All UK & Rest of Europe articles – Page 51
-
 News
NewsA single cell’s siesta
Researchers show how non-moving single-celled organisms manage to avoid bright light.
-
 News
NewsGlobal antibiotic consumption has increased by more than 21 percent since 2016
An analysis of antibiotic sales data from 67 countries from 2016-2023 shows a decrease in consumption in high-income countries countered by an increase in middle-income countries.
-
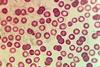 News
NewsScientists uncover structure of hemezoin crystals crafted by malaria parasite
A new study reveals in unprecedented detail the structure of crystals that the malaria parasite builds in order to survive. The new findings could lead to improved antimalarial medications.
-
 News
NewsReducing antimicrobial resistance: accelerated efforts are needed to meet the EU targets
Marking European Antibiotic Awareness Day on 18 November and the start of World Antimicrobial Resistance Awareness Week, ECDC presents new data on antimicrobial consumption and resistance.
-
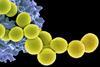 News
NewsAntibacterial material restores the efficacy of antibiotics against resistant bacteria
Research shows that resistant bacteria can regain susceptibility to antibiotics when the treatment is combined with a material equipped with antibacterial peptides.
-
 News
NewsFunding boost to bring engineering biology technologies to market
Part of a £2.8 million UKRI seed corn fund has been awarded to the Environmental Biotechnology Innovation Centre (EBIC) to bridge the gap between research and market-ready products and technologies, with comprehensive support and resources for researchers.
-
 News
NewsStudy uncovers first evidence of resistance to standard malaria treatment in African children with severe malaria
Researchers have uncovered evidence of partial resistance to artemisinin derivatives — the primary treatment for malaria — in young children with severe, or ’complicated’ malaria.
-
 News
NewsA new technology to isolate immunostimulatory members of the human gut microbiota
Scientists have developed a new technology to isolate a specific subset of gut bacteria that are recognized by IgA antibodies. These ‘IgA-coated’ bacteria are associated with an array of diseases and this proposed new technology has the potential to uncover the mechanisms behind these correlations.
-
 Careers
CareersHow the PATH-SAFE programme has driven forward our understanding of AMR in UK animals
Tamsin Dewé, Anju Kirby and Rachel Baird explain how the UK’s PATH-SAFE programme has filled evidence gaps relating to AMR in animals and furthered our understanding of AMR transmission pathways within agri-food systems.
-
 News
NewsHow do microbiomes influence the study of life?
Researchers from the awardwinning One Health Microbiome Center reveal how holobiont biology underpins a holistic understanding of how life’s forms and functions, from human disease to agricultural output, depend upon the relationships between microbes and hosts.
-
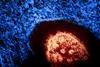 News
NewsMeasles cases surge worldwide, infecting 10.3 million people in 2023
Worldwide, there were an estimated 10.3 million cases of measles in 2023, a 20% increase from 2022, inadequate immunization coverage globally is driving the surge in cases.
-
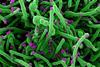 News
NewsNew therapeutic approach for severe COVID-19
A new clinical study shows that an inhibitor of Fas ligand, also called CD95 ligand, led to a faster recovery of COVID-19 patients and reduced mortality.
-
 News
NewsNew technique reveals the living microbes in Earth’s driest desert
An international team of researchers describes a new way to separate extracellular from intracellular genetic material, providing better insights into microbial life in low-biomass environments such as the Atacama Desert.
-
 News
NewsClimate change threatens key ocean plankton groups
Planktonic foraminifera species may face unprecedented environmental conditions by the end of this century, potentially surpassing their survival thresholds, with extinctions impacting marine ecosystems and the ocean’s carbon storage capacity.
-
 News
NewsChildren’s gut bacteria - and a superfood grain - may hold the key to diarrhea treatment
Diarrhea claims the lives of 500,000 children a year in low- and middle-income countries. Now researchers have linked chronic diarrhea to a specific pattern of gut bacteria, a discovery that could pave the way for new treatments.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal significant burden of liver cancer attributable to hepatitis B and alcohol globally
A new study analyzes and compares the epidemiological trends of liver cancer attributed to hepatitis B (LCHB) and alcohol use (LCAL) over the past 32 years.
-
 News
NewsWe may be overestimating the association between gut bacteria and disease, study finds
Many bacterial-linked illnesses, such as inflammatory bowel disease or colorectal cancer, are associated with an overgrowth of gut bacteria thought to be bad actors. But when researchers used a machine learning algorithm to predict the density of microbes—called microbial load, from their gut microbiomes, they found that changes in microbial ...
-
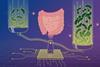 News
NewsMicrobial load can influence disease associations, new model reveals
Scientists have developed a new machine-learning model to predict microbial load — the density of microbes in our guts — and used it to demonstrate how microbial load plays an important role in disease-microbiome associations.
-
 News
NewsGlobal researchers unite their expertise to boost infectious diseases research across the Asia-Pacific region
Singapore’s Agency for Science, Technology and Research Infectious Diseases Labs and France’s Institut Pasteur have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to address the urgent health threats posed by the rise of tropical infectious diseases in the Asia-Pacific region.
-
 News
NewsScientists exploit shape change to reveal how immune cells sniff out pathogens
Researchers are using an innovative method to watch immune receptors go about their business, based on the fact that cells tend to change their form when they come into contact with a signal molecule.
