All USA & Canada articles – Page 3
-
 News
NewsOysters play unexpected role in protecting blue crabs from disease
Oysters famously filter their surrounding water, but it turns out they are removing more than algae and excess nutrients. New research shows they can also reduce the spread of disease in nearby marine species, including Chesapeake Bay’s prized blue crabs.
-
 News
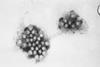
NewsBreakthrough in human norovirus research: Researchers overcome major obstacle to grow and study the virus
Researchers have overcome a major obstacle that limited their ability to continuously grow human norovirus. They identified factors that restrict viral replication and developed a way to overcome them to optimize long-term viral cultivation.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals a minimalist bacterial defense that disrupts viral assembly
Researchers describe how a single protein named Rip1 recognizes bacteriophages, the viruses that infect bacteria, and cause infected bacteria to die prematurely, thereby ending the chain of transmission.
-
 News
NewsPreviously unknown viruses discovered in groundwater
Researchers have created a comprehensive picture of viral diversity and function in a groundwater system. They identified over 257,000 viral operational taxonomic units, i.e. viruses at species level, 99 % of which were previously unknown.
-
 News
NewsResearchers urge focus on child obesity and gut health to reduce risk of diabetes
Researchers are calling for more study of obesity, gut bacteria and metabolic conditions that arise in childhood and adolescence, with an eye to curbing the global rise of type 2 diabetes.
-
 News
NewsScientists demonstrate first-ever single-shot HIV vaccine neutralization success
Scientists have developed an HIV vaccine candidate that achieves something never before observed in the field: inducing neutralizing antibodies against HIV after a single immunization in nonhuman primates.
-
 News
NewsRisk for Lyme disease in Ohio is equal to Connecticut, study shows
The risk for being bitten by a tick infected with bacteria that cause Lyme disease is as high in Ohio as it is for those living in Northeast states that have dealt with Lyme disease for over 50 years, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsGenes from corn’s wild ancestor change soil microbial community, improve sustainability
Corn bred with genes from wild relatives can reshape soil microbial communities and reduce nitrogen loss — with no yield reduction, according to new research. It’s the first time corn’s genetic makeup has been linked with inhibition of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria.
-
 News
NewsWhy aren’t more older adults getting flu or COVID-19 shots?
This winter’s brutal flu season isn’t over, and COVID-19 cases have risen recently too. But a new poll taken in recent weeks shows that vaccination against both viruses lags among people 50 and over, and the US survey reveals key reasons why.
-
 News
NewsLab-grown algae removes microplastics from water
Scientists have applied a revolutionary strain of algae toward capturing and removing harmful microplastics from polluted water. The aim is to repurpose the collected microplastics into safe, bioplastic products such as composite plastic films.
-
 News
NewsCommon bacteria discovered in the eye linked to cognitive decline
Chlamydia pneumoniae can linger in the eye and brain for years and may aggravate Alzheimer’s disease. Research suggests this bacterium can amplify Alzheimer’s disease and points to potential interventions including inflammation-limiting therapies and early antibiotic treatment.
-
 News
NewsHow fire-loving fungi learned to eat charcoal
Wildfire causes most living things to flee or die, but some fungi thrive afterward, even feasting on charred remains. A new study is among the first to investigate how fungi that are barely detectable in the soil before a fire are able to proliferate wildly once an area has burned.
-
 News
NewsNew dashboard helps predict and plan for disease outbreaks
When infectious diseases surge, response often comes down to whether communities can position the right people and supplies before case counts spike. Researchers have designed a new platform to translate academic disease forecasting into actionable guidance for decision-makers.
-
 News
NewsLaunch of clinical trial of investigative nasal spray medicine to prevent illnesses from respiratory viruses
A new clinical trial will test a new experimental intranasal spray designed to boost immune defenses and reduce illness from respiratory viruses.
-
 News
NewsGenetic system makes worker cells more resilient producers of nanostructures
Researchers report the development of a new genetic regulatory system to improve cell viability during the production of gas vesicles.
-
 News
NewsResearchers enable microorganisms to build molecules with light
Researchers are continually looking for new ways to hack the cellular machinery of microbes to make useful products. A new study shows they can expand the biosynthetic capabilities of these microbes by using light to help access new types of chemical transformations.
-
 News
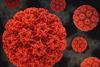
NewsStudy suggests far fewer cervical cancer screenings are needed for HPV‑vaccinated women
In a modeling study of women vaccinated against human papillomavirus (HPV), researchers found that cervical cancer screening could be done far less often than current recommendations without compromising health benefits.
-
 News
NewsOne of Earth’s most abundant organisms is surprisingly fragile
A group of ocean bacteria long considered perfectly adapted to life in nutrient-poor waters may be more vulnerable to environmental change than scientists realized. The bacteria, known as SAR11, dominate surface seawater worldwide and can make up as much as 40% of marine bacterial cells.
-
 News
NewsNew research finds crosstalk inside cells helps pathogens evade drugs
Biologists have uncovered a new mode of communication inside cells that helps bacterial pathogens learn how to evade drugs. Their findings describe how these mechanisms drive antimicrobial resistance in Listeria monocytogenes, the foodborne bacteria that causes listeriosis.
-
 News
NewsGut bacteria may tip the balance between feeding tumors and fueling immunity
A new study reveals how bacteria in the gut can help determine whether the amino acid asparagine from the diet will feed tumor growth or activate immune cells against the cancer.
