All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 35
-
 News
NewsFoxtail barley serves as a host for fungal pathogens attacking barley
Researchers report that foxtail barley (Hordeum jubatum), a wild relative of the cultivated crop, can harbor several fungal pathogens and may play a role in the disease epidemiology of barley, potentially serving as reservoirs of inoculum to initiate some diseases.
-
 News
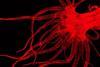
NewsResearchers capture first high-res images of deadly yellow fever virus
Researchers have captured the first high-resolution images of the yellow fever virus (YFV), a potentially deadly viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes that affects the liver.
-
 News
NewsAccessible imaging technique can predict cardiac risks in patients with Chagas disease
A simple imaging exam capable of assessing myocardial deformation during contraction has emerged as a promising tool for predicting the risk of cardiac complications in patients with chronic Chagas disease.
-
 News
NewsPlasma strategy boosts antibacterial efficacy of silica-based materials
Scientists have developed a novel two-step plasma strategy to modify mesoporous silica-supported silver nanoparticles, enabling them to achieve strong antibacterial activity and accelerated wound healing.
-
 News
NewsNew insights on gut microbes that prevent formation of cancer-causing compounds
Gut microbes metabolize dietary nitrates and nitrites and prevent the formation of cancer-causing compounds called nitrosamines. New research sheds light on these processes and pinpoints which types of bacteria are most important.
-
 News
NewsUK’s failure to retain and scale science and technology causing economy to bleed out, warns Lords Committee
The UK’s failure to retain and scale its science and technology companies has now reached crisis point and is causing the UK economy to bleed out, warns a damning report.
-
 News
NewsResearch finds higher rare risk of heart complications in children after COVID-19 infection than after vaccination
A whole-population study showed that although these conditions were rare, children and young people were more likely to experience heart, vascular or inflammatory problems after a COVID-19 infection than after having the vaccine — and the risks after infection lasted much longer.
-
 News
NewsDemographic shifts could boost drug-resistant infections across Europe
The rates of bloodstream infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria will increase substantially across Europe in the next five years, driven largely by aging populations, according to a new paper.
-
 News
NewsNew approach expands possibilities for studying viruses in the environment
A new method vastly improves on the existing approach for single-cell genetic sequencing, enabling scientists to read the genomes of individual cells and viral particles in the environment more quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
-
 News
NewsTiles, leaves and cotton strips offer practical, affordable method for measuring river health
With the aim of standardising methods for assessing river health and providing a simple, accessible guide for environmental management bodies, researchers analysed the performance of different materials that enable the decomposition processes and organic matter production to be measured.
-
 News
News‘Rotten egg’ gas could be the answer to treating nail infections, say scientists
Hydrogen sulphide, the volcanic gas that smells of rotten eggs, could be used in a new treatment for tricky nail infections that acts faster but with fewer side effects, according to scientists.
-
 News
NewsHIV significantly affects sleep, with many living in a state akin to chronic jet lag
A new study describes how people living with HIV experience higher rates of sleep issues even when virally suppressed, which has been associated with a higher risk for heart disease, depression and cognitive decline.
-
 News
NewsNovel technique reveals insights into soil microbe alarm clock
A new study yields clues about when dormant microscopic bacteria and fungi in soil ‘wake up’ and colonize roots, which influences plant growth and health.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals critical impact of universal cCMV screening on early detection of hearing loss in newborns
A comprehensive eight-year study reveals that approximately one-third of congenital cytomegalovirus-related hearing loss develops after the newborn period—cases that would be missed without universal screening programs.
-
 News
NewsMyths about rapid spread of the Black Death influenced by single ‘literary tale’, experts show
Modern portrayals of the Black Death quickly moving across Asia, ravaging Silk Route communities, following the course of traders, have been incorrect because of centuries of misinterpretation of a rhyming fourteenth-century literary tale, experts have found.
-
 News
NewsReview probes mechanical and durability properties of microorganism based self-healing concrete
Microorganism-based self-healing concrete, which uses bacteria to induce calcite precipitation for crack sealing, has emerged as a promising solution, but existing studies lack systematic reviews of its mechanical properties and durability performance.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals not all bats carry equal viral risk
A groundbreaking study sheds new light on the relationship between bats and dangerous viruses, showing that contrary to widespread assumptions, not all bats carry viruses with high epidemic potential, only specific groups of species.
-
 News
NewsAdvanced disease modelling shows some gut bacteria can spread as rapidly as viruses
Escherichia coli (E. coli), a type of bacteria commonly found in the human gut, could spread as quickly as swine flu, new research suggests. For the first time, researchers are able to predict the rate at which one person could transmit gut bacteria to those around them.
-
 News
NewsResearchers screen microbial strains to reduce H2S and CH4 emissions from wastewater
A new study demonstrates that S. cerevisiae and B. subtilis effectively reduce H2S and CH4 emissions from wastewater by altering microbial community composition and metabolic pathways, offering a sustainable approach for wastewater treatment.
-
 News
NewsHow algae help corals bounce back after bleaching
A $1.1 million project will uncover how reefs regain life-giving algae after suffering from heat stress. The three-year project will use advanced imaging and living experimental systems to learn what’s happening on a cellular level when algae return to bleached reefs.
