Escalating antimicrobial resistance is a global threat, emphasizing the need to explore alternative treatment options.
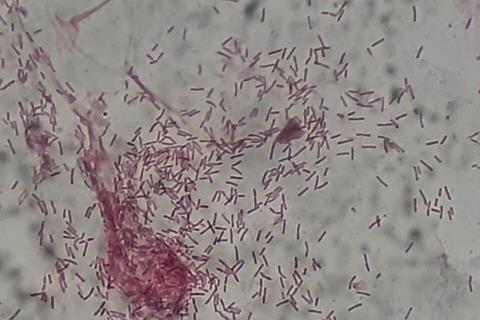
Hence, a team of scientists in Pakistan aimed to explore the in-vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam (CAZ-AVI) in clinical isolates of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria.
READ MORE: Genomic surveillance studies reveal circulation of multidrug-resistant Enterobacterales in Europe
READ MORE: Breaking down bacterial barriers using bovine gut enzyme
This was an observational, cross-sectional study conducted at the Microbiology Department of Indus Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan, from January 2023 to October 2024. Carbapenem-resistant gram-negative rods isolated from clinical specimens received from the outpatient, emergency, and inpatient departments were included.
Consecutive, non-probability sampling was employed for the collection of isolates. Identification of the organisms was confirmed using API® ID strips, and antimicrobial susceptibility for carbapenems and CAZ-AVI was determined via the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method.
The findings
A total of 158 bacterial isolates were characterized as carbapenem-resistant. Of these, 92 (58%) were Enterobacterales, and 66 (42%) were Pseudomonas aeruginosa. CAZ-AVI was susceptible in 17 (11%) of the isolates, of which four (24%) were Klebsiella spp. and Escherichia coli each, and nine (52%) were P. aeruginosa.
CAZ-AVI-susceptible strains were predominant among patients aged 26–50 years (n = 6; 35%), most of whom were females (n = 10; 59%) and inpatients (n = 8; 47%). Clinical samples from patients with urinary tract infections grew the most CAZ-AVI-susceptible strains (n = 9; 53%).
The study demonstrated low CAZ-AVI susceptibility in the carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacterial strains. Understanding regional antimicrobial patterns in multidrug-resistant bacteria is crucial for the effective use of CAZ-AVI, along with the strict implementation of strategies for controlling antimicrobial resistance.
The study was recently published in the Journal of Exploratory Research in Pharmacology.





No comments yet