All Parasites articles
-
 News
NewsA rapid test using a mobile phone will be able to identify the most severe cases of imported malaria within minutes
A new malaria tool uses a mobile phone to combine rapid diagnostic tests with video analysis and is capable not only of detecting the infection in under six minutes but also of predicting which patients may develop severe forms of malaria.
-
 News
NewsScientists find hidden diversity inside common brain parasite
Scientists have found that Toxoplasma gondii is far more complex than previously believed. Until now, cysts were believed to contain a single, uniform type of parasite lying dormant until reactivated, but have now been found to contain multiple distinct subtypes of parasites, each with different biological roles.
-
 News
NewsThe brain’s sneakiest houseguest: how a parasite rewrites neuron messages and alters neuroplasticity
A new study describes how Toxoplasma gondii manipulates the behaviour and brain function of its hosts. It explored a new angle by looking at nanoparticles called extracellular vesicles, which cells use to send messages to one another, and carry small regulatory molecules known as microRNAs.
-
 News
NewsCommon brain parasite can infect your immune cells. Here’s why that’s probably OK
Researchers have determined how our immune systems fight back against the parasite Toxoplasma gondii when it makes it inside the CD8+ T cells meant to destroy it.
-
 News
NewsHow the parasite that ‘gave up sex’ found more hosts – and why its victory won’t last
A study has revealed a genetic shortcut that may help Giardia duodenalis and many other parasites jump to new hosts at the cost of long-term survival. The findings may also help explain how parasites evolve drug resistance.
-
 News
NewsHigh levels of Chagas disease parasite found in bugs near US-Mexico border
Researchers have found unusually high levels of parasitic infection in the insects that transmit Chagas disease in the Borderlands. The bugs were collected near homes and natural areas along the U.S.-Mexico border.
-
 News
NewsScientists identify potential therapy and diagnostic markers for cerebral malaria
Researchers examined whether methylene blue could mitigate brain injury during severe malaria, and whether a practical set of blood biomarkers could help clinicians identify cerebral malaria early and track how patients respond to treatment.
-
 News
NewsNew antimalarial drug candidate shows potential for fighting resistance and reducing malaria transmission
Researchers have developed a new antimalarial drug candidate designed to address the growing challenge of drug resistance and potentially reduce malaria transmission.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover fungus that kills toxic algae threatening human health
A team of researchers have discovered a previously unknown species of marine fungus that can kill harmful, bloom-forming algae. The new species, Algophthora mediterranea, is a form of microscopic chytrid fungus that can occupy a broad range of hosts.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals that parasite-produced dopamine can alter host behaviour
A new study has shed light on how Toxoplasma gondii, the causative agent of toxoplasmosis, can alter host behaviour. The research findings show that such behavioural changes are achieved, at least in part, through dopamine manipulation caused by dopamine produced by the parasite itself.
-
 News
NewsNew tools saved a million lives from malaria last year but progress under threat as drug resistance rises
Wider use of new tools against malaria, including dual-ingredient nets and WHO-recommended vaccines helped to prevent an estimated 170 million cases and 1 million deaths in 2024, according to WHO’s annual World Malaria Report.
-
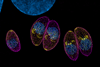 News
NewsToxoplasmosis: How a deadly parasite infects its host cells
Researchers have discovered how the parasite Toxoplasma gondii builds a specialised structure that allows it to move and invade host cells. They identified two proteins that control how the conoid complex is assembled - this acts like an engine for movement and cell-invasion.
-
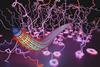 News
NewsMalaria parasites move on right-handed helices
After penetrating the skin, the malaria parasite moves with helical trajectories, almost always turning toward the right. Researchers demonstrated that the pathogen uses these right-handed helices to control its motion as it transitions from one tissue compartment to another.
-
 News
News$3.7 million awarded for research into sand flies, vectors of parasitic disease leishmaniasis
Professor Gideon Wasserberg at UNC Greensboro has been awarded a prestigious $3.7 million National Institutes of Health R01 grant to advance his research on controlling sand flies, the vectors of the parasitic disease leishmaniasis.
-
 News
NewsAMI warns that the threat of antimicrobial resistance in viruses and other pathogens cannot be underestimated
Applied Microbiology International (AMI) has urged global policymakers to strengthen the revised Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (GAP-AMR), calling for a more inclusive, clear and equitable approach to tackling one of the world’s most urgent health challenges.
-
 News
NewsSingle-dose malaria treatment combining four existing drugs as effective as more onerous multi-day, multi-dose regimen
Hundreds of malaria patients participating in a clinical trial in Gabon in West Africa were cured via a single dose of a treatment that utilizes four widely available malaria drugs, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsCracking leishmaniasis: new DNA test to track infection
A new study offers an innovative way to track the spread of leishmaniasis, a parasitic disease affecting both animals and humans. Researchers developed a fast, reliable method to identify sand fly species, detect Leishmania parasites, and determine the source of their blood meals from a single sample.
-
 News
NewsAccessible imaging technique can predict cardiac risks in patients with Chagas disease
A simple imaging exam capable of assessing myocardial deformation during contraction has emerged as a promising tool for predicting the risk of cardiac complications in patients with chronic Chagas disease.
-
 News
NewsWarmer Nordic springs double the incidence of avian malaria
A unique long-term study, in which biological samples were collected from the same population of blue tits over a 30-year period, shows that rising spring temperatures have doubled the incidence of avian malaria in southern Sweden.
-
 News
NewsMalaria risk in the Amazon is higher in regions with intermediate forest degradation
Research shows that areas with 50% deforestation near residential areas or fragmented vegetation allow greater contact between mosquitoes and humans. The study helps us understand the link between forest destruction and the spread of the disease.
