More UK & Europe News – Page 96
-
 News
NewsElectrons and microbes are key to bio-based nylon process
Researchers have developed a process that can produce adipic acid, one of two building blocks of nylon, from phenol through electrochemical synthesis and the use of microorganisms.
-
 News
NewsGene expression in apicoplast could be target for malaria treatment
Gene expression within the apicoplast, an organelle in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum is regulated by melatonin in host blood, and intrinsic parasite cues, via a factor called ApSigma, a recent study reveals.
-
 News
NewsFrequent use of antibiotics linked to severe Covid outcomes
Frequent and diverse use of antibiotics may be associated with developing more severe outcomes after a COVID-19 infection, including death, a new study has shown.
-
 News
NewsNew bacterial blueprint will help fight antibiotic resistance
Scientists have gained high-res structural insights into a key bacterial enzyme, which may help chemists design new drugs to inhibit it and thus suppress disease-causing bacteria.
-
 News
NewsAlarming antibiotic resistance discovered in war-torn Ukraine
Microbiologists investigating bacterial resistance among the war-wounded Ukrainian patients treated in hospitals have warned that the entire European region is under threat after finding that many were affected by bacteria that exhibited an extremely high level of antibiotic resistance.
-
 News
NewsNew enzyme designed using Antarctic bacteria and computer calculations
For the first time, researchers have succeeded in predicting how to change the optimum temperature of an enzyme using large computer calculations and based on a cold-adapted enzyme from an Antarctic bacterium.
-
 News
NewsFuture medicines could feature ingredients targeting bacterial motility and chemotaxis
Future medicines will probably be made up of a cocktail of compounds that inhibit different bacterial targets, including some that act against their motility and chemotaxis mechanisms, a new review suggests.
-
 News
NewsCyanotriazole compounds can rapidly cure trypanosome infections in mice
Scientists have identified a class of cyanotriazoles (CTs), which exhibit potent trypanocidal activity and lead to rapid clearance of parasites both in vitro and in mouse models of Chagas disease and human African trypanosomiasis.
-
 News
NewsFlaws in COVID-19 weather studies spark call for improved publishing practices
Research that linked the weather with the spread of COVID-19 during the pandemic was inaccurate and poorly scrutinised by fellow scientists, suggests a new study.
-
 News
NewsD-amino acids play role in cholera bacterium’s bid to escape
Cholera bacteria use specific D-amino acids to escape unfavourable niches and form complex ecological systems, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsWarning as third of toddlers found to have unmet vaccination needs
A third of under-fives attending a Paediatric Emergency Department (PED) and who are eligible for pre-school boosters have unmet vaccination need according to new research.
-
 News
NewsStreptomycetes reveal their arsenal of signalling compounds
Streptomyces bacteria produce a group of signalling molecules that trigger a variety of processes, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsSmall ruminant farms could spread human diarrhoea causing bug
Goat and sheep dairy farms are a potential transmission source for a bacteria that can cause human gastroenteritis, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsStudy unveils gene expression of photosynthetic symbiont in marine diatom
A new study explores the genetic expression of a photosynthetic symbiont that lives inside an abundant marine organism.
-
 News
NewsMonitoring bats can help ID coronaviruses with pathogen potential
Researchers who found novel coronaviruses in UK bats say genetic surveys of the viruses should be regularly conducted, even if none of those viruses can infect humans yet.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how Captain Cook microbe forms clumps
Researchers have described for the first time how the marine microorganism Trichodesmium filaments form aggregates through a simple yet exquisitely effective behavioural strategy.
-
 News
NewsGlobal warming accelerates CO2 emissions from soil microbes
Emissions of CO2 by soil microbes into the Earth’s atmosphere are not only expected to increase but also accelerate on a global scale by the end of this century, a new study suggests.
-
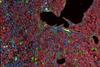 News
NewsEngineered lung cells light up when Covid sparks immune response
Scientists have engineered lab-grown lung epithelial cells to light up red in colour once they launch an immune response, creating a tool that can be used to screen for drugs that can help treat COVID-19 and other emerging infections.
-
 News
NewsHorseradish roots switched out for biolab-made enzyme
Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in the production of important enzymes that were previously extracted from horseradish roots, but now can be produced recombinantly in the laboratory.
-
 News
NewsSolving by-product problem paves way for bacterium to produce chemicals
An engineering technique that domesticates Vibrio natriegens to overcome the production of an unwanted by-product could pave the way for the bacterium to become a producer of chemicals, researchers have found.
