More Healthy Land – Page 5
-
 News
NewsRainfall and temperature shape mosquito fauna in Atlantic Forest bromeliads, including malaria vectors
Results from a study of mosquito larvae conducted in a natural area in the municipality of São Paulo (Brazil) may help estimate the effects of climate change on disease transmission risk in the biome.
-
 News
NewsHigher methane emissions from warmer lakes and reservoirs may exacerbate worst-case climate scenario
Emissions of the greenhouse gas methane from lakes and reservoirs risk doubling by the end of the century due to climate change according to a new study. This in turn could raise Earth’s temperature more than suggested by the UN climate panel IPCC’s current worst-case scenario.
-
 Careers
CareersSummer studentship: Jonas investigates how metals influence bacterial ecosystems
Jonas Flohr from Portsmouth reports back on his AMI-sponsored summer studentship at Durham University investigating how metals influence bacterial ecosystems.
-
 News
NewsBacteriophage characterization provides platform for rational design
Researchers have described the bacteriophage Bas63 in unprecedented detail, supporting new mechanistic understanding of how these viruses function.
-
 News
NewsBacteria spin and dye rainbow-colored, sustainable textiles
Researchers demonstrate that bacteria can both create fabric and dye it in every color of the rainbow—all in one pot. The approach offers a sustainable alternative to the chemical-heavy practices used in today’s textile industry.
-
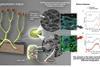 News
NewsAdvanced imaging reveals new fungus species in 407-million-year-old plant fossil from Scotland
Researchers have identified a new species of ancient symbiotic fungus preserved within a 407-million-year-old plant fossil from Scotland. The discovery provides unprecedented three-dimensional insight into one of the earliest known plant–fungus partnerships.
-
 News
NewsDestroying crazy ant nest structure makes them vulnerable to pathogens
Scientists have devised a reliable way to introduce a natural pathogen in colonies, so that invasive tawny crazy ant populations collapse and other native species can recover.
-
 News
NewsBacterial spores offer promise of sustainable smart materials
By embedding Bacillus spores within engineered living materials, researchers have created living materials that not only endure harsh environments but can also be programmed to perform specific tasks. These materials may be a sustainable replacement for fossil-based materials.
-
 News
NewsCracking leishmaniasis: new DNA test to track infection
A new study offers an innovative way to track the spread of leishmaniasis, a parasitic disease affecting both animals and humans. Researchers developed a fast, reliable method to identify sand fly species, detect Leishmania parasites, and determine the source of their blood meals from a single sample.
-
 News
NewsMissing links for rabies in Peru highlights global threats of health inequity
Researchers found that efforts to track dog-related rabies in poorer areas of Peru’s second largest city were lacking even though more dogs were found to have the disease there than in wealthier neighborhoods.
-
 News
NewsWild grass offers new genetic clues to combat deadliest pathogen of wheat
A new study has identified Aegilops cylindrica, a wild grass closely related to wheat, as a powerful genetic reservoir for resistance against the devastating fungal pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici—the cause of Septoria tritici blotch (STB).
-
 News
NewsGrassland degradation reshapes relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality
Grassland degradation fundamentally reshapes how biodiversity supports ecosystem multifunctionality, shifting it from being plant-dominated to being mediated by soil microbes, according to a new study of alpine grassland on the Tibetan Plateau.
-
 News
NewsHorizon Awards 2025: Professor Joana Falcao Salles named as winner of Basil Jarvis Award
Professor Joana Falcao Salles, a professor of Microbial Community Ecology at the University of Groningen, has been named as the newest winner of the Basil Jarvis Food Security and Innovation Award.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how cyanobacteria use ’sunscreen’ to adapt to climate
Using single particle spectroscopy, researchers revealed insights into how different types of photosynthetic bacteria can use a shared mechanism to protect themselves from too much sunlight.
-
 News
NewsHow life first got moving: nature’s motor from billions of years ago
Research has cast light on the evolutionary origins of one of nature’s first motors, which developed 3.5 billion to 4 billion years ago to propel bacteria. Scientists have created the most comprehensive picture yet of the evolution of bacterial stators.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover global patterns and drivers of orchid mycorrhizal interactions
A global meta-analysis of orchid-fungal associations leads to a general conclusion: an orchid’s fungal community is driven more strongly by its ecophysiology and biogeography than by its phylogeny.
-
 News
NewsCould tiny airborne plastics help viruses spread? Scientists warn of a hidden infection risk
While plastics are already recognized as a global environmental threat, a new commentary highlights that their microscopic airborne forms could also play a hidden role in human infection.
-
 News
NewsHow are metabolism and cell growth connected? — A mystery over 180 years old
A research team has identified a novel principle in biology that mathematically explains why the growth of organisms slows as nutrients become more abundant—a phenomenon known as “the law of diminishing returns.”
-
 News
NewsResearchers reveal novel mechanisms for decoding bacterial frequency modulation in signal processing
A study reveals the fundamental physical principles underlying bacterial FM signal processing, and demonstrated that FM decoding mechanisms enable bacteria to increase information entropy by approximately 2 bits compared to traditional AM in three-gene regulatory systems.
-
 News
NewsHeatproof microbes reveal molecular secrets of nature’s hottest recycling system
This study reveals how thermophilic bacterial communities withstand temperatures of up to 87°C by remodeling their molecular machinery. Scientists uncovered a heat-defense network centered on heat shock proteins that refold damaged enzymes and preserve protein structure.
