The identification of non-tuberculosis (TB) mycobacterial (NTM) infection remains a significant challenge. This study, published in Journal of Thoracic Disease, aims to investigate the diagnostic value of multicolour nested real-time fluorescence quantitative nucleic acid amplification detection technology [Xpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB)/rifampicin (RIF)] in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) acid-fast smear-positive cases.
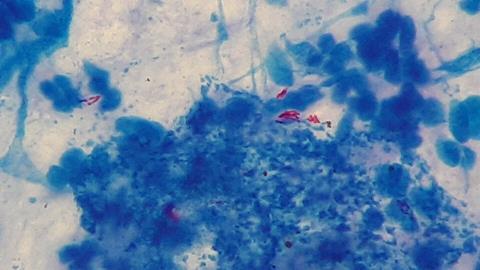
Between 1 January 2017 and 30 June 2022, 365 patients who underwent fibreoptic bronchoscopy and had positive acid-fast smears of BALF were examined using Xpert MTB/RIF.
READ MORE: The growing threat of nontuberculous mycobacteria infections
READ MORE: New enzymatic cocktail can kill tuberculosis-causing mycobacteria
The mycobacteria growth indicator tube (MGIT) 960 was used for rapid sputum culture and traditional drug sensitivity testing. Combined with mycobacterial culture and drug sensitivity results, Xpert results of alveolar lavage fluid were analysed to guide diagnosis and treatment.
The sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of Xpert detection for diagnosing NTM lung disease in acid-fast smear-positive cases were 100% (45/45), 99.68% (310/311), 97.83% (45/46) and 100% (310/310), respectively.
Xpert MTB/RIF in alveolar lavage fluid can not only detect RIF resistance but also distinguish pulmonary TB from NTM pulmonary disease in patients with positive acid-fast smears.
Highlights
Key findings
• Xpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampicin (Xpert MTB/RIF) in alveolar lavage fluid can not only detect rifampicin resistance but also distinguish pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) from non-tuberculosis mycobacterial (NTM) pulmonary disease in patients with positive acid-fast smears.
What is known and what is new?
• GeneXpert MTB/RIF for rapid diagnosis of TB and rifampicin resistance.
• Xpert MTB/RIF in alveolar lavage fluid can not only detect rifampicin resistance but also distinguish pulmonary TB from NTM pulmonary disease in patients with positive acid-fast smears.
What is the implication, and what should change now?
• The GeneXpert MTB/RIF technology can be extended to the diagnosis of tuberculosis and can be combined with other NTB diagnostic methods.





No comments yet