All Research News articles – Page 19
-
 News
NewsEarthquakes shake up Yellowstone’s subterranean ecosystems
Researchers chronicled the ecological changes in subsurface microbial communities that took place after a swarm of small earthquakes rattled the Yellowstone Plateau Volcanic Field in 2021.
-
 News
NewsFestive cheer: Soaked raisins ferment to turn water into wine
Scientists have discovered that soaking sun-dried raisins in water is a successful method of creating wine. It was thought that ancient wine production relied on the natural fermentation process of storing crushed grapes in jars, but Saccharomyces cerevisiae rarely colonizes grape skins.
-
 News
NewsHospital infections associated with higher risk of dementia
A large-scale meta-analysis shows that adults hospitalized with infections have a significantly higher risk of developing dementia. Among the types of infections studied, sepsis carried the highest risk, followed by pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin or soft tissue infections.
-
 News
NewsIs malaria messaging working? African biostatisticians have the data
New analysis shows malaria messaging works. Using advanced causal methods, researchers found that exposure to prevention messages increases insecticide-treated net use among women and children in Uganda, offering rare causal evidence to guide policy.
-
 News
NewsStaphylococci compete with other bacteria for biotin in the nasal cavity
A recently published study reveals that competition plays a major role in the nutrient-poor habitat of the human nose. There’s an active contest between S. aureus and nasal commensals for the vitamin biotin, which affects the fitness of S. aureus.
-
 News
NewsExperimental mRNA therapy shows potential to combat antibiotic-resistant infections
Researchers have reported early success with a novel mRNA-based therapy designed to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. In preclinical studies, the therapy slowed bacterial growth, strengthened immune cell activity, and reduced lung tissue damage in models of multidrug-resistant pneumonia.
-
 News
NewsOceanographers present new conceptual framework to answer age-old question: What happens to carbon as it sinks through the ocean?
New research spanning multiple ocean regions has found upper ocean ecosystem conditions, such as nutrient availability and microbial interactions, play a major role in shaping the composition of carbon-rich particles sinking into the deep ocean.
-
 News
NewsPesticides and other common chemical pollutants are toxic to our ‘good’ gut bacteria
A large-scale laboratory screening of human-made chemicals has identified 168 chemicals that are toxic to bacteria found in the healthy human gut. These chemicals stifle the growth of gut bacteria thought to be vital for health.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals how a common antibiotic disrupts nitrogen cycling and boosts greenhouse gas emissions in estuaries
Antibiotics may have far reaching impacts on wetland chemistry, according to a new study that identifies the bacteria responsible for breaking down the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole and links this process to increased emissions of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
-
 News
NewsMalaria parasites move on right-handed helices
After penetrating the skin, the malaria parasite moves with helical trajectories, almost always turning toward the right. Researchers demonstrated that the pathogen uses these right-handed helices to control its motion as it transitions from one tissue compartment to another.
-
 News
NewsPrebiotic in diet linked to less impulsivity in gambling rats with traumatic brain injury
Using a prebiotic to influence bacterial activity in the gut after a traumatic brain injury may help reduce impulsive behavior, one of the common symptoms to follow a moderate blow to the head, a new study in rats suggests.
-
 News
NewsMarine viruses use ‘hijacked’ genes to take over bacteria and exploit their energy systems
Marine viruses deploy a sophisticated Trojan horse maneuver that enables them to dismantle the energy systems of ocean bacteria and use the breakdown products for self-replication, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsGut microbiome connects obesity to cancer, impacting public health
A new review highlights growing scientific evidence that imbalances in gut bacteria can influence metabolism, trigger inflammation, and increase cancer risk. These insights offer new possibilities for disease prevention, early detection, and personalized health care.
-
 News
NewsCircadian rhythms as a modulator of gut microbiota-tumor microenvironment crosstalk
A new review examines how circadian disruption modifies the diversity and metabolic functions of gut microbiota, resulting in alterations of microbial metabolites, including short-chain fatty acids and secondary bile acids.
-
 News
NewsNew study identifies key mechanism driving HIV-associated immune suppression
Using humanized mouse models and blood samples from people living with HIV, resarchers found that reducing overactive plasmacytoid dendritic cells helped restore antiviral T cell function and shrink the viral reservoir.
-
 News
NewsHospital bug jumps from lungs to gut, raising sepsis risk
A hospital-acquired bacterium that causes serious infections can move from the lungs to the gut inside the same patient, raising the risk of life-threatening sepsis, new research reveals.
-
 News
NewsFive new phages discovered in university’s Botanical Gardens
Five new bacteriophages have recently been discovered in the ponds of Lund University’s Botanical Gardens. Phages thrive wherever bacteria are found, which often means ponds and watercourses that are rich in organic material.
-
 News
NewsEmerging human and canine leptospirosis in New South Wales shows separate transmission pathways
A geospatial study of leptospirosis outbreaks in New South Wales suggests that humans and dogs may have largely independent transmission pathways.
-
 News
NewsNew super pest combines broad spectrum of microbes
Researchers investigating what role the reed leafhopper’s microbial flora might have played in its rapid spread as a pest found it hosts at least seven species of bacteria and appears to be completely dependent on three of these species, which inhabit specific organs.
-
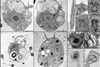 News
NewsClues to origins of complex life revealed with discovery of new unicellular organism and phylum
A new paper describes the discovery of Solarion arienae, a previously unknown unicellular organism that provides new insight into the earliest stages of complex life on Earth. This microscopic protist displays two distinct cell types and a unique predatory structure unlike any seen before.
