All Bacteria articles – Page 58
-
 News
NewsAfter lockdown, immune system reacts more strongly to viruses and bacteria
The lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on people’s immune response to microorganisms. During the lockdown, inflammation level in the body was low, but afterwards, the immune system reacted more intensely to viruses and bacteria.
-
 News
NewsSyphilis had its roots in the Americas, archaeological bone reveals
New research supports a root in the Americas for syphilis and its known relatives, and their introduction to Europe starting in the late 15th century is most consistent with the data, scientists say.
-
 News
NewsCheese starter cultures yield insights into history of domestication of bacteria
A new study shows that the bacteria used to produce Gruyère, Emmental and Sbrinz cheese show signs of ancient domestication.
-
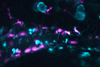 News
NewsBad bacteria can trigger painful gut contractions; new research shows how
After a meal of questionable seafood or a few sips of contaminated water, bad bacteria can send your digestive tract into overdrive. Your intestines spasm and contract, efficiently expelling everything in the gut. Source: Parthasarathy Lab and Guillemin Lab Immune cells (magenta) and cells expressing a reporter of ...
-
 News
NewsScientists find a vulnerability in antibiotic resistance mechanism
Superbugs, bacteria that are immune to multiple antibiotics, pose a great challenge to modern medicine. Researchers from the B CUBE - Center for Molecular Bioengineering at TUD Dresden University of Technology and Institut Pasteur in Paris identified a weakness in the bacterial machinery that drives antibiotic resistance adaptation. Their findings, ...
-
 News
NewsCases of whooping cough growing, but knowledge about it is lacking
Many in the public are not familiar with symptoms of whooping cough. Almost a third of respondents (30%) are not sure if pertussis is the same as whooping cough and not sure (30%) whether a vaccine exists to prevent it.
-
 News
NewsWhat a century-old grapevine reveals about a disease that plagues wine country
Researchers used bacterial DNA from a 120-year-old herbarium specimen to reconstruct the history of Pierce’s disease in California.
-
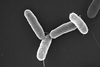 News
NewsScientists lift lid on Salmonella dry surface biofilm
Food scientists have revealed key characteristics of the foodborne pathogen Salmonella dry surface biofilm (DSB), a previously overlooked type of biofilm that commonly exists in dry food processing environments.
-
 News
NewsStaphylococcus aureus thwarts vaccines by turning on a protein that halts immune response
Approximately 30 clinical trials to date have failed to result in an effective human vaccine for Staphylococcus aureus but researchers have now identified a key reason for these failures, indicating that it may be possible to modify the vaccines to work in humans.
-
 News
NewsRoyal Veterinary College awarded international grants to advance research into cattle vaccines
The Royal Veterinary College (RVC) has been awarded two pump-prime grants from the International Veterinary Vaccinology Network (IVVN) to advance crucial research into Bovine Babesiosis and Bovine Tuberculosis vaccines to support cattle welfare.
-
 News
NewsFrom Yemen to Mayotte, the spread of a highly drug-resistant cholera strain
Scientists have revealed the spread of a highly drug-resistant cholera strain. The strain is resistant to ten antibiotics – including azithromycin and ciprofloxacin, two of the three recommended for treating cholera – and was identified for the first time in Yemen in 2018-2019.
-
 News
NewsScientists collect ‘microbial fingerprints’ found in household plumbing
Scientists sampled faucets in eight homes for seven days to see the flow and change of different bacteria populations. They found that, though houses generally shared major categories of bacteria, down to the species level, there was wide variation from house to house.
-
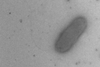 News
NewsDeep-sea hydrothermal vent bacteria hold key to understanding nitrous oxide reduction
Scientists have unearthed a clue to the molecular mechanisms involved in N2O reduction by deep-sea hydrothermal vent bacteria.
-
 News
NewsLeptospirosis in China: Current status, insights, and future prospects
A new study offers a concise overview of the current status of leptospirosis in China, the findings from epidemiologic studies on leptospirosis, and the impact of animal and environmental factors on leptospirosis.
-
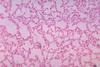 News
Newsβ-ionone shows promise in preventing ulcerative colitis through gut barrier protection and microbiota regulation
New research demonstrates that β-ionone can alleviate ulcerative colitis symptoms in mice by protecting the gut barrier and restoring the gut microbiota, offering hope for future dietary supplements or therapeutics aimed at managing UC.
-
 News
NewsDiverse phage populations coexist on single strains of gut bacteria
A new study shows that a single bacterial species, the host of a phage, can maintain a diverse community of competing phage species. Several phage species coexist stably on a population of a genetically uniform strain of E. coli.
-
 News
NewsResearchers call for global discussion about possible risks from ‘mirror bacteria’
A group of researchers has published new findings on potential risks from the development of mirror bacteria — synthetic organisms in which all molecules have reversed chirality (i.e. are ‘mirrored’).
-
 News
NewsCould we engineer stability in the microbiome? New research opens the door
New work could revolutionize our understanding of how the composition of the gut microbiome is determined and open the door to microbiome engineering.
-
 News
NewsMore attention should be paid to the health of deep soil in low-yield farmland
A recent study identified that a higher soil health index in low-yielding fields may be an important factor to maintain wheat yield as food demand grows rapidly.
-
 News
NewsNew, simple, and natural method for producing vitamin B2
Researchers have succeeded in developing a natural and simple method for producing vitamin B2: by gently heating lactic acid bacteria. This could be a game-changer in developing countries, where many suffer from vitamin B2 deficiency
