All Asia & Oceania articles – Page 22
-
 News
NewsNovel Bocaparvovirus identified in goats in China
Researchers identified a novel Bocaparvovirus in goat fecal samples using metagenomic techniques, with detection in goats from 3 regions in China: Sichuan, Hunan and Chongqing.
-
 News
NewsPediatric investigation study re-examines chikungunya in neglected pediatric victims
Researchers and policymakers must recalibrate their outlook on pediatric chikungunya to develop effective control measures, a new paper warns.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how dengue rewires the immune system, reshaping vaccine response
Just as a computer’s operating system can be rewritten after a major update, dengue infection can ‘re-programme’ the body’s immune system, leaving a long-lasting genetic imprint that influences how people respond to future infections—an effect not seen with vaccination.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows how diet and gut microbiota can counter the baby blues
Microbiome diversity and relative abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria were associated with high levels of depressive mood. But a diet rich in fermented foods, soy products, mushrooms, and seaweed may help regulate the gut environment and contribute to preventing depression.
-
 News
NewsPeanut shell biochar composite shows promise for removing antibiotic-resistant bacteria from aquaculture wastewater
Researchers have developed a novel, low-cost catalyst that efficiently removes antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) from aquaculture wastewater, offering a potential new solution to one of today’s most pressing environmental and public health challenges.
-
 News
NewsFrailty fuels gut imbalance and post-surgery gastrointestinal risks
Scientists found that residual intra-abdominal microbes, especially in frail patients, drive gastrointestinal complications after bladder cancer surgery.
-
 News
NewsDe-mystifying common misconception about the prevalence of Legionella bacteria
There is a common misconception that Legionella is only found in air conditioners and water towers - however, a new study has found people are likely exposed to the bacteria through other sources, including through soil.
-
 News
NewsScientists unveil viral mechanism behind nasopharyngeal cancer spread
Researchers have discovered that the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a common human virus closely linked to nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), can change the 3D structure of the human genome inside cancer cells, much like assembling building blocks.
-
 News
NewsFungi–biochar partnership boosts soil health and crop growth under cadmium stress
A study reports that combining arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) with biochar can reshape soil microbiomes, reduce cadmium uptake, and dramatically improve plant growth, offering a sustainable strategy for restoring farmland contaminated with heavy metals.
-
 News
NewsHeme-based sulfide sensing in bacteria: a new target for antibiotics
Heme binding to a bacterial transcription factor is critical for hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) signaling, a new study reveals. Heme binding promotes the reaction of H₂S with the transcription factor, leading to structural changes that can regulate stress tolerance in bacteria.
-
 News
NewsGame-changing biotech for engineering pathogen-resistant crops
Researchers have identified an ancient protein that has the potential to help defend plants against tens of thousands of different bacteria and other pathogens. Dubbed “SCORE”, this receptor detects cold-shock protein—variations of which are found in more than 85% of known bacteria, as well as fungi and insects.
-
 News
NewsBiodegradable PET alternative bioproduced at unprecedented levels
The PET-alternative PDCA is biodegradable and has superior physical properties. A team of bioengineers has engineered E. coli bacteria to produce the compound from glucose at unprecedented levels and without byproducts — and opened up a realm of possibilities for the future of bioengineering.
-
 News
NewsProtein discovery gives new hope for longer COVID protection
Scientists have discovered that the body’s immune system strongly reacts to an internal protein from SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, which mutates less frequently than the surface-spike protein currently targeted by vaccines.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop first-of-its-kind RNA tool to advance cancer and infectious disease research and treatment
Scientists have developed a powerful tool capable of scanning thousands of biological samples to detect transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) modifications — tiny chemical changes to RNA molecules that help control how cells grow, adapt to stress and respond to diseases such as cancer and antibiotic‑resistant infections.
-
 News
NewsStress-tolerant corals could help buy time for reefs in a warming world
New research demonstrates how corals that naturally thrive in extreme environments could be used in restoration efforts to protect vulnerable reef systems.
-
 News
NewsReview explores critical role of microbiome in cancer development and treatment
The human microbiome plays a pivotal role in cancer initiation, progression, and treatment response, according to a major review article published in the open-access journal iMeta. The study, led by an international team of researchers, details how bacteria, viruses, and fungi interact with tumors and the immune system to either promote or inhibit cancer growth.
-
 News
NewsStudy suggests link between hepatitis B immunity and lower risk of developing diabetes
A research study shows that overall HBV immunity is linked with a 15% lower risk of diabetes, with higher protection in younger people and those with higher immunity shown by higher antibody levels.
-
 News
NewsUnlocking how bacteria bounce back after antibiotics
A groundbreaking study has uncovered how Escherichia coli (E. coli) persister bacteria survive antibiotics by protecting their genetic instructions. The work offers new hope for tackling chronic, recurring infections.
-
 News
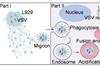
News‘Migrion’ – a chimeric structure of virus and migrasome, a novel unit for intercellular viral transmission
Researchers found that in infected cells, nucleic acids and proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) are actively transported into migrasomes, newly characterized cellular structures generated specifically during cell migration.
-
 News
NewsNew pimple patches deliver a powerful remedy to unwanted zits
Researchers have designed a two-stage pimple patch set with an array of tiny spikes that grabs onto the pimple and delivers antibacterial or anti-inflammatory compounds. Human clinical trials confirmed that the pimples disappeared after seven days of treatment.
