All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 276
-
 News
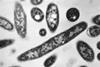
NewsRespiratory tract microbiome influences the severity of bacterial pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection of the lung alveoli caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. It is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, representing a clinical and economic burden and a global public health problem. Source: CDC/ Dr. Francis Chandler Transmission electron microscopic (TEM) image ...
-
 News
NewsMore people develop sepsis than we thought — but more survive
The observed increase in cases is largely due to more people developing sepsis repeatedly, rather than dying the first time they contract it, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsUltrathin nanotech promises to help tackle antibiotic resistance
Researchers have invented a nano-thin superbug-slaying material that could one day be integrated into wound dressings and implants to prevent or heal bacterial infections.
-
 Careers
CareersThe lure of microbes: Getting to know some of the new junior editors at Letters in Applied Microbiology
Applied Microbiology International has just appointed 14 junior editors to its flagship journal Letters in Applied Microbiology (LAM) - so we got to know some of the new crew.
-
 News
NewsSurveillance system detected infection linked to eye drops months before outbreak declared
An infectious diseases surveillance system successfully flagged cases of a drug-resistant infection spread by eye drops months before national public health officials announced an outbreak.
-
 News
NewsRapid acting oral vaccines are on the way
Researchers studying SARS-CoV-2 may have developed new methods to administer vaccines orally, which would be both easier to administer and more effective at combatting illnesses.
-
 News
NewsStudy of bacteria in day care settings reveals links with children’s lung health
Particular combinations of bacteria found in dust at day care facilities have been linked to wheezing in young children in a study presented at the European Respiratory Society International Congress in Milan, Italy.
-
 News
News‘Regular testing needed’ following massive blue green algal bloom in UK’s largest lake
Water in the UK’s largest freshwater lake needs to undergo routine testing for cyanobacteria species in the future, following a devastating bloom, scientists have warned. Parts of Lough Neagh, which supplies around 40% of Northern Ireland’s drinking water, have been mired in thick green sludge following a massive bloom over ...
-
 News
NewsTwo autopsies reveal secrets of HIV reservoirs
A research team shows for the first time that HIV reservoirs are concentrated in the spleen and lymph nodes, and that they can travel throughout the body.
-
 News
NewsTetrazolium salt tech speeds up bacterial testing in food
Scientists have developed a technology that can rapidly and accurately determine the number of viable bacteria in food products electrochemically, using tetrazolium salt (MTT), a water-soluble molecule.
-
 News
NewsClimate change can alter the risk of succumbing to infectious diseases
A new Europe-wide study has found that he prevalence of potentially pathogenic protozoans, bacteria and viruses in birds and bats is associated with temperature or rainfall.
-
 News
NewsSelf-decontaminating fabric burns out viruses but is safe for skin
A new material that packs deadly heat for viruses on its outer surface while staying cool on the reverse side could transform the way we make and use personal protective equipment (PPE).
-
 News
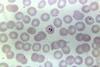
NewsMalaria parasites resistant to treatment and detection emerge in Ethiopia
Genomic surveillance by scientists has revealed mutations in malaria-causing parasites that will complicate efforts to eradicate the disease in Africa.
-
 News
NewsOptical device kills pathogens on surfaces
Researchers at Osaka University have created a new optical device that can be used to kill pathogens on surfaces while remaining safe for humans.
-
 News
NewsE coli bacteria engineered to generate electricity from wastewater
Scientists have reported a groundbreaking achievement in bioelectronics, advancing the capabilities of common E. coli bacteria to generate electricity.
-
 News
NewsAI method refines biome labeling for microbial community samples
Researchers have introduced Meta-Sorter, an AI-based method that leverages neural networks and transfer learning to significantly improve biome labeling for thousands of microbiome samples in the MGnify database.
-
 News
NewsNew strains of influenza A virus in pigs potentially pose pandemic risk
A new study addresses gaps in understanding of swine influenza A virus evolution and highlights need for early warning of disease emergence.
-
 Careers
CareersHealthy guts with diverse and mature bacteria linked to less allergy-related wheezing and asthma in early childhood
Babies and young children with more mature communities of bacteria present in their gut are less likely to develop allergy-related wheezing or asthma.
-
 Careers
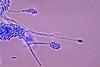
CareersFungi-produced silver nanoparticles could be useful for wound healing
Scientists have synthesized silver nanoparticles using fungi, mainly of the genus Fusarium.
-
 Careers
CareersNew research IDs 28 genetic regions linked to susceptibility and severity of COVID-19
A study identifies 51 significant genome-wide loci associated with both COVID-19 severity and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility, providing valuable information about the disease.
