All Innovation News articles – Page 4
-
 News
NewsHarnessing solar energy for environmental cleanup: Iron mineral-bacterial biofilms degrade pollutants
Researchers offer a sustainable, efficient, and scalable method for addressing soil and groundwater pollution, opening new possibilities for clean-up strategies in diverse ecosystems. This process significantly enhances the degradation of antibiotics like tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH) and chloramphenicol (CPL).
-
 News
NewsMaking yeast more efficient ‘cell factories’ for producing valuable plant compounds
Researchers have discovered a new way to make yeast cells more efficient “factories” for producing valuable plant compounds. By studying a plant membrane protein called AtMSBP1, they uncovered a mechanism that helps yeast cells better support plant cytochrome P450 enzymes.
-
 News
NewsAn edible fungus could make paper and fabric liquid-proof
Researchers report a way to waterproof materials using edible fungus. In a proof-of-concept study, the fungus grew an impervious film on common materials such as paper, denim, polyester felt and thin wood, revealing its potential to replace plastic coatings with sustainable materials.
-
 News
NewsSpectral signatures reveal hidden pine defenses: New tech enhances fusiform rust Resistance screening
A research team has developed a novel way to detect disease resistance in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) using near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, offering a faster and more objective alternative to traditional visual inspection.
-
 News
NewsAI tool beats humans at detecting parasites in stool samples, study finds
Scientists have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) tool that detects intestinal parasites in stool samples more quickly and accurately than traditional methods, potentially transforming how labs diagnose parasitic infections around the world.
-
 News
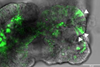
NewsBacteria deliver synthetic, animal-free way to grow organoids in 3D
Researchers have developed a completely animal-free gel to grow organoids, miniature three dimensional versions of organs. By combining the bacterial protein invasin with a synthetic gel, they created an environment in which organoids can grow and expand long-term.
-
 News
NewsArtificial ocean carbon recycling system converts seawater CO2 into valuable chemicals
Researchers have developed an artificial ocean carbon recycling system that captures CO2 from seawater and uses microbes to directly convert it into succinic acid.
-
 News
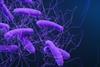
NewsScientists develop a way to track donor bacteria after fecal microbiota transplants
Researchers have developed a new technology to track beneficial bacteria for up to 5 years after fecal microbiota transplants (FMT). The method allows scientists to distinguish even closely related bacterial strains and identify each one’s unique genetic “fingerprint.”
-
 News
NewsNew platform for the production of versatile active ingredients
With the help of a newly developed chemo-enzymatic platform, researchers have succeeded in producing a large number of different furanolides in larger quantities and characterizing their biological activity.
-
 News
NewsScientists turn algae and crop waste into valuable fuels and nanomaterials
Researchers have developed a clean and efficient process to transform microalgae and agricultural residues into a range of high-value products, including biofuels, bio-adsorbents, and fluorescent carbon nanodots.
-
 News
NewsEngineers solve the sticky-cell problem in bioreactors and other industries
Their system uses electrochemically generated bubbles to detach cells from surfaces, which could accelerate the growth of carbon-absorbing algae and lifesaving cell therapies.
-
 News
NewsAll-in-one POM-based nanoreactor with oxidase-like activity for versatile detection and antibacterial action
A research team has developed a novel nanoreactor that enables dual-mode biomarker detection and effective antibacterial treatment.
-
 News
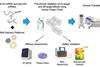
NewsHuman Organ Chip technology sets stage for pan-influenza A CRISPR RNA therapies
Human lung alveolus chip infection model enables investigation of viral replication, inflammatory responses, and genetic off-target effects of a novel pan-influenza CRISPR therapy.
-
 News
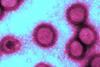
NewsSafer, more effective vaccines with new mRNA vaccine technology
A new messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) vaccine technology could make future vaccines safer, more effective, and less burdensome for patients. The new approach uses albumin-recruiting lipid nanoparticles to deliver mRNA precisely to lymph nodes while bypassing the liver.
-
 News
NewsScientists unbolt gateway to sharper CRISPR gene editing
Identifying the passwords for a certain CRISPR tool is a major stumbling block in discovering and characterising the CRISPR tool - but a team of scientists has cracked the code.
-
 News
NewsResearchers developing new easy-to-use viral biosensor test, giving patients more accurate and immediate results
An interdisciplinary team of researchers is creating a single low-cost test to detect HIV & Hepatitis B and C simultaneously, that may be used in resource-limited settings. With quicker and more accessible results, the test has potential to save lives.
-
 News
NewsScientist invents MICROCAP, an algae-based oxygen generator that removes CO₂ and purifies indoor air
A lecturer in Thailand has invented the MICROCAP air purifier, which uses photosynthetic algae to absorb carbon dioxide and produce 20 times more oxygen than trees.
-
 News
NewsRevolutionizing bioplastics: a microbial platform for fully bio-based long-chain polyesters
Researchers have developed a scalable, end-to-end microbial process transforming plant oils into sustainable polyesters comparable to petroleum-based plastics.
-
 News
NewsFrom glucose to gourmet: engineered bacteria churn out key food additive
Researchers used E. coli as the chassis to produce inosinic acid (IMP), a popular umami enhancer. By reprogramming the metabolic flux network of E. coli and introducing amino acid mutations in the key enzymes in the synthesis pathway, the yield was significantly increased.
-
 News
NewsChemobiological platform enables renewable conversion of sugars into core aromatic hydrocarbons of petroleum
Researchers have developed a chemobiological platform that converts renewable carbon sources such as glucose and glycerol into oxygenated precursors, which are deoxygenated in the same solvent system to yield benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and p-xylene (BTEX).
