All Research News articles – Page 30
-
 News
NewsImportant algal phenomenon discovered in the Arctic – could boost marine life
The shrinking sea ice in the Arctic Ocean is, overall, a disaster. But paradoxically, the melting of the ice can also fuel the engine of the Arctic food chains: algae. A new study indicates there will probably be more of it in the future than previously thought.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes at Red Sea vents show how life and geology shape each other
A new study led by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST; Saudi Arabia) Professor Alexandre Rosado has revealed an unusual microbial world in the Hatiba Mons hydrothermal vent fields of the central Red Sea, a site first discovered by one of his co-authors and colleagues, Assistant Professor Froukje ...
-
 News
NewsNew role of gut bacteria provides hope for a novel IBS treatment
Research clarifies the complex interaction between gut bacteria and IBS, identifying two bacteria that together can produce serotonin: Limosilactobacillus mucosae and Ligilactobacillus ruminis.
-
 News
NewsHydrothermal plumes - and microbes - revealed as invisible transport pathways for iron
A new review highlights how hydrothermal vents on the seafloor shape iron availability and influence the global oceanic element cycles.
-
 News
NewsCrop-killing pathogen found to disable plant ‘alarm system’
An international team has discovered that the pathogen Phytophthora infestans - which caused the Irish potato famine - employs special enzymes, called AA7 oxidases, to disable the plants’ early warning system, weakening their defenses before they can respond.
-
 News
NewsNew insights into malaria could reshape treatment
A sodium pump essential to the malaria parasite’s survival, PfATP4, has emerged as one of the most attractive drug targets. A new study presents the first high-resolution 3D structure of PfATP4 and identifies a previously unknown but essential binding partner.
-
 News
NewsUS funding cuts could result in nearly 9 million child tuberculosis cases, 1.5 million child deaths
A new study projects that US funding cuts to global health aid will have a catastrophic effect on pediatric TB, with children in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia likely to experience a spike in preventable cases and deaths over the next decade.
-
 News
NewsMosquito saliva may hold clues to fighting chikungunya inflammation
Scientists have uncovered a surprising mechanism showing how mosquito saliva can alter the human body’s immune response during chikungunya virus (CHIKV) infection - it not only transmits the virus but also influences how the body’s immune system responds.
-
 News
NewsCofactor engineering with phosphite dehydrogenase enables flexible regulation of lactate-based copolymer biosynthesis in E. coli
A new breakthrough enables higher yields of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-lactate) [P(3HB-co-LA)] without disrupting bacterial growth, paving the way for more sustainable bioplastic manufacturing.
-
 News
NewsNovel fungal phyla and classes revealed by eDNA long reads
Via a thorough analysis of the EUKARYOME long-read database, an international team has discovered that a large proportion of unknown eukaryotes uncovered with long-read sequencing belong to deep, hitherto undescribed fungal lineages.
-
 News
NewsExercise counteracts junk food’s depression-like effects through gut-brain metabolic signaling
New research into metabolic pathways demonstrates that voluntary running exercise can mitigate depression-like behaviors induced by high-fat, high-sugar diets associated with both circulating hormones and gut-derived metabolites.
-
 News
News’Footprint of Death’ gives new clues to cell life, spread of disease
Scientists at La Trobe University have discovered a previously unknown way viruses could spread around the body, potentially paving the way for more effective drug development. Source: La Trobe University Dead cells after the self-destruction and fragmentation process. The large green areas are the “eat me” signals ...
-
 News
NewsAre there living microbes on Mars? Check the ice, researchers say
By recreating Mars-like conditions in the lab, researchers demonstrated that fragments of the molecules that make up proteins in E. coli bacteria, if present in Mars’ permafrost and ice caps, could remain intact for over 50 million years.
-
 News
NewsSurprising bacteria discovery links Hawaiʻi’s groundwater to the ocean
A new species of bacteria has been discovered off the coast of Oʻahu, shedding light on how unseen microbial life connects Hawaiʻi’s land and sea ecosystems.
-
 News
NewsDual feeding strategy helps Mediterranean coral thrive in rising sea temperatures
An exceptional “dual feeding” strategy underlies a Mediterranean coral’s resilience to rising sea temperatures, according to a study. The stony coral Oculina patagonica is known to feed itself with or without algae.
-
 News
NewsMiniature noses to help prevent infections and promote nasal health
To better understand how different bacteria interact with the lining of the human nose, researchers used a miniature model of the human nose to study how bacteria can live in nasal passages.
-
 News
NewsNew antivirals could help prevent cold sores by changing cell structures
A class of antivirals called Pin1 inhibitors could reduce or stop outbreaks of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), the common infection behind oral herpes, according to new research.
-
 News
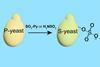
NewsSulfated yeast could help recover rare earth metals from waste liquids
Electronics, optical fibers, and superconducting materials heavily rely on rare earth metals, but innovative recycling solutions are lacking. Now researchers in Japan have successfully achieved selective recovery of metals with S-yeast, a sulfated yeast.
-
 News
NewsIn the midst of a global dengue epidemic, Wolbachia kept a Brazilian city safe
In the middle of the world’s worst global dengue epidemic, a city in Brazil was effectively protected by an innovative program that introduced the bacterium Wolbachia into the local mosquito population, lowering the rate of dengue by almost 90 per cent.
-
 News
NewsGlobal analysis reveals how biochar supercharges composting and cuts greenhouse gases
By analyzing data from 125 studies across the world, researchers showed that adding biochar to composting systems significantly boosts compost quality while slashing harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
