All Innovation News articles – Page 5
-
 News
NewsEngineered bacterial therapy activates immune response in cancer preclinical studies
Researchers have developed a new bacterial immunotherapy that delivers immune-activating proteins directly to solid tumors, which can often suppress the immune system. ACTM-838 targets phagocytic immune cells within the tumor microenvironment.
-
 News
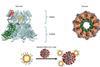
NewsProtein nanorings designed to detect and neutralize SARS-CoV2 virus
Scientists have generated a new ring-shaped protein nanomaterial capable of strongly binding to and neutralising the SARS-CoV2 virus. The new nanomaterial is formed by a scaffold based on recombinant ring-like proteins (RLPs), to which mini proteins were incorporated.
-
 News
NewsIn a nasal spray, gold nanoparticles deliver a targeted treatment to the brain
In the form of a ‘nasal spray’, tiny gold particles act as carriers, delivering a treatment directly to the brain: a new nanotechnological device for the treatment and prevention of neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases and infections.
-
 News
NewsSoil bacteria and minerals form a natural ‘battery’ that breaks down antibiotics in the dark
Researchers have unveiled a surprising new way that soil microbes can use sunlight energy. The team developed a “bio-photovoltage soil-microbe battery” that can capture, store, and release solar energy to power the breakdown of antibiotic pollutants in the dark.
-
 News
NewsNew antibiotic targets IBD — and AI predicted how it would work before scientists could prove it
The new antibiotic, enterololin, attacks and kills only a specific group of disease-causing bugs, which includes the type of E. coli that drives Crohn’s disease. It is a promising new treatment option for people affected by Crohn’s and other IBD-related conditions.
-
 News
NewsGenetic ‘Trojan horse’ selectively kills cancer cells linked to Kaposi’s sarcoma
A highly targeted gene therapy that could revolutionize treatment for cancers linked to a common herpesvirus harnesses an adeno-associated virus (AAV) to deliver a genetic “Trojan horse” into infected cells.
-
 News
NewsGene editing, traditional crossbreeding produce disease-resistant cacao plants
Researchers reported that they edited the gene TcNPR3 in cacao plants, ultimately resulting in disease-resistant cacao plants that had 42% smaller disease lesions when infected with phytophthora, compared to non-edited plants.
-
 News
NewsEngineers use bacterial nanowires to create first artificial neurons that could directly communicate with living cells
Engineers have created an artificial neuron with electrical functions that closely mirror those of biological ones. Using protein nanowires synthesized from electricity-generating bacteria, the discovery could herald immensely efficient computers built on biological principles.
-
 News
NewsBacteria transform waste polystyrene into nylon precursors
Scientists have succeeded in getting bacteria to break down the molecular building blocks of polystyrene and convert them into useful chemicals.
-
 News
NewsBalance is key: Strategies to boost protein production from engineered cells
New research demonstrates how to engineer ‘cell factories’ that last longer and produce more chemicals, without needing antibiotics or complex engineering methods, paving the way for sustainable biotech that lasts.
-
 News
NewsNew one-hour, low-cost HPV test could transform cervical cancer screening in Africa and beyond
A team of researchers has developed a simple, affordable human papillomavirus (HPV) test that delivers results in less than an hour with no specialized laboratory required.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop a virus cocktail to combat superbugs
Researchers have developed a bespoke phage therapy, Entelli-02, a five-phage cocktail designed specifically to target Enterobacter cloacae complex (ECC), a group of bacteria responsible for severe, often difficult-to-treat infections.
-
 News
NewsNew single-dose, temperature-stable rabies vaccines could expand global access
Researchers have discovered a new way to make human rabies vaccines that could greatly expand access to immunization across the globe. The new method creates shots that are temperature-stable—meaning they don’t need to be stored at cold temperatures.
-
 News
NewsNext-gen anti-bacterial and anti-viral surface modification technology inspired by Korean mussels
Researchers have successfully developed a next-generation surface modification technology with anti-bacterial and anti-viral contamination properties.While maximizing the bactericidal effect, a polydopamine layer, combined with an antibiotic, inhibits the adsorption of coronavirus.
-
 News
NewsEngineered gut bacteria improves survival outcomes in colorectal cancer tumors
A genetically modified Salmonella typhimurium strain can colonise tumours and release a therapeutic protein, LIGHT, to induce the formation of mature tertiary lymphoid structures (mTLSs) in laboratory models.
-
 News
NewsSteel sludge transformed into powerful water cleaner for antibiotic pollution
Researchers have developed an innovative way to turn steel industry waste into a low-cost material that can clean antibiotics out of water, offering a promising solution to one of today’s growing environmental challenges.
-
 News
NewsNew genome editing method inspired by bacteria’s defense strategies
Researchers have developed a new method for precisely editing DNA. Their aim was to make genetic changes in bacteria, plants, and human cells even more accurate and gentle.
-
 News
NewsResearchers find a more precise way to edit the genome
A genome-editing technique known as prime editing holds potential for treating many diseases. However, the process carries a small chance of inserting errors that could be harmful - but researchers have now found a way to dramatically lower the error rate.
-
 News
NewsAI-powered CRISPR could lead to faster gene therapies, study finds
A new AI tool can help scientists better plan gene-editing experiments. CRISPR-GPT acts as a gene-editing “copilot” supported by AI to help researchers — even those unfamiliar with gene editing — generate designs, analyze data and troubleshoot design flaws.
-
 News
NewsNew CRISPR test could make tuberculosis screening as simple as a mouth swab
Researchers have developed an enhanced CRISPR-based tuberculosis test that works with a simple tongue swab, a potential breakthrough that could allow easier, community-based screenings for the world’s deadliest infectious disease.
