M42, a global health leader powered by technology, artificial intelligence (AI) and genomics, has unveiled landmark findings from a large-scale population study on AI-powered tuberculosis (TB) screening, published in the prestigious scientific journal npj Digital Medicine - Nature.
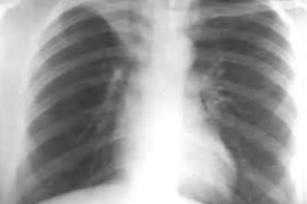
Conducted in collaboration with Capital Health Screening Centre (CHSC) in Abu Dhabi, part of the M42 group, the study is among the largest real-world clinical validations of an AI-driven healthcare solution to date, analyzing over one million chest X-rays (CXRs) to evaluate the efficacy and scalability of AI in TB screening.
READ MORE: AI accelerates the search for new tuberculosis drug targets
READ MORE: AI software at least as good as radiologists at detecting TB from chest X-rays
The study assessed AI Radiology in Screening TB (AIRIS-TB), M42’s cutting-edge AI model engineered to streamline routine tuberculosis screenings, allowing radiologists to focus on more complex or urgent cases. AIRIS-TB demonstrated exceptional performance, achieving an Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUROC) of 98.5% - a clear indicator of its high efficiency in triaging CXRs for TB.
Real-world impact
With an estimated 10.8 million people falling ill from TB and a total of 1.25 million people dying from it in 2023, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), and recent reports of TB returning to being the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, M42’s AIRIS-TB demonstrates the potential of AI solutions delivering real-world impact.
AIRIS-TB reported an unprecedented 0% false-negative rate for tuberculosis-specific cases across the full dataset – an achievement that reinforces its safety and reliability as a workflow automation tool.
In practical application, the model has the potential to safely automate up to 80% of routine CXR assessments, directly alleviating radiologist workload pressures, minimizing the risk of human error, and delivering significant cost efficiencies in high-throughput low-prevalence settings. Presently, CXR review remains labor-intensive and prone to oversight and error, potentially leading to missed or delayed diagnoses, with a prior study stating a 26.6% increase in missed findings when radiologists double their annotation speed, and a rise in errors after 9 hours into their shift.[1]
Strong performance
Importantly, AIRIS-TB delivered consistently strong performance across a wide range of demographic groups, including variations in gender, age, HIV status, income levels, and a diverse population covering six World Health Organization (WHO) regions, highlighting the model’s robustness, fairness and generalizability across diverse global populations. These results underscore AIRIS-TB’s potential to significantly enhance clinical workflows and drive earlier, more equitable screening of TB in high-volume programs worldwide.
Dimitris Moulavasilis, Group CEO of M42, said: “This landmark study marks a pivotal moment in the potential power of AI in the global fight against tuberculosis. Our AIRIS-TB model stands as a compelling testament to the unmatched accuracy, safety and scalability that AI can deliver, particularly in resource-limited settings where there is a shortage of radiologists and the need to tackle TB is greatest.
”In regions with a high prevalence of TB, we now have a scalable technological solution that can bridge the divide, expand radiologist capacity and help save lives. These results signal the transformative role AI can play in reshaping global public health and redefining how healthcare is diagnosed, delivered and experienced worldwide.”
Diagnostic capacity
Dr. Laila Abdel Wareth, CEO of Capital Health Screening Centre added: “The outcomes of this study reaffirm that AI models like AIRIS-TB can not only match – but safely surpass – human-level accuracy and efficiency in clinical practice. By automating high-volume, routine screenings with precision, we are equipping radiologists to concentrate on complex and high-risk cases, unlocking greater diagnostic capacity. This shift holds immense potential to elevate patient outcomes, streamline healthcare delivery and bolster public health infrastructure on a global scale.”
The study underwent rigorous peer review and ethical oversight by the Department of Health – Abu Dhabi, ensuring transparency, accountability, and the highest standards of clinical integrity. Its publication in a leading scientific journal reinforces M42’s position as a global pioneer in AI-led health solutions and solidifies the UAE’s growing prominence as a global, data-driven hub for cutting-edge medical innovation and technology. The full study is accessible through npj Digital Medicine.





No comments yet