic research partnership to co-develop and evaluate next generation self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) vaccines targeting seasonal and pandemic influenza.
