Circadian rhythms play a pivotal role in regulating diverse physiological functions, notably the composition and activity of gut microbiota. Accumulating evidence indicates that circadian rhythm disruption can induce dysbiosis of the gut microbiome, which in turn is implicated in influencing the tumor microenvironment (TME) and facilitating cancer progression.

This review integrates and analyzes recent advances elucidating the complex interplay where circadian rhythms modulate gut microbiota, and how these circadian-driven microbial changes affect the TME. This review analyzes recent advances in elucidating the complex interplay among circadian rhythms, gut microbiota, and the TME.
READ MORE: Researchers uncover role of fungal circadian clock in pathogenicity
READ MORE: Circadian disruption and gut microbiome changes linked to colorectal cancer progression
The authors examine how circadian disruption modifies the diversity and metabolic functions of gut microbiota, resulting in alterations of microbial metabolites, including but not limited to short-chain fatty acids and secondary bile acids. These metabolic alterations have the potential to modulate immune cell function, vascular remodeling, and tumor cell metabolism within the TME.
The study investigates the potential mechanisms through which gut microbial dysbiosis induced by circadian misalignment could promote an immunosuppressive TME and accelerate tumor growth. Additionally, it evaluates emerging therapeutic strategies that leverage the circadian-microbiome axis, encompassing chronotherapy, probiotic supplementation, and fecal microbiota transplantation.
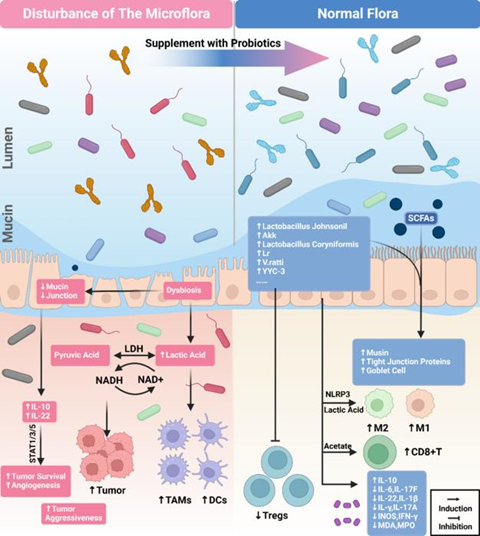
The integration of circadian biology, microbiology, and cancer immunology presents promising avenues for the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. However, significant challenges persist in translating these findings into viable clinical applications. Further research is imperative to elucidate the molecular pathways interconnecting circadian rhythms, gut microbiota, and the TME, and to develop personalized chronobiological interventions for cancer prevention and treatment.





No comments yet