All Bacteria articles – Page 14
-
 News
NewsTraces of bacteria inside brain tumors may affect tumor behavior
Scientists have uncovered unexpected traces of bacteria within brain tumors. This discovery offers new insights into the environment in which brain tumors grow and sets the stage for future studies seeking to improve treatment outcomes.
-
 News
NewsNext-generation microbiome medicine may revolutionize the treatment of Parkinson’s and similar disorders
Scientists have engineered the probiotic bacterium Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 as a drug-delivery system that continuously produces and delivers the gold-standard Parkinson’s drug Levodopa, which is converted to dopamine in the brain. E. coli Nissle strain was chosen for its century-long record of safely treating gastrointestinal disorders in humans.
-
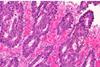 News
NewsNew bioelectroceutical platform triggers dual cell death, reverses immunosuppression in colorectal cancer
Scientists have developed a new “microbial fuel cell” platform that integrates electrogenic bacteria with piezoelectric nanoparticles to cooperatively eradicate colorectal tumors, reverse immunosuppression, and remodel the gut microbiome.
-
 News
NewsBacterial scents behind oak tree decline may be luring deadly beetles
The deadly decline of Britain’s native oak trees may be driven by an unexpected accomplice: their own smell. Scientists have discovered that trees affected by Acute Oak Decline (AOD) emit distinct odours that are highly attractive to the beetle Agrilus biguttatus, a key contributor to the decline.
-
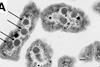 News
NewsNew blueprint for nature’s carbon-capturing nanomachines revealed
Researchers have uncovered how bacterial organelles assemble, opening new routes for bioengineering and climate innovation. The team has unveiled the most detailed picture yet of how bacteria construct microscopic compartments known as carboxysomes – natural nanomachines that play a vital role in capturing and converting carbon dioxide (CO₂).
-
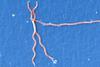 News
NewsNew test could allow for more accurate Lyme disease diagnosis
Researchers have developed a new way to detect the Lyme disease bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, allowing for faster and more accurate diagnosis.
-
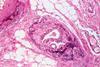 News
NewsNew DNA analysis approach could transform understanding of disease evolution
By adapting techniques originally used to study ancient DNA from archaeological specimens, researchers were able to recover genetic information from nearly century-old medical samples.
-
 News
NewsManganese is Lyme disease bacterium’s double-edged sword
For decades, Lyme disease has frustrated both physicians and patients alike. Caused by the corkscrew-shaped bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the infection, if left untreated, can linger for months, leading to fever, fatigue and painful inflammation. Source: U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention This digitally colorized scanning electron microscopic ...
-
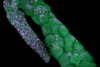 News
NewsImaging reveals bacterial symbionts in the ovaries of tiny, aquatic crustaceans
Researchers have imaged a heritable form of bacterial symbiosis inside the reproductive system of tiny crustaceans known as ostracods. Bacteria from the genus Cardinium live inside the egg cells and tissues of ostracod ovaries, transmitted from mothers to offspring.
-
 News
NewsScientists find way to find the gut microbiome into a longevity factory
A team of researchers has found a way to turn the bacteria living in the digestive tracts of animals into factories that can produce compounds that promote longevity in their hosts—showing a potential new drug development strategy.
-
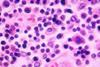 News
NewsTyphoid conjugate vaccine demonstrates strong safety and immunogenicity: Results from Phase 3 study
PATH and EuBiologics Co., LTD have announced Phase 3 results from a clinical trial of a typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV), EuTYPH-C Inj.® Multi-dose. EuTYPH-C Inj.® Source: CDC/ Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Charles N. Farmer This photomicrograph reveals some of the histopathology exhibited in a lymph node tissue ...
-
 Careers
CareersSummer studentship: Jonas investigates how metals influence bacterial ecosystems
Jonas Flohr from Portsmouth reports back on his AMI-sponsored summer studentship at Durham University investigating how metals influence bacterial ecosystems.
-
 News
NewsStudy finds high rates of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in raw milk
Raw cow and sheep milk is frequently contaminated with antibiotic-resistant bacteria that could pose a threat to human and animal health, reports a new study.
-
 News
NewsBacteria spin and dye rainbow-colored, sustainable textiles
Researchers demonstrate that bacteria can both create fabric and dye it in every color of the rainbow—all in one pot. The approach offers a sustainable alternative to the chemical-heavy practices used in today’s textile industry.
-
 News
NewsBacterial spores offer promise of sustainable smart materials
By embedding Bacillus spores within engineered living materials, researchers have created living materials that not only endure harsh environments but can also be programmed to perform specific tasks. These materials may be a sustainable replacement for fossil-based materials.
-
 News
NewsEgypt becomes the seventh country in the Eastern Mediterranean Region to eliminate trachoma as a public health problem
The World Health Organization (WHO) today announced that Egypt has successfully eliminated trachoma as a public health problem, marking a historic public health milestone for the country and WHO’s Eastern Mediterranean Region (WHO EMR).
-
 News
NewsRepurposed antibiotic shows promise against Central Nervous System Tuberculosis
Researchers at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), have demonstrated that doxycycline, a commonly available and inexpensive antibiotic, can improve survival rates and neurological outcomes in Central Nervous System Tuberculosis (CNS-TB) in a preclinical non-human study. Published in the Journal of Neuroinflammation, the ...
-
 News
NewsBlood-based immunological signatures for extrapulmonary tuberculosis decoded
Scientists have deciphered the immunological properties of extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) in the blood of affected patients. The results may help to develop new targeted treatments and tests for this important disease.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how cyanobacteria use ’sunscreen’ to adapt to climate
Using single particle spectroscopy, researchers revealed insights into how different types of photosynthetic bacteria can use a shared mechanism to protect themselves from too much sunlight.
-
 News
NewsHow life first got moving: nature’s motor from billions of years ago
Research has cast light on the evolutionary origins of one of nature’s first motors, which developed 3.5 billion to 4 billion years ago to propel bacteria. Scientists have created the most comprehensive picture yet of the evolution of bacterial stators.
