All Medical Microbiology articles – Page 5
-
 News
NewsNew phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoids discovered from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii
Three new phenolic bisabolane sesquiterpenoids (PBS) derivatives (±)-aspersydonol A (1a/1b) and aspersydonol B (2), along with 12 known analogues, have been isolated from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii LF51.
-
 News
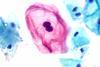
NewsHPV integration: Moving from carcinogenesis mechanisms to clinical applications
The clinical significance of HPV integration into the host genome is substantial, particularly in cervical cancer screening programs. Integration testing has emerged as a valuable triage tool for detecting high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN III+).
-
 News
NewsNew Center of Excellence to respond to the challenge of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Boston Children’s Hospital and Tulane University have received $25 million in funding from NIAID/NIH to establish a Center of Excellence for Translational Research (CETR) called IMPACT (Immunization against Multidrug-resistant Pathogens: Activating T Cell Immunity).
-
 News
NewsType 2 diabetes may double risk of sepsis, large community-based study suggests
Living with type 2 diabetes (T2D) may double the risk of developing sepsis—with those aged younger than 60 years and men particularly susceptible, according to a long-term community-based study in Australia.
-
 News
NewsMedications leave lasting mark on the gut microbiome, even years after use
Analysing stool samples and prescription records from over 2,500 Estonian Biobank participants, researchers found that the majority of drugs studied were linked to microbiome changes, with a substantial number of them also showing long-term effects detectable years after patients stopped taking them.
-
 News
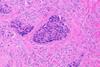
NewsMicrobial allies: Bacteria help fight against cancer
An international team of scientists have discovered that microbes associated with tumours produce a molecule that can control cancer progression and boost the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
-
 News
NewsPediatric investigation study re-examines chikungunya in neglected pediatric victims
Researchers and policymakers must recalibrate their outlook on pediatric chikungunya to develop effective control measures, a new paper warns.
-
 News
NewsEven healthy children can be severely affected by RSV
It is not only premature babies and children with underlying diseases who suffer from serious respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections. Even healthy, full-term babies are at significant risk of intensive care or prolonged hospitalisation – especially during the first three months of life.
-
 News
NewsFrailty fuels gut imbalance and post-surgery gastrointestinal risks
Scientists found that residual intra-abdominal microbes, especially in frail patients, drive gastrointestinal complications after bladder cancer surgery.
-
 News
NewsDe-mystifying common misconception about the prevalence of Legionella bacteria
There is a common misconception that Legionella is only found in air conditioners and water towers - however, a new study has found people are likely exposed to the bacteria through other sources, including through soil.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop first-of-its-kind RNA tool to advance cancer and infectious disease research and treatment
Scientists have developed a powerful tool capable of scanning thousands of biological samples to detect transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) modifications — tiny chemical changes to RNA molecules that help control how cells grow, adapt to stress and respond to diseases such as cancer and antibiotic‑resistant infections.
-
 News
NewsAre probiotics worth the cost to prevent infection after a colon removal surgery?
A study found that taking an 8-strain probiotic daily may reduce the risk of pouchitis, a common inflammatory condition that occurs after colon removal surgery for ulcerative colitis, but the treatment may not be worth the cost depending on a patient’s likelihood of flare-ups.
-
 News
NewsOne dose of antibiotic treats early syphilis as well as three doses
Researchers have found that a single injection of the antibiotic benzathine penicillin G (BPG) successfully treated early syphilis just as well as the three-injection regimen used by many clinicians. These findings from a late-stage clinical trial suggest the second and third doses of conventional BPG therapy do not provide a health benefit.
-
 News
NewsClinical study shows that nasal spray containing azelastine reduces risk of coronavirus infection by two-thirds
In addition to showing a marked reduction in coronavirus infections, the azelastine group also displayed fewer symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections, a lower overall number of confirmed respiratory infections, and, unexpectedly, a reduced incidence of rhinovirus infections, another major cause of respiratory illness.
-
 News
NewsNew pimple patches deliver a powerful remedy to unwanted zits
Researchers have designed a two-stage pimple patch set with an array of tiny spikes that grabs onto the pimple and delivers antibacterial or anti-inflammatory compounds. Human clinical trials confirmed that the pimples disappeared after seven days of treatment.
-
 News
NewsOne shot of RSV vaccine effective against hospitalization in older adults for two seasons
One shot of an RSV vaccine protects adults ages 60 or older from RSV-associated hospitalization and critical illness during two consecutive RSV seasons, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsNew sepsis diagnostic could reduce critical time to save patients
A new diagnostic method would confirm sepsis infections earlier, cutting critical hours in the “race against time” to save patients’ lives. The process uses a centrifuge to separate bacteria from blood cells, and automatic microscopy for detection.
-
 News
NewsGuideline on respiratory infections in leukemia revised
People with leukemia have a weakened immune system due to the disease itself and treatment, which leads to an increased susceptibility to infections. In a revised guideline, experts summarize the findings of the past ten years on all viruses that cause respiratory infections.
-
 News
NewsPertussis resurgence in Tuscany outlines importance of timely vaccination in Italy
Research analysing 2016-2024 data from all pertussis-related hospitalisations in Tuscany, Italy, finds a ninefold increase in pertussis cases in 2024 among children and adolescents.
-
 News
NewsGI tumor microbes may predict prognosis and inform treatment
Intratumor microbes can play a role in disease progression and response to treatment. Researchers have identified core tumor microbiota associated with disease progression and risk, developing a microbiota-based risk score that can predict response to therapy.
