Researchers from Rothamsted Research and the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul tested two popular viral vectors - barley stripe mosaic virus (BSMV) and foxtail mosaic virus (FoMV) - to see if they could temporarily switch genes on or off in rice (Oryza sativa). These virus-enabled reverse genetics (VERG) techniques are regularly used in plants to study gene function without permanent genetic modification.

These methods have worked well at Rothamsted in wheat and blackgrass producing clear results: plants turn white when a chlorophyll gene is silenced, or glow green when a fluorescent protein is expressed. In rice, no such changes occurred. Despite extensive optimisation across six rice cultivars, the team found no evidence that these VERG techniques work in rice.
“Although we don’t know why they didn’t work, it’s clear they don’t,” said Guilherme Turra, lead author and PhD student at the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul. “Rather than chase every possible explanation, we focused on rigorously testing variations of established protocols and inoculation methods across different rice types. By using robust scientific methods and clear visual phenotypes, we can be confident these tools simply don’t deliver in rice.”
Robust data
Building on that point, Dr Dana MacGregor, senior author at Rothamsted, said: “It’s important to trust robust data, even when it challenges your original hypothesis. As scientists, we need to stay open to the possibility that our approach or assumption was wrong. We assumed what works in wheat would work in rice, but our data clearly show otherwise. By sharing these results, we hope to help others avoid the same pitfalls.”
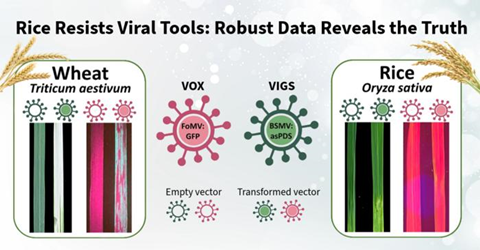
The findings, now peer-reviewed and published in Annals of Applied Biology, underscore the species-specific nature of VERG and the importance of sharing negative results to guide future research. By publishing these data, the team hopes to prevent others from repeating unsuccessful experiments and to encourage innovation in viral systems tailored to rice.
The work was supported by the UK’s Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), Rio Grande do Sul State’s Research Support Foundation (FAPERGS) and Brazil’s CAPES programme.
Topics
- Agriculture
- barley stripe mosaic virus
- blackgrass
- Dana MacGregor
- Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul
- Food Security
- foxtail mosaic virus
- Guilherme Turra
- Healthy Land
- Microbiological Methods
- Oryza sativa
- Research News
- Rothamsted Research
- Soil & Plant Science
- The Americas
- UK & Rest of Europe
- viral vectors
- virus-enabled reverse genetics
- Viruses
- wheat





No comments yet