All Research News articles – Page 6
-
 News
NewsMaternal microbiome compound may hold key to preventing liver disease
Children born to mothers who consume a high-fat, high-sugar diet during pregnancy and breastfeeding face a higher risk of developing fatty liver disease later in life. New research suggests that risk may be reduced by supplementing with a naturally occurring compound produced by healthy gut bacteria.
-
 News
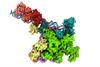
NewsA new study reveals how cholera virulence is activated
A new study provides a long-sought structural explanation of the regulatory cascade that allows Vibrio cholerae to colonize the human gut and produce the cholera toxin that causes life-threatening diarrhea.
-
 News
NewsTB and HIV treatments are not enough for a full recovery
Existing treatments control TB and HIV, but the immune system does not revert to normal, helping explain why people living with HIV remain susceptible to infections and underscoring the need for immunotherapies.
-
 News
NewsAboard the International Space Station, viruses and bacteria show atypical interplay
In a new study, terrestrial bacteria-infecting viruses were still able to infect their E. coli hosts in near-weightless “microgravity” conditions aboard the International Space Station, but the dynamics of virus-bacteria interactions differed from those observed on Earth.
-
 News
NewsWhy don’t antibiotic-making bacteria self-destruct?
Scientists discovered a promising new antibiotic in a soil sample. The molecule, lariocidin, is produced by the microbe Paenibacillus and shows broad activity against pathogenic bacteria. Now, the researchers report how Paenibacillus avoids harm by its own antibiotic.
-
 News
NewsScientists observe infections by cancer-causing retroviruses in koalas as they occur
Scientists analysed the ongoing colonization by two retroviruses of the germline of koalas and resulting deaths from cancer in multi-generational pedigrees of over 100 koalas in US and European zoos. They calculated genetic risk scores (GRS) that can help guide koala breeding programs.
-
 News
NewsWhen a virus releases the immune brake: New evidence on the onset of multiple sclerosis
A study investigating the links between Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis shows that EBV can interfere with the control of B cells. One viral protein mimics a crucial “approval” signal that B cells usually require from other immune cells. Self-reactive B cells can then survive even when they should be shut down.
-
 News
NewsResearch reveals hidden diversity of E. coli driving diabetic foot infections
New research has shed light on the diversity and characteristics of E. coli strains that drive diabetic foot infections, providing the first comprehensive genomic characterisation of E. coli strains isolated directly from diabetic foot ulcers across multiple continents.
-
 News
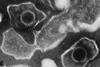
NewsNew mechanism links Epstein-Barr virus to MS
Scientists investigating the links between the Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis show that when the immune system fights EBV, certain T cells – which normally attack the virus – can also react to a protein in the brain called Anoctamin-2 (ANO2), a phenomenon called molecular mimicry.
-
 News
NewsNot only toxic but also a nutrient: guanidine as a nitrogen source
Cyanobacteria are key ecological players of global carbon and nitrogen cycles. They are also becoming increasingly important for carbon-neutral biotechnology. They could serve as green cell factories for a light-driven and sustainable production of chemicals and fuels – a central pillar of the sustainable bioeconomy. Source: André Künzelmann/UFZ ...
-
 News
NewsGenetic risk factor and viral infection jointly contribute to MS
One of the leading triggers for multiple sclerosis (MS) is an infection with the Epstein-Barr virus. However, certain gene variants also play an important role. Researchers have shown that it is the molecular interaction between environmental and genetic risk factors that ultimately triggers the disease.
-
 News
NewsRare microbial wrinkle structures - signs of ancient life - turn up in an unexpected place
Deep water sediment layers in the Dadès Valley in the Central High Atlas Mountains of Morocco have revealed rare microbial wrinkle structures formed far from sunlight.
-
 News
NewsFirst extensive study into marsupial gut microbiomes reveals new microbial species and antimicrobial resistance
New research provides the first metagenomic data for 13 marsupial species , including the red kangaroo and the common brushtail possum. They revealed that host family, animal location, and diet all contributed towards variance between different microbiomes.
-
 News
NewsA protein found in the GI tract can neutralize many bacteria
The mucosal surfaces that line the body are embedded with defensive molecules that help keep microbes from causing inflammation and infections. One of these molecules, intelectin-2, has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacteria found in the GI tract.
-
 News
NewsGut bacteria protect mice with influenza A from bacterial pneumonia, study finds
Select gut bacteria protect mice against post-influenza virus secondary bacterial pneumonia, according to a study which sought to define whether intestinal bacteria influenced some individuals’ vulnerability to secondary bacterial infections following primary respiratory viral infection.
-
 News
NewsCat disease challenges what scientists thought about coronaviruses
Researchers have uncovered new details about how a once-deadly coronavirus disease in cats spreads through the immune system. For years, the prevailing belief was that the virus behind feline infectious peritonitis infected just one type of immune cell.
-
 News
NewsGamma rays quickly toughen nitrogen‑fixing bacteria
Heat‑resilient biofertilizers could help crops cope with rising temperatures but engineering them has been slow and uncertain. A new study shows that pairing experimental evolution with controlled gamma‑ray mutagenesis can accelerate the path to heat‑tolerant nitrogen‑fixing bacteria.
-
 News
NewsResearcher reveals secrets of bacteria that can swim upstream
Rather than washing pathogens away, strong fluid currents act as “guide rails” that align bacteria and accelerate their upstream migration. They discovered that this creates a “two-way invasion” where pioneer cells reach the source within minutes, seeding colonies that spread threefold faster than in still water.
-
 News
NewsTeam shows how viral lysis of blue-green algae enhances ecosystem-scale productivity
Newly published interdisciplinary research shows viral infection of blue-green algae in the ocean stimulates productivity in the ecosystem and contributes to a rich band of oxygen in the water.
-
 News
NewsHow wheat protects itself from fungi
Researchers have conducted in-depth studies to establish how the powdery mildew fungus is able to infect wheat despite the presence of resistance genes. The researchers discovered a previously unknown interplay between resistance factors in wheat and disease factors in powdery mildew.
