All Microbial Genomics articles
-
 News
NewsGolden Gate method enables rapid, fully-synthetic engineering of therapeutically relevant bacteriophages
Researchers have described the first fully synthetic bacteriophage engineering system for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In this method, researchers engineer bacteriophages synthetically using sequence data rather than bacteriophage isolates.
-
 News
NewsEarly intervention of cyanobacterial risks starting from the genome?
A new study proposes using “~3 Mbp” as a threshold to establish a genome size-oriented proxy indicator for cyanobacterial risk early warning.
-
 News
NewsResearch reveals hidden diversity of E. coli driving diabetic foot infections
New research has shed light on the diversity and characteristics of E. coli strains that drive diabetic foot infections, providing the first comprehensive genomic characterisation of E. coli strains isolated directly from diabetic foot ulcers across multiple continents.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals evolutionary and domestication history of button mushroom
A large-scale population genomic study has shed new light on the evolutionary and domestication history of the button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus), one of the most widely cultivated edible fungi in the world.
-
 News
NewsScience army mobilizes to map US soil microbiome
A small army of researchers are working to catalog the vast and largely unknown soil microbiome of the United States. The project, one of the biggest microbiome studies ever attempted, has already resulted in the discovery of more than 1,000 new strains of bacteria and never-before-seen microbes.
-
 News
NewsAsia PGI and partners unveil preview of PathGen: New AI-powered outbreak intelligence tool
Asia Pathogen Genomics Initiative (Asia PGI) has offered the first public preview of PathGen, an AI-powered sense-making and decision-making support platform of pathogen genomics and contextual data.
-
 News
NewsA new gateway to global antimicrobial resistance data
To support global AMR research, EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) has launched the AMR portal, a central hub that connects bacterial genomes, resistance phenotypes, and functional annotations, all in one place. The AMR portal ensures long-term availability, standardisation, and reusability of AMR data.
-
 News
NewsAncient viral DNA shapes modern human placentas
Researchers have uncovered how ancient viral DNA controls a gene linked to placenta development and pre-eclampsia, a life-threatening pregnancy disorder. The research could help identify pre-eclampsia risk much earlier.
-
 News
NewsCHIKVdb: A comprehensive genomic resource for chikungunya virus surveillance and outbreak response
Scientists have developed the Chikungunya Virus Database (CHIKVdb), a comprehensive genomic resource. CHIKVdb integrates 8,193 nucleotide sequences and 10,637 protein sequences from five major host categories across 99 countries, spanning 40 years.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal functional RNA splitting mechanism behind origin of Type V CRISPR systems
Researchers have uncovered the molecular innovation that led to the origin of Type V CRISPR-Cas immune systems. Their findings show that the functional splitting of transposon-derived RNAs was the critical innovation driving the emergence of Type V CRISPR-Cas immunity.
-
 News
NewsResearchers find a more precise way to edit the genome
A genome-editing technique known as prime editing holds potential for treating many diseases. However, the process carries a small chance of inserting errors that could be harmful - but researchers have now found a way to dramatically lower the error rate.
-
 News
NewsHow HIV enters the genome – researchers identify previously unknown mechanism
Researchers have decoded a previously unknown mechanism by which HIV-1 selects its integration targets in the human genome. A research team identified RNA:DNA hybrids (R-loops) as molecular signposts for the virus.
-
 News
NewsMethod probing dark matter uncovers hundreds of new bacteria, and two potential antibiotics
A new approach to exploring untapped soil resources circumvents the need to grow bacteria in the lab by extracting very large DNA fragments directly from soil to piece together the genomes of previously hidden microbes, and then mines resulting genomes for bioactive molecules.
-
 News
NewsHow plants rot: New method decodes hidden decomposers of wood and leaves
Researchers have developed a new method to identify the molecular tools that different species use to decompose dead plant material. Their analysis of over 18,000 species found that some invertebrates also evidently have a whole range of such tools at their disposal.
-
 News
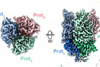
NewsAncient viruses in human genomes offer new avenue for stopping cancers, autoimmune diseases, and more
Researchers have revealed the first three-dimensional structure of a protein from an ancient human endogenous retrovirus (HERV) found within the human genome.
-
 News
NewsNew genomic study reveals key drivers of strangles transmission in UK horses
A novel study has revealed new insights into how the highly contagious disease strangles spreads amongst horses in the UK. It marks a significant step forward in understanding how to more effectively manage and prevent outbreaks of this devastating equine disease.
-
 News
NewsAlign announces new collaboration with ATCC to bring AI-ready microbial datasets to life
The Align Foundation has announced a collaboration with ATCC to create the world’s largest public, AI-ready microbial phenotyping dataset.
-
 News
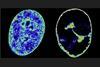
NewsHerpes virus plays interior designer with human DNA
Researchers have discovered the cold sore virus reshapes the human genome’s architecture, rearranging its shape in three-dimensional space so that HSV-1 can access host genes most useful for its ability to reproduce.
-
 Features
FeaturesGenome sleuths: using DNA to trace the evolution of animal-to-human pathogens
Zoonotic spillovers have become a significant focus of global health, with outbreaks like SARS and COVID-19 underscoring how quickly these events can escalate into worldwide crises. Genomics is crucial in tracing the origins and predicting the emergence of zoonotic threats.
-
 News
News Ribosome profiling identifies thousands of new viral protein-coding sequences
With the help of a technique called Massively Parallel Ribosome Profiling (MPRP), scientists have identified more than 4000 open reading frames (ORFs) across 679 human-associated viral genomes.
