All Veterinary Medicine & Zoonoses articles – Page 7
-
 News
NewsWorld-first koala chlamydia vaccine approved
In a world first, a vaccine has been approved to protect Australia’s endangered koalas from infection and death caused by chlamydia.
-
 News
NewsNovel Bocaparvovirus identified in goats in China
Researchers identified a novel Bocaparvovirus in goat fecal samples using metagenomic techniques, with detection in goats from 3 regions in China: Sichuan, Hunan and Chongqing.
-
 News
NewsWarming climate drives disease surge, study shows
Projections suggest future warming could raise dengue incidence by 49%–76%, depending on emissions scenarios, if other factors remain constant. Cooler areas are expected to see the biggest increases, while hotter locations may experience slight declines.
-
 News
NewsGray seals perplex scientists with lack of response to flu infection
Something strange happens when two kinds of seals living in the waters around Cape Cod get infected with influenza – harbor seals get sick but gray seals don’t. This perplexing phenomenon led scientists to investigate if a difference in a piece of the immune system called cytokines could be responsible for this difference.
-
 News
NewsInfectious disease modelling teams invited to strengthen global response to highly pathogenic avian influenza
An international modelling challenge is calling on experts across disciplines to help tackle one of Europe’s most pressing health threats: highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI). The initiative, which is now open for applications, seeks to improve outbreak modelling readiness and to foster international collaboration among researchers and decision makers.
-
 News
NewsDeadly infectious bone disease wiped out long-necked dinosaurs in Brazil
Researchers found sauropod bones with signs of osteomyelitis, an infectious disease that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or protozoa and that killed the animals quickly. The discovery suggests that favorable conditions for the disease existed.
-
 News
NewsNew bacterium discovered in the Amazon is closely related to Andean species that causes human bartonellosis
A new species of bacteria of the genus Bartonella has been found in the Amazon National Park in the state of Pará, Brazil, in phlebotomine insects, also known as sand flies. Its DNA is similar to that of two other Andean species of bacteria.
-
 News
NewsKiss goodbye to deadly disease – new research finds ‘Pac-Man’ antibodies for killer parasite
Researchers have successfully produced antibodies that kill the parasite carried by the ‘kissing bug’ that causes the potentially deadly Chagas disease. The research is a vital step towards the development of the first effective vaccine.
-
 Opinion
OpinionSafety and nutritional claims for raw milk
Robert F Kennedy Jr. famously advocates drinking raw milk and promotes its benefits. But how safe is unpasteurised milk? Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue, who sit on Applied Microbiology International’s Food Security Scientific Advisory Group, take a deep dive into the science.
-
 News
NewsBacteria strains infecting cattle and humans in US are highly similar
Salmonella Dublin, a type of bacteria that primarily infects cattle but some strains also can adapt to infect humans, is increasingly becoming resistant to antibiotics, making it a growing public health threat.
-
 News
NewsNew African swine fever vaccine candidate shows promise against some virus strains
An international team of scientists has found that a promising African swine fever (ASF) vaccine can protect pigs against some strains of the virus but offers little or no protection against others.
-
 News
NewsFlu fighters: researchers take a closer look at immune response to influenza
Researchers sought to identify which immune cells in pigs have receptors that are most reactive to influenza. They accomplished this by customizing a technology called single-cell RNA sequencing for pigs to learn more about how a body’s cells operate at a highly detailed level.
-
 News
NewsBee and frog proteins: nature’s double defense against farm superbugs
A new study reveals that combining natural antimicrobial peptides can significantly slow the development of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Using two peptides together prevents harmful bacteria from mutating as quickly, offering a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsScientists trace the evolution of the H5N1 virus
Researchers have discovered that the currently circulating 2.3.4.4b clade of H5N1 has specific mutations in its genome that increase its human adaptive potential.
-
 News
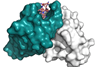
NewsMalaria vaccine mimics natural immunity with high precision
A detailed analysis reveals one of the reasons why the R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine works so well: the antibodies generated following vaccination are indistinguishable from those found in people who have been infected by the parasites.
-
 News
NewsChemical trick could turn losing malaria drug into a winner
A new generation of malaria drugs failed clinical trials, in part because they were hard to swallow. Chemists have remodeled their structures to make them more soluble, while maintaining their effectiveness against drug-resistant parasites.
-
 News
News4,000-year-old sheep reveals that livestock played a role in prehistoric plague infections
An ancient Yersinia pestis genome recovered from sheep sheds new light on a mysterious infectious disease that plagued prehistoric Eurasia for over 2000 years.
-
 News
NewsKenya achieves elimination of human African trypanosomiasis as a public health problem
The World Health Organization (WHO) has validated Kenya as having eliminated human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) or sleeping sickness as a public health problem, making it the tenth country to reach this important milestone.
-
 News
NewsNew network to address malaria among school-aged children in sub-Saharan Africa
A new network aims to improve malaria prevention among school-aged children in sub-Saharan Africa. The new partnership will unite researchers, policymakers, healthcare practitioners and other stakeholders across multiple countries to better understand and address the burden of malaria in children.
-
 News
NewsThe microbiome of the indri, a critically endangered lemur, has been described
An international study has ascertained the composition of the intestinal microbiome of the indri, a critically endangered lemur in Madagascar. It has found up to 47 unknown species of bacteria, and revealed the indri’s microbiome is transmitted within their social group.
