All Research News articles – Page 11
-
 News
NewsBeing infected or vaccinated first influences COVID-19 immunity
A new study analysing the immune response to COVID-19 sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? According to the results, the order of the events does alter the outcome.
-
 News
NewsFungal denitrification dominates soil N2O emissions after vegetation restoration in the Karst region
A new study demonstrates that soil fungal nirK-derived N2O in the karst region are significantly distinct between cropland and forest, soil NO3‒-N and sand are important drivers of the soil N2O emissions variation, especially after vegetation restoration.
-
 News
NewsScientists identify potential therapy and diagnostic markers for cerebral malaria
Researchers examined whether methylene blue could mitigate brain injury during severe malaria, and whether a practical set of blood biomarkers could help clinicians identify cerebral malaria early and track how patients respond to treatment.
-
 News
NewsAntibiotic resistance is ancient, ecological, and deeply connected to human activity, new review shows
Antibiotic resistance genes are often portrayed as a modern medical problem driven by the overuse of antibiotics in hospitals and farms. A new comprehensive review published in Biocontaminant reveals a much deeper and more complex story. Antibiotic resistance is an ancient feature of microbial life, shaped by millions of years ...
-
 News
NewsCytomegalovirus breakthrough could lead to new treatments
Researchers have developed a new type of antibody with a modified structure that can outsmart cytomegalovirus and neutralize its ability to evade the immune system.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how ocean’s most abundant bacteria diversify
New research has found that SAR11 marine bacteria are not a single, uniform population as often thought. Instead, they are organized into stable, ecologically distinct groups, essentially specialized “teams” adapted to specific environments, such as the coast versus the open ocean.
-
 News
NewsThe COVID-19 virus manipulates host cell RNA to shut down the immune system
Researchers have discovered that SARS-CoV-2 uses a sophisticated tactic to evade the human body’s defense system. In addition to evading the immune system before invading the host cell, SARS-CoV-2 manipulates the host cell’s genetic material in a way never before seen in other pathogens.
-
 News
NewsProtists revealed as key players in soil carbon storage: Dual role uncovered in long-term study
A groundbreaking 27-year field study reveals that how soil protists differentially control fungal and bacterial necromass accumulation—a key process governing SOC storage.
-
 News
NewsFeeding plant remnants to fungi produces tasty protein to fortify vegan, vegetarian diets
Researchers fed the side streams of carrot production to fungi, generating a sustainable source of protein. They incorporated the new protein into proof-of-concept vegan patties and sausages that testers ranked as tastier than food made from plant-based proteins.
-
 News
NewsReal-world data gives Africa a smarter path to fighting HIV and TB
African biostatisticians have offered a powerful, data-driven alternative that can accurately inform HIV policy, reduce healthcare costs, and save more lives.
-
 News
NewsAn enzyme neutralizes pathogens by cleaving a bacterial toxin
Researchers have discovered an enzyme that neutralizes the virulence factor malleicyprol in the bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei, considered one of the most dangerous bacterial pathogens in the tropics.
-
 News
NewsThe antibiotic delafloxacin emerges as a potential therapeutic alternative against Legionella
A study shows, in an experimental laboratory model, that delafloxacin inhibits the intracellular replication of Legionella more effectively than one of the current standard treatments.
-
 News
NewsA coral reef’s daily pulse reshapes microbes in surrounding waters
A new study shows that coral reefs don’t just provide a home for ocean life, they also help set the daily “schedule” for tiny microbes living in the water nearby. Over the course of a single day, the quantity and types of microbes present can shift dramatically.
-
 News
NewsProbiotics can restore gut microbiome in breastfed infants
A new study has found that supplementing exclusively breastfed infants with a probiotic, Bifidobacterium infantis EVC001, between 2 and 4 months of age can successfully restore beneficial bacteria in their gut.
-
 News
NewsYour genes may influence gut microbiome of others, rat study shows
New research, carried out by studying more than four thousand animals, reveals that the composition of the rat gut microbiome is shaped not only by an individual’s own genes but also by the genes of the individuals they share a living space with.
-
 News
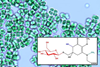
NewsA new natural sunscreen: novel compound discovered from thermophilic cyanobacteria
Natural sunscreens shield the skin from harmful radiation, without triggering allergic reactions. Researchers have discovered a novel compound, β-glucose-bound hydroxy mycosporine-sarcosine, which is produced in thermal cyanobacteria under UV-A/UV-B and salt stress.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how excess hydrogen triggers metabolic shifts and viral defense in syngas microbiomes
Syngas biomethanation—converting CO/CO₂/H₂ into renewable methane—relies on coordinated microbial interactions. A study reveals that excess hydrogen disrupts this balance, reducing methanogenesis efficiency and triggering major shifts in microbial metabolism and viral dynamics.
-
 News
NewsRare earth elements: of peptides and the origins of life
Elements from the group of rare earth metals are of great importance today, also in technical applications. Researchers have published two new studies - one examining peptides, which can bind these elements, while the other highlights the potential role of the elements in the origins of life.
-
 News
NewsMicroalgal–Bacterial granules show resilience to estrogen pollution but face structural collapse at high contamination levels
A study reveals both the adaptive biodegradation potential and the vulnerability of MBGS under estrogenic stress, offering new insights for developing robust, biologically based wastewater treatment technologies.
-
 News
NewsEnvironmental traces of antibiotics found to boost gene transfer among bacteria
Using models of vertical inheritance and horizontal transfer, researchers have found that low doses of tetracycline, ampicillin, kanamycin, and streptomycin stabilize resistance and promote gene transfer across species.
